How is a brain attack different from a cerebral thrombosis?
How is a brain attack different from a cerebral thrombosis?
What is the difference between a brain attack and a cerebral thrombosis? This is a question that many people want to ask, and it is also a question that many people have been confused. Today, Dr. Zhang will talk about the relationship between the two, hoping that it can help you.
Cerebral infarction is a kind of cerebrovascular disease, which is strictly speaking called "ischemic stroke" in medicine, and its causes are many, the most common of which is in situ cerebral thrombosis. In addition to cerebral thrombosis, there are other causes, such as atrial fibrillation. Simply put, cerebral infarction includes many causes, one of the most common of which is in situ cerebral thrombosis. And this kind of cerebral infarction of cerebral thrombosis has atherosclerotic lesions or atheromatous plaques as its pathological basis.
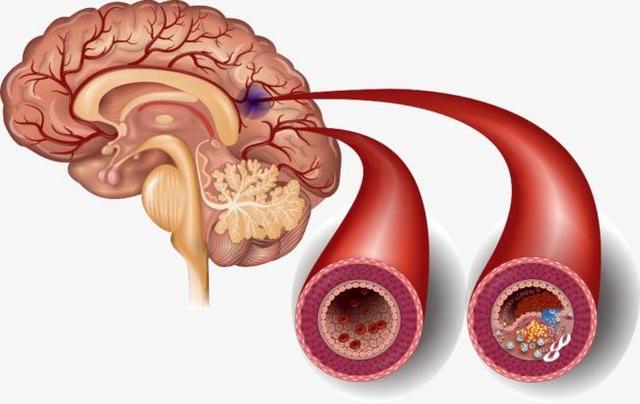
And atherosclerotic plaque is a common chronic lesion whose occurrence and development are affected by many factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and other factors. If a person's long-term high blood pressure, high blood glucose, and high blood lipids are not managed, it is likely to lead to the development of atherosclerotic plaques in different parts of the body's arteries, and this atherosclerotic plaque, once it occurs in the cerebral arteries, will lay the groundwork for the occurrence of cerebral thrombosis. For example, with the passage of time, blood pressure, blood sugar, blood lipids are still not controlled, the atheromatous plaque will become bigger and bigger, more and more unstable, at this time once the atheromatous plaque becomes too big, or suddenly rupture, there will be in-situ thrombosis, arterial vessels become blocked, and cerebral infarction also occurs.
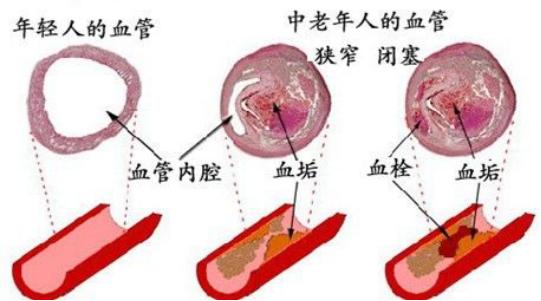
In fact, this is one of the most easily understood conditions of cerebral infarction. There are other causes that can lead to cerebral infarction, such as atrial fibrillation, which is often heard of, and if emboli are formed in the atria, these emboli can lead to cerebral infarction after they fall off. Therefore, atrial fibrillation is also an important cause of cerebral infarction. Of course, the cerebral infarction caused by atrial fibrillation and the cerebral infarction caused by cerebral atherosclerosis and cerebral thrombosis, the pathological basis is completely different, and the usual treatment is also different, one is to strengthen the antiplatelet therapy, and the other is to pay attention to anticoagulation therapy.
I hope that Dr. Zhang's answer to this question today can help you correctly understand the relationship between cerebral infarction and cerebral thrombosis, and initially understand the causes of the formation of these diseases, which will also help you to pay attention to improving your lifestyle, control medical risk factors, and thus reduce the incidence of cerebrovascular disease.

A brain attack is a little different than a brain clot. A cerebral thrombosis is actually a type of cerebral infarction.
