What are the symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion?
What are the symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion? 
You squat for a long time and then suddenly stand up, your eyes will suddenly go black and your brain will be dizzy for a few seconds. This is a sign of insufficient blood supply to the brain. This occurs due to the sudden standing up after squatting for a long time, and the blood cannot be pumped into the brain for a while. The above situation can happen to every normal person and there is no need to be nervous.
Today I'm going to focus on the symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the brain that we need to be aware of (suggesting that there is a disease or that a disease is about to occur)
Our brain cells are very delicate, they do not store energy and live on oxygen and glucose from fresh blood. As soon as the blood supply to the brain is blocked, symptoms immediately appear and within minutes brain cells begin to die, causing irreversible damage.
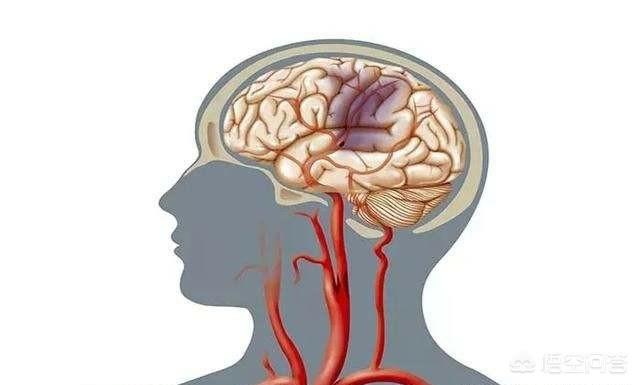
The blood supply to the brain comes mainly from two blood vessels, the internal carotid artery located at the front of our neck and the vertebral artery located at the back of our neck. These are the two main lifelines that keep the brain functioning properly.
The internal carotid artery supplies mainly the first two thirds of the brain
The vertebral arteries supply mainly the posterior third of the brain and the cerebellum
Since the parts of the brain are divided differently, the symptoms caused by two vascular lesions are different.
Symptoms seen in patients with insufficient blood supply to the internal carotid artery are: Headaches, dizziness (the whole person feels groggy and uninspired), poor memory, poor sleep, facial tingling, body feels numb, limb weakness, eyes tend to black out, fainting.
insufficient blood supply from the vertebral arterySymptoms include tinnitus, hearing loss, vertigo (different from dizziness, which is the feeling that things are spinning around you), vomiting, unsteady holding of things, unsteady walking, unsteady standing, and swaying.
Mild insufficiency of blood supply often causes mild symptoms or lasts for a short period of time, a few minutes or a few hours, usually no more than 24 hours. This condition we call a TIA (transient ischemic attack)
A severe lack of blood supply, such as a cerebral infarction, is a complete blockage of one of the branches supplying the brain, resulting in the death of brain cells in the area supplied by that blood vessel and a complete loss of function. A cerebral infarction results in serious symptoms such as hemiplegia, blindness in one eye, and a complete lack of sensation on one side of the body.
There are many causes of insufficient blood supply, such as low blood pressure, carotid plaque, various heart diseases, anemia, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cervical spondylosis, which can cause insufficient blood supply to the brain.
This problem can not be ignored, if the above symptoms occur frequently, you should have to go to the hospital in time to avoid the eventual development of cerebral infarction. It will be more miserable when you are paralyzed at that time.
Cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is all too common among the elderly, but nowadays it is not uncommon among young people under 30 years of age. A quick check of the literature shows that two thirds of people over 60 years of age suffer from chronic hypoperfusion, and 80% of people over 80 years of age suffer from chronic hypoperfusion. However, in recent years, the number of young people with cerebral insufficiency due to cervical spondylosis has been on the rise. Severe cerebral insufficiency of blood supply can lead to serious diseases such as cerebral infarction and dementia, and we need to pay attention to it.
1. What is meant by insufficient blood supply to the brain?
It is simply a common term for cerebral ischemia, which is a lack of blood supply to the brain due to impaired circulation in the cerebral arteries.
The brain is the center of our life, the command of the human body, is the most important seat of life functions, normal operation requires a constant supply of oxygen, glucose, etc. to feed the brain cells. And all the nutrients rely entirely on the blood supply, every 100 grams of brain tissue needs 40-60 ml of arterial blood per minute, when the arterial blood supply to the brain is less than the normal amount of need, the symptoms of insufficient blood supply will occur.

2. What are the manifestations of insufficient blood supply to the brain?
After the cerebral blood supply is insufficient, the brain is prone to lack of oxygen and energy, and the lack of energy in the brain cells appears a series of symptoms, and the common symptoms are some of the following.
- Dizziness, headache: drowsiness all day, head, especially forehead and back of the head, swelling and dull pain.
- Fatigue, lethargy: mental depression, easy fatigue, poor concentration', memory loss.
- Mood changes: irritability, anxious or depressed mood.
- Sleep disorders: daytime sleepiness, not enough sleep, but not enough sleep at night.
- Weakness or stiffness in the limbs and unsteady walking;
- Sudden and brief blindness, hearing loss, tinnitus;
- Malignant, vomiting;
- Uncontrollable spasms of a single limb or an area;
- Unilateral numbness of face, hands and feet;
- Fainting.

3. What are the complications of insufficient blood supply to the brain?
- clinical depression
- neurosis
- cerebral infarction
- vascular dementia
- Alzheimer's disease (i.e. dementia)
4. What can cause insufficient blood supply to the brain?
Our brain is at the highest point of the body, and the blood supply to the brain is like the water supply at the top of a tall building, the blood vessels are like the water pipes, and the heart is like the water pump. There are two keys to normal blood supply to the brain;Blood vessels should be open and the heart should be pumping adequately. Then, there are two main clinical causes of insufficient blood supply to the brain, a vascular problem and a heart problem.
