How is the hour after a blood sugar meal calculated?
How is the hour after a blood sugar meal calculated? 
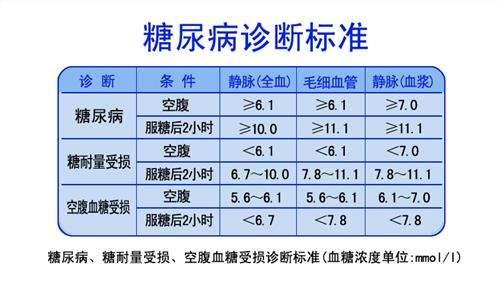
Postprandial blood glucose is usually measured 2 hours after a meal, not 1 hour after a meal. Why not 1 hour after a meal or 3 hours after a meal? There is a reason.

Someone took the test and surprised themselves with the results!
"I ate half a roast duck at 5:00 p.m. and measured my blood sugar at 7:00 p.m. It was only 5.9. After eating so much meat, my blood sugar didn't go up at all, and I didn't believe myself. 1 hour later, I measured my blood sugar again, and it was even 10.5. It's already been 3 hours since I ate the roast duck, so why is it that my blood sugar is higher at 3 hours than at 2 hours?"
Figuring out postprandial blood sugar numbers starts with understanding how blood sugar rises after eating.
Blood glucose peaks around 1 hour after eating, then, as the body secretes insulin to lower blood glucose, blood glucose gradually falls back, blood glucose will fall back to ≤ 7.8 2 hours after the meal, to 3 hours after the meal, blood glucose that is restored to the level of fasting.
1 hour after meal: 6.7 to 9.4
2 hours after meal: ≤ 7.8
3 hours after meal: ≤ 6.1
This is talking about a normal person's blood sugar, a diabetic would have to rely on medication to help their blood sugar get closer to normal.
Causes of high blood glucose at 3 hours postprandial -
Roast duck is particularly high in fat, and fat slows down gastric emptying. Excess fat also exacerbates insulin resistance, and if at the same time the person has gastrointestinal absorption problems, this ultimately leads to a delayed hyperglycemic curve, where 2 hours after a meal is normal, but 3 hours after a meal is abnormally high.
And a high 1-hour postprandial glucose--
It is mostly seen in eating foods that are absorbed and metabolized quickly, like potatoes and rice porridge, which cause blood sugar to rise and fall quickly, and may not be very high at 2 hours after a meal, but very high at 1 hour after a meal.
If we look at it this way, will we have to measure the 1-hour and 3-hour ones in addition to the 2-hour ones after meals? Then our fingers will be tied up in a sieve.
Not really. Measuring blood glucose 2 hours after a meal refers to the blood glucose from the first bite of the meal to 2 hours after the meal. Eating is generally more appropriate to eat 30 minutes, and then since the first bite of food to 2 hours after the meal, almost is the body's blood glucose peak moment, this time to measure blood glucose, basically will be able to understand the situation of postprandial blood glucose.
Therefore, daily monitoring of blood glucose 2 hours after a meal is sufficient.
This article is to remind you not to assume that you're OK after you've feasted and measured your blood sugar for 2 hours and it's not too high.
This kind of high 1 hour or 3 hours after meals, blood sugar suddenly rise and fall like a roller coaster, in medicine is called blood sugar fluctuation.
Just like the red curve indicates blood glucose, in recent years, it has been found that this kind of sudden rise and fall of blood glucose, the damage to the vascular endothelial cell morphology and function is more serious than that of the continuous and stable high glucose, which will greatly increase the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Ideally postprandial blood glucose should resemble a yellow curve, rising and falling slowly and very smoothly.
Both healthy people and diabetics should get themselves a smooth postprandial glucose profile through healthy eating habits.
Ways to get smooth postprandial blood sugar
1. Reduce the intake of meat and oily foods
2. Increase intake of coarse grains and vegetables
3. Moderate protein food intake
4. The total amount of food in a day remains the same, and eating in separate meals can ease blood sugar fluctuations
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.