Cerebral infarction is called cerebral infarction, formerly also called cerebral infarction, which is a very common disease and has a very heavy burden on patients and families. It is one of the ischemic diseases of the brain. In addition to cerebral infarction, there are other ischemic diseases of the brain, such as transient ischemic attack.
Cerebral thrombosis is actually a kind of cerebral infarction, which is the most common type of cerebral infarction, mostly due to the narrowing or even occlusion of the lumen of the main stem of the cerebral artery or some cortical branches due to various reasons (e.g., atherosclerosis, arteritis, etc.), and then secondary to the formation of local thrombus, which results in the ischemic necrosis of the brain tissues, and the appearance of the corresponding symptoms and signs.
Cerebral thrombosis is mostly seen in the internal carotid artery system and generally includes several conditions such as large cerebral infarcts, watershed cerebral infarcts, hemorrhagic infarcts, and multiple cerebral infarcts.
Regardless of the type of cerebral infarction, once the onset of the disease is suspected, the patient should be sent to a stroke center or a qualified medical institution as soon as possible. If the embolized blood vessel can be reopened as soon as possible, more brain cells will be saved, and thus a better prognosis can be obtained with a relatively small therapeutic risk, but the later the blood vessel is opened, the higher the therapeutic risk will be, and the patient's prognosis will be even worse, and if the opening of the blood vessel is exceeded, only relatively conservative treatment can be adopted, and the patient's prognosis will be even worse. If the vessel is opened later, the risk of treatment is higher and the patient's prognosis is worse; if the vessel is opened later, the patient's prognosis is worse.
(Images from the Internet, if there is any infringement, please contact to delete)
Cerebral infarction and cerebral thrombosis are cerebrovascular diseases that people often hear about, and they both have high rates of death and disability, seriously threatening patients' lives and health.
What is the difference between a brain attack and a blood clot?
Although cerebral infarction and cerebral thrombosis are cerebrovascular diseases, their pathogenesis and treatment modalities are different, and attention should be paid to clarifying the cause of the disease at the time of its onset, and then active treatment should be carried out.

1. The difference between cerebral infarction and cerebral thrombosis:Cerebral infarction, also known as cerebral infarction, is ischemic stroke, is a kind of stroke, is also the most common cerebrovascular disease, is because of various reasons due to the cerebral blood vessel blockage induced by cerebral tissue ischemia, lack of oxygen and make the brain tissue necrosis, and then appear a series of serious symptoms. Cerebral thrombosis is a kind of cerebral infarction, which is also caused by the blockage of blood vessels in the brain.Atherosclerosis makesFormed by thickening of blood vessels, narrowing and occlusion of the lumen, and thrombosis.
That is to say, cerebral infarction includes cerebral thrombosis, which is caused by the blockage of blood vessels in the brain due to the dislodgement of various emboli, and its main components include cerebral thrombosis, lacunar infarction and cerebral embolism. Among them, cerebral thrombosis is mostly due to atherosclerosis, while cerebral embolism is mostly of cardiac origin, i.e., due to dislodgment of emboli caused by heart diseases. Cerebral thrombosis is the most common type of cerebral infarction, and high-risk groups must be vigilant.

2. Prevention and treatment of cerebral infarction:The occurrence of cerebral infarction is related to many factors, excluding age, heredity and other factors, but also closely related to disease factors, lifestyle factors and so on. Therefore, the prevention of cerebral infarction should start from various aspects.
