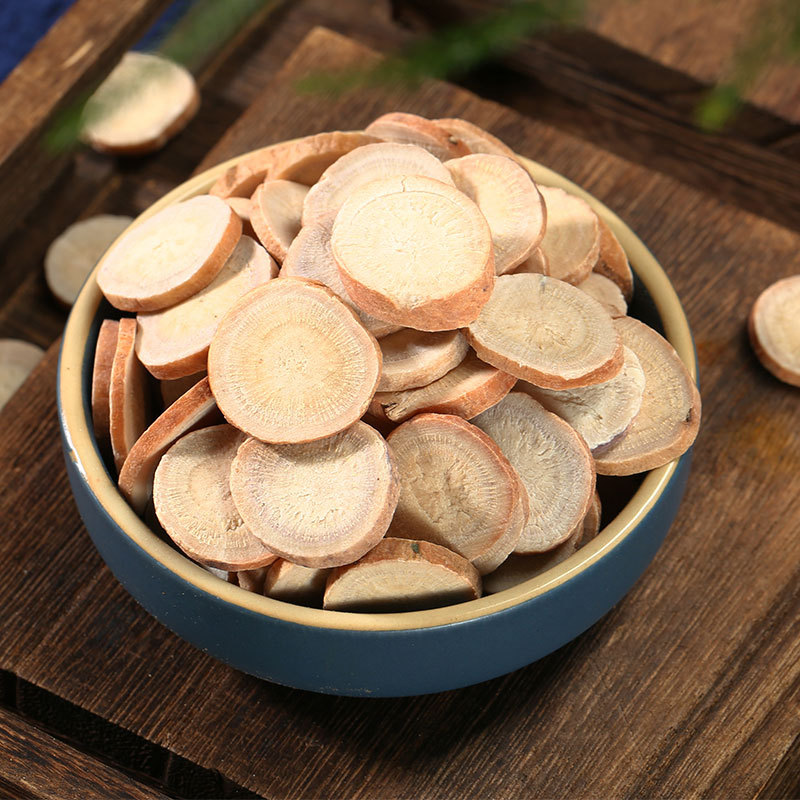
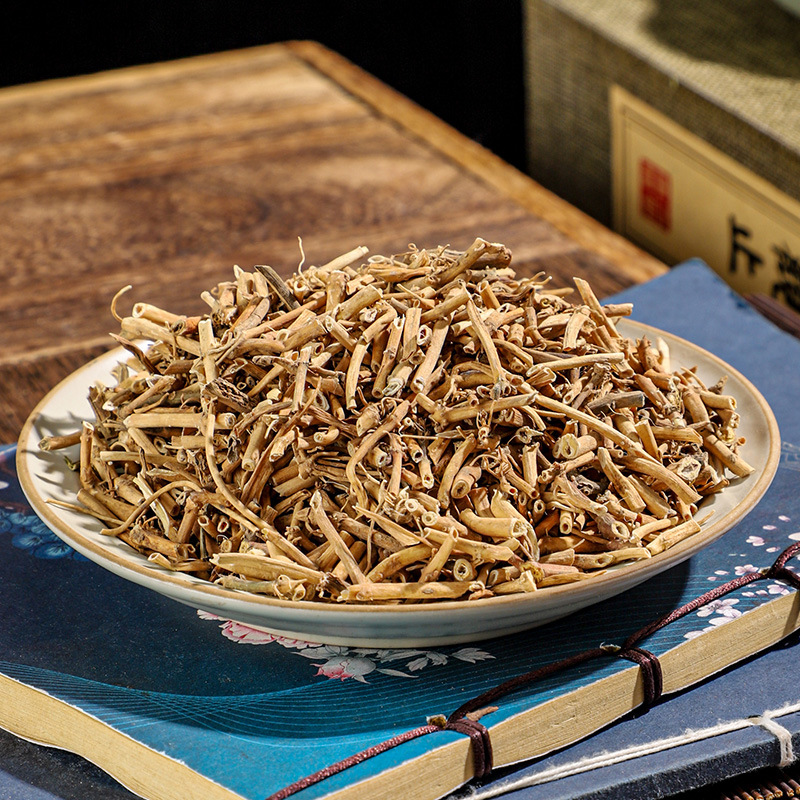
Nowadays, many people suffer from poor sleep, especially the elderly, who are particularly prone to insomnia at night. Their minds simply cannot calm down, as they constantly dwell on trivial matters. Moreover, after falling asleep, they are easily awakened, sensitive to even the slightest disturbance outside. They may also experience occasional palpitations, shortness of breath, chest tightness, fatigue, accompanied by symptoms such as loss of appetite, pale lips, and poor complexion. This type of insomnia is mostly caused by deficiency of both the heart and spleen.