First of all, middle-aged and elderly people belong to the high-risk group of cerebral infarction, they are often accompanied by vascular aging, atherosclerosis, hypertension, high blood pressure, high blood lipids, high blood sugar and other underlying diseases, should pay attention to the active treatment of related diseases, and regular physical examination, especially pay attention to the monitoring of the degree of vascular stenosis, the carotid artery atherosclerosis plaque formation size and stability, etc., in order to prevent the occurrence of cerebral infarction. Patients in the active use of antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering drugs and other treatments for primary diseases at the same time, if necessary, also need to take medication to control the plaque to continue to grow, to prevent the formation of blood clots, such as taking aspirin and so on. Secondly, high-risk groups must change their bad habits, pay attention to diet low in fat, low in calories, low in cholesterol, low in sugar, low in salt, eat less animal food, fried food, eat more fruits and vegetables, coarse grains; quit smoking and drinking; strengthen the exercise, adhere to the moderate exercise every day; avoid staying up too late for a long period of time, overwork, overstress, etc., and keep a good mindset to ensure sufficient sleep.
Thanks for the question invitation!

"Cerebral infarction" is the clinical abbreviation for cerebral infarction, while "cerebral thrombosis" is less commonly used in clinical practice, and is more commonly used among the public, probably because it was more commonly used in the past. It should be said that both "cerebral infarction" and "cerebral thrombosis" belong to ischemic cerebrovascular disease or ischemic stroke, and a large part of them overlap, but the names are different, and naturally there is also a certain distinction. This question is concerned with the differences between the two, and Dr. Elf will answer it for you below.
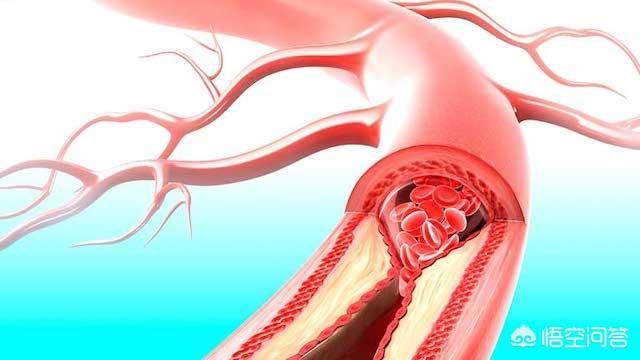
Let's start by talking about cerebral infarction. This term is commonly used nowadays and focuses on emphasizing the necrosis of nerve cells in certain areas of the brain due to certain causes of interruption of blood supply. Depending on the cause of the ischemia, there are different types of cerebral infarction. If the infarction of a large blood vessel has a large infarcted area, it can cause severe neurological deficits; if it is an occlusion of a small blood vessel, although a small amount of nerve cell death may occur, it may not have the clinical manifestations of neurological deficits, which is also known as cavernous cerebral infarction; if nerve cell death occurs at the junction of the two regions of the brain that are supplied with blood because of insufficient intracranial blood perfusion, this is called a Watershed cerebral infarction; if the interruption of blood flow is due to the flow of emboli from certain blood vessels to the brain, it is called cerebral embolism.
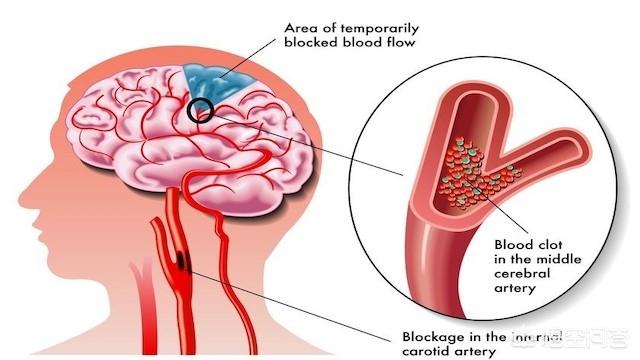
Having introduced cerebral infarction, let's take a look at cerebral thrombosis. As you may notice from the name, it emphasizes the cause of cerebral infarction rather than the result of nerve cell death. From the point of view of the cause, it also does not completely cover ischemic stroke, but mainly emphasizes the formation and occlusion of atherosclerotic plaques in the large and medium-sized blood vessels, as well as the blockage of blood fluidity clots in the skull. Therefore, we can see that the concept of cerebral infarction can cover cerebral thrombosis, and its more emphasis on the results, which is very relevant to the essence of the disease and the prognosis, and because of this reason, after the two concepts are confused for a period of time, and finally united for cerebral infarction to refer to this large group of diseases.
Dr. Duan speaks about science ☞ Bringing you together to increase your knowledge!The real relationship between cerebral infarction (i.e., cerebral infarction or cerebral infarction) and cerebral thrombosis: Cerebral thrombosis is the most common type of cerebral infarction.
I. Cerebral infarction
Also known as cerebral infarction, or cerebral infarction, or ischemic stroke, refers to the blockage of blood circulation in the brain, ischemia, hypoxia caused by local ischemic necrosis or softening of brain tissue, the corresponding symptoms and signs.
II. Cerebral thrombosis
The real name is "atherosclerotic thrombotic cerebral infarction", which is the most common type of cerebral infarction. It is the most common type of cerebral infarction. It refers to localized ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissue caused by plaque rupture and ulcer formation on the basis of cerebral atherosclerosis, which promotes the formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
Thus, a cerebral infarction is a larger, generalized concept and scope, and a cerebral thrombosis is a specific, largest branch of a cerebral infarction. To draw an analogy: a brain attack is the trunk of a large tree, and a thrombus is the largest branch of that trunk.
III. Other types of cerebral infarction
(1) Cerebral embolism: Emboli in the blood (mainly from the heart) enter the cerebral arteries with the blood flow and block the blood vessels, causing necrosis of the brain tissues in the area supplied with blood.
(2) Cavernous cerebral infarction: small penetrating arteries deep in the cerebral hemispheres or brainstem, on the basis of long-term hypertension, the vessel wall lesions lead to lumen occlusion, forming small infarct foci.
(3) Cerebral watershed infarcts: infarcts occurring in the limbic zone between adjacent blood supplies in the brain.
Now, have you figured out the difference between a cerebral infarction and a cerebral thrombosis?
☞ Follow Dr. Duan for health and wellness!
(Cerebral infarction) (Diagnostic points) 1, there is a primary lesion and the corresponding performance. 2, the onset of disease is acute, headache, vomiting, transient loss of consciousness, if the aorta embolism, can lead to coma, severe cases can be seen in limited convulsive episodes. 3, tethered parts of the cerebral middle cerebral artery system (symptoms, signs and symptoms of the same as the cerebral thrombosis). 4, air tethered, there is a rapid onset of headache, nausea, vertigo, and then blind, dyspnea, cyanosis, seizures and other manifestations, fat embolism, most often occurring hours after fracture, often pulmonary tethering, manifested by cough, dyspnea, cyanosis, tachycardia, followed by delirium, convulsions and convulsions, etc. Fat embolism, mostly occurring a few hours after the fracture, often appears as pulmonary tethering, manifested by cough, dyspnea, cyanosis, tachycardia, followed by delirium, convulsions, coma, skin petechiae, and fat particles in the urine. (Cerebral thrombosis) (Diagnostic points) 1, 1 or 2 days before the onset of daily prodromal symptoms: such as headache, dizziness, numbness of the limbs, memory loss, or speech impediments. 2, mostly occurring during sleep, waking up to find a crooked mouth, slurred speech, monoparesis or hemiparesis. 3, mostly conscious. 4, no obvious changes in vital signs. 5, no obvious changes in the cerebrospinal fluid. 6, CT shows a hypodense lesion that can be localized. 7, the cerebral spinal fluid is not changed. 8, the cerebrospinal fluid is not altered. 9, the cerebrospinal fluid is not altered. 10, the cerebrospinal fluid is not changed.