Traditional Chinese Medicine believes that a calm mind leads to restful sleep, and that "the spleen generates blood" while "the heart governs blood." When both the heart and spleen are deficient, they cannot produce qi and blood. Insufficient heart blood fails to nourish the mind. To address this condition, today I recommend a "fast sleep formula" created by the Medicine King Sun Simiao. It can nourish blood, promote qi circulation, calm the mind, and aid sleep. The formula consists of jujube and scallion white. Although it contains only two simple ingredients, it has been used from ancient times to the present and has become an effective remedy for insomnia, with good clinical validation.
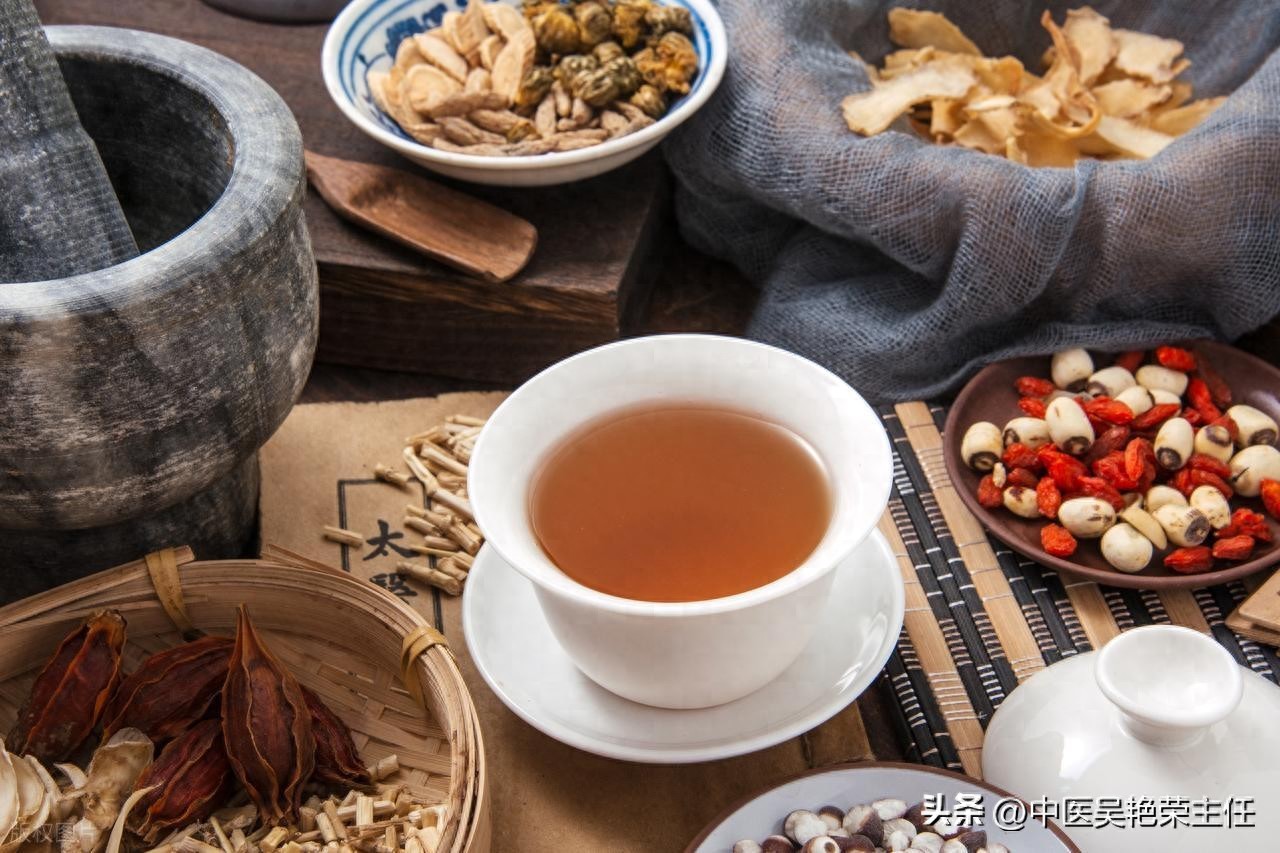

Among them, long-term consumption of jujube can effectively nourish the heart and spleen, replenish qi and blood, and strengthen the bones and muscles. Scallion white is a yang-promoting herb that can disperse the qi mechanism in our body and unblock the qi throughout the entire body. The combination of these two herbs, by tonifying qi and blood and harmonizing the nutritive and defensive aspects, can effectively alleviate insomnia issues.
Finally, a reminder to everyone that these two herbs are only suitable for insomnia caused by deficiency of both the heart and spleen. If your insomnia is due to other reasons, you should adjust the medication promptly under the guidance of a professional traditional Chinese medicine practitioner, based on your individual constitution and physical symptoms.