Thank you for the platform invitation:
First of all it must be worthy of recognition, I think you have asked a very good question, because many patients in the clinic, can't tell the difference, and this question helps everyone to recognize the difference.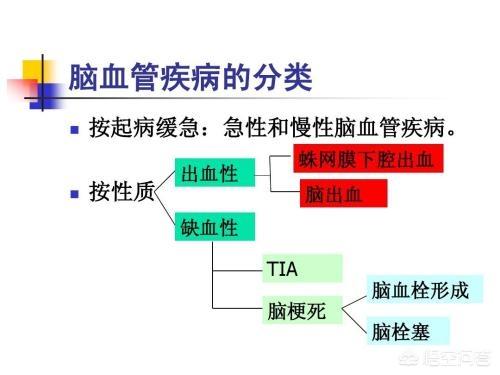
1, first of all, see what is cerebral infarction, cerebral infarction, also known as ischemic stroke (cerebral ischemic stroke), refers to the blood supply obstacle in the brain, ischemia, hypoxia, resulting in limited ischemic necrosis or softening of brain tissue. The common clinical types of cerebral infarction are cerebral thrombosis, lacunar infarction and cerebral embolism.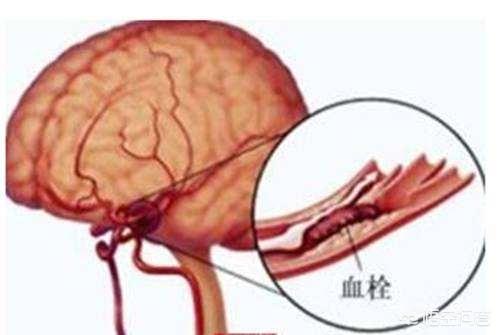
2, from the above definition we can easily see that cerebral infarction is a big concept, cerebral thrombosis is only a type of cerebral infarction.
3. The concept of cerebral embolism: it refers to the various emboli in the blood (such as wall-attached thrombus in the heart, atherosclerotic plaque, fat, tumor cells, fibro-cartilage, or air, etc.) enter the cerebral artery along with the blood flow and obstruct the blood vessel, and cause ischemic necrosis of brain tissues in the area supplied by this artery and focal neurological deficits when the collateral circulation fails to compensate for it.
4, so that a comparison of the answer at a glance, here a little expansion, cerebral embolism is often accompanied by heart function problems, clinical we found that cerebral embolism patients, often accompanied by atrial fibrillation, this abnormal heartbeat pattern, often attached to the wall of the heart of the thrombus off, with the body's blood circulation to reach the brain, resulting in cerebral embolism.
5, for patients with atrial fibrillation, we have to actively prevent the harm caused by atrial fibrillation, atrial fibrillation patients cerebrovascular risk is higher than normal people about 60%, how to intervene in atrial fibrillation, the old treatment method of warfarin drug use (the negative effect is the increase in the risk of bleeding, and regularly to the hospital to review the coagulation function), and now tend to use a new type of anticoagulant drugs (for example: dabigatran or rivaroxabandol drugs), the safety factor is much higher. The safety factor is much higher.
I hope my answer helps you to answer your questions, thank you, if you have any other questions you can pay attention to Li, in my personal home page has a lot of related articles
Cerebral infarction, cerebral thrombosis, lacunar cerebral infarction, cerebral stroke, stroke, cerebrovascular accident, how can we get so many terms, look at the people are dazzled, how to differentiate?
First of all, stroke, stroke, cerebrovascular accident, these three is a meaning, different people called differently. For example: unclear speech, crooked mouth, weakness of one side of the arms and legs of these symptoms, the first reaction of our common people is - may be a stroke; but in the hospital, called - stroke or cerebrovascular accident. As you can see, the former is a common name, the latter is a medical term.
For a better understanding of their classification, they are summarized in the following diagram:

What is the difference between a cerebral thrombosis and a cerebral embolism in a brain attack?
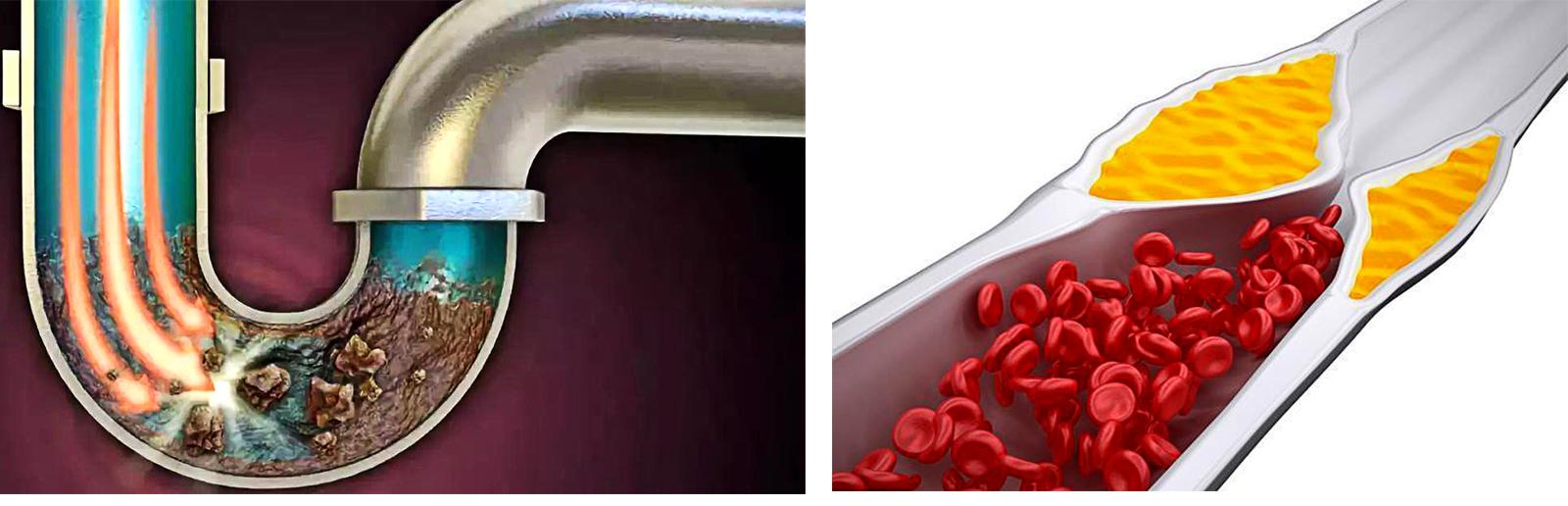
Using a commercial building as an example, it is understandable that the occupants of the upper floors are compared to brain cells, and the plumbing from the lower to the upper floors is compared to blood vessels.

cerebral thrombosis
When water pipes are rusty, aged or dirt build-up, making the pipe lumen narrow or even clogged, the water does not flow up to the upper floors. Imagine: water that was originally supplied to 10 households is now only available to one household because the water flow has been reduced, and the other nine households are not affected by the lack of water supply.
Taking the human body, water pipe aging is like atherosclerosis, atherosclerosis produces plaque is like "rust-colored spots", "dirt".
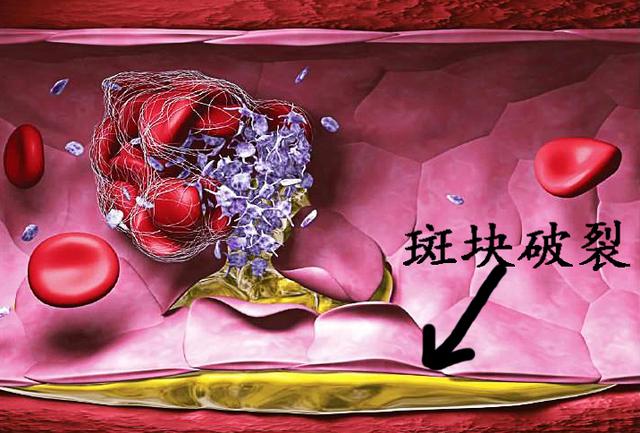
The point of difference is that plaque ruptures and promotes thrombosis, which is the cause of acute attacks of cardiovascular disease.
Actually thrombosis is a protective mechanism:
For example, if our skin breaks and bleeds, it will stop bleeding automatically, which is the work of thrombosis. After thrombosis, the break is blocked, and the bleeding stops. But this break occurs in the plaque in the blood vessel, out of the broken place of its own repair, thrombus will form, but in the blood vessel localized, limited space, will make the blood vessel local narrowing, or even occlusion.
The side effect of the antithrombotic medications chosen to prevent the treatment of thrombosis is that they tend to cause bleeding.
cerebral embolism
Although both cerebral embolism and cerebral thrombosis are caused by acute occlusion or severe narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the brain, cerebral embolism is not significantly related to the cerebral arteries themselves (i.e., the cerebral arteries are not altered), but rather is due to the blockage of the arteries by emboli.
This embolus, like the moss that is shed in a water pipe, can move around with the flow of water and tends to clog the pipe when it flows into a smaller pipe or where the pipes cross. This is called a cerebral embolism within the blood vessels of the brain.
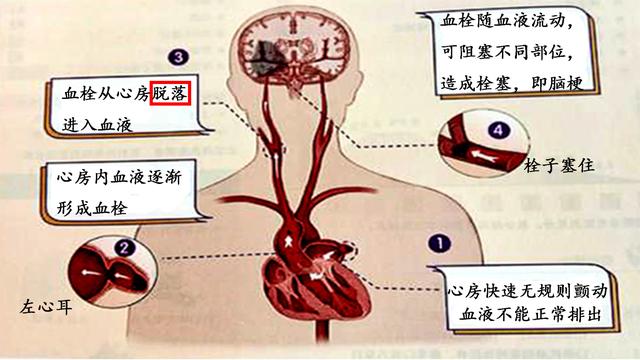
Some people call cerebral embolism as cardiogenic cerebral embolism, which shows that the common cause of cerebral embolism is in the heart, and abnormal lesions of the heart tend to produce emboli. Diseases of the heart that tend to produce emboli include: atrial fibrillation, rheumatic heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, artificial heart valves, and so on.
Another type of lacunar cerebral infarction is the small artery occlusion type of cerebral infarction.
Small artery atherosclerosis is now considered to be its main etiologic factor, so lacunar cerebral infarction is most often reported in people with risk factors associated with atherosclerosis, such as advanced age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking, and family history.
Finally, it can be seen that the prevention of cerebral infarction, in addition to the prevention of atherosclerosis and the treatment of atherosclerosis risk factors, the aspect of heart disease should also be emphasized and treated, so that, with the cerebral infarction to go farther and farther.
Many friends, who do not understand blood clots and cerebral infarction, often think that they are the same thing, in fact, cerebral infarction and blood clots have a close relationship, but they are not the same thing.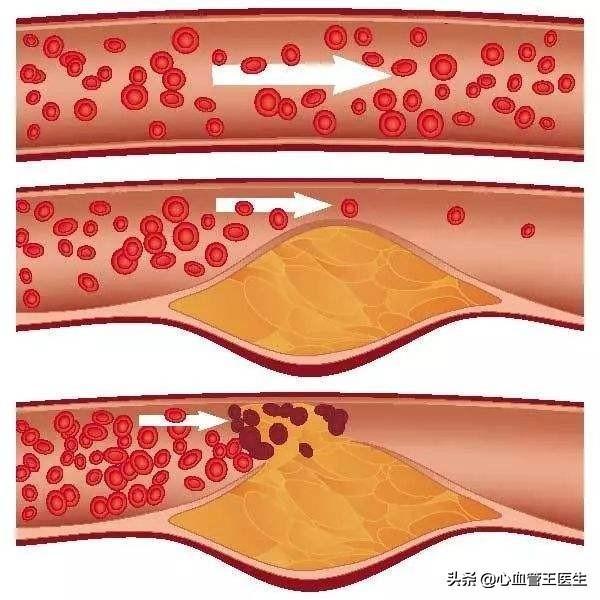
The short answer is that blood clots cause brain attacks, and blood clots are a major cause of brain attacks. However, blood clots can also be the result of other conditions, such as acute myocardial infarction, such as blood clots in other parts of the blood vessels, and so on. That is, a thrombus that occurs in the relevant cerebral vascular site will form a cerebral infarction. But it is not a cerebral infarction in other parts of the brain.
Broadly speaking, there are two types of blood clots that can lead to cerebral infarction: atherosclerosis, which accounts for the vast majority of atherosclerosis, in which plaque ruptures and forms clots; and clots formed by atrial fibrillation, which is a cardiac arrhythmia.
Carotid arteries, if severe plaque occurs, or unstable plaque, this plaque once ruptured will form blood clots, these blood clots will run to the cerebral blood vessels, thus blocking the cerebral blood vessels, causing cerebral infarction.
The main reason for the formation of carotid plaque is atherosclerosis, the main reason for the formation of atherosclerosis is unhealthy diet, smoking and drinking, obesity, sedentary without exercise, late at night and high stress, three highs without control, genetic and other reasons. Especially unhealthy life and do not pay attention to three high, then atherosclerosis will accelerate. So the prevention of atherosclerosis is to develop a healthy lifestyle from childhood.
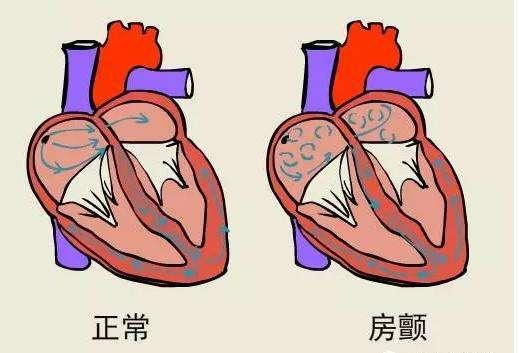
There is also a type of blood clot that is formed by arrhythmia atrial fibrillation, where every beat of our normal heart delivers all the blood in the heart, leaving no residual blood in the heart. However, when atrial fibrillation occurs, a portion of the blood flow is retained in the heart, and when the blood is retained for a long period of time, the blood will clot and form a blood clot, or thrombus. These clots then flow with the blood vessels to the cerebral blood vessels, thus blocking the cerebral blood vessels and causing a cerebral infarction. The way to prevent this kind of cerebral infarction is that once atrial fibrillation is detected, it must be treated formally, no matter whether it is anticoagulation therapy, surgery to cure atrial fibrillation, left ear blockage, etc., it must be found to specialize in specialist doctors, professional treatment.
In conclusion, blood clots are the most direct and fundamental cause of cerebral infarction, and the only way to prevent cerebral infarction is to prevent blood clots.
[Copyright Dr. Cardiovascular Wang]
Both cerebral thrombosis and cerebral infarction are hypoxic-ischemic lesions and necrosis of brain tissue caused by blockage of cerebral blood vessels.
Cerebral infarction has a broader scope, including cerebral embolism, cavernous cerebral infarction, cerebral thrombosis, and so on. Cerebral infarction is a brain lesion caused by a blood supply disorder. Cerebral thrombosis is one of the most common types of cerebral infarction, accounting for about 60% of cerebral infarctions. In terms of pathogenesis, cerebral infarction and cerebral thrombosis are considered to be two different segments.
While cerebral thrombosis is only one of the links and triggers of pathogenesis, cerebral infarction is the end result.
Usually, the onset of both processes is very slow, and the aura of cerebral infarction is not specific and lasts for a short period of time, so it is easy to be overlooked. However, the onset of cerebral thrombosis will be accompanied by aura symptoms, such as dizziness, slurred speech, blurred vision and so on.
Learn more about interventional therapy, focus on [Ozone Intervention Specialist He Xiaofeng].
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.