① Vascular factors (most common): including the blood vessels leading to the brain and the blood vessels in the brain are not smooth, there are two main causes: atherosclerosis and cervical spondylosis.
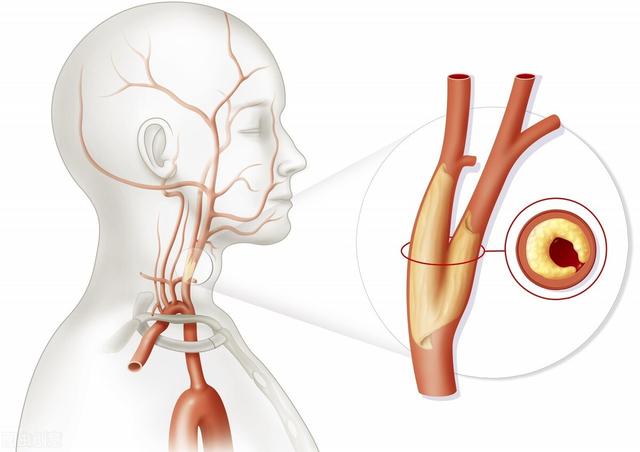
- a. Atherosclerosis:This is the most common cause. It affects both the patency of the arteries leading to the brain and the internal cerebral arteries.The carotid artery is one of the most important arteries supplying blood to the brainAtherosclerosis leads to the formation of plaque in the carotid arteries. Atherosclerosis leads to the formation of plaque in the carotid arteries, plaque formation leads to narrowing of the lumen of the vessel, and narrowing of the lumen leads to insufficient blood flow to the brain.
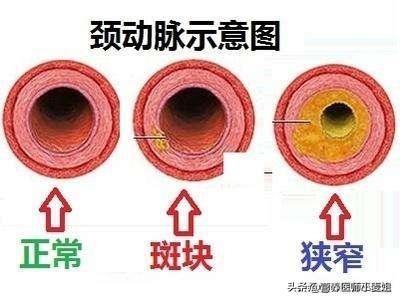
Atherosclerosis involves arteries throughout the body, and the arteries within the brain are not immune to it, which results in poor blood flow to both the blood vessels leading to the brain and the blood vessels within the brain, a double effect that affects the blood supply to the brain, leading to insufficient blood supply to the brain.Atherosclerosis is the most important cause of inadequate blood supply in the elderly.
- b. Cervical spondylosis:The most common type of whiplash is carotid.Many young people thus occur cerebral blood supply insufficiency, cell phone people, computer people and so on electronic equipment popularization and work needs, and then insufficient exercise, leading to the current young people neck push disease increased. And to the brain blood supply another important blood vessels arevertebral arteryCarotid spondylosis leads to misalignment of the cervical joints and prolapsed cervical discs that compress the vertebral arteries, causing narrowing and spasm of the arterial lumen, leading to a reduction in blood flow through the arteries and triggering a lack of blood supply to the brain.
② Cardiac factors (rare): decreased pumping function.
The arterial blood of any organ in our body is pumped out by the heart, and the brain is located at the top of the human body. Insufficient pumping function of the heart will obviously affect the blood supply to the brain. Common heart diseases that affect blood pumping are chronic heart failure, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, etc., leading to a decrease in the amount of blood ejected from the heart, resulting in cerebral ischemia.
4. What are the predisposing factors for cerebral hypoperfusion?
Factors that induce and aggravate the degree of atherosclerosis:
- Increase in age.
- Obese or overweight.
- Smoking.
- Irregular life.
Factors that cause or aggravate cervical spondylosis:
- Undesirable sitting position
- sedentary lifestyle
- the person with one's head down
- physical inactivity
5. What can I do to improve my cerebral blood supply?
cerebral hypoperfusionThe key is to find the cause of the disease, whether the cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is vascular or cardiac factors, according to the cause of the targeted interventionThe cerebrovascular circulation can be improved with medication or surgery, and daily attention is paid to maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Medication: use of anticoagulant drugs such asAspirin, clopidogreletc., which prevents thrombosis and opens up the blood vessels; the use of vasodilator drugs such asnimodipine (loanword)etc., can dilate blood vessels in the brain and improve cerebral blood supply; the use ofstatin (loanword)Drugs that stabilize arterial plaque, prevent new plaque formation, and improve atherosclerosis.
- Surgical treatment. If carotid plaque causes >70% narrowing of the arterial lumen, considercarotid endarterectomy or stenting.The goal of the surgery is to open up the blood vessels and restore blood supply to the brain.
- Pay attention to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Quit smoking and limit alcohol; avoid sedentary activities and exercise appropriately; eat a balanced diet, requiring low-fat, low-sugar and low-salt diets, reducing refined sugar intake, and increasing intake of dietary fibers, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, to maintain a balanced dietary intake of nutrients.
- Control of associated risk factors: active treatment of primary diseases such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment. Chinese medicine believes that insufficient blood supply to the brain is caused by insufficiency of the liver and kidney, deficiency of qi and blood, etc. Treatment includes tonifying the kidney, calming the liver, activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis, plus acupuncture, massage and other Chinese medicine techniques have a certain effect on the symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Summary: Cerebral blood supply insufficiency is due to cerebral arterial circulation disorders, the common cause is caused by cervical spondylosis, atherosclerosis, a small number of heart pumping insufficiency caused by dizziness, headache, fatigue, memory loss, and other symptoms, the improvement measures are mainly medication, surgery, etc., and the treatment is based on the treatment of the primary disease, the control of risk factors, and the improvement of the way of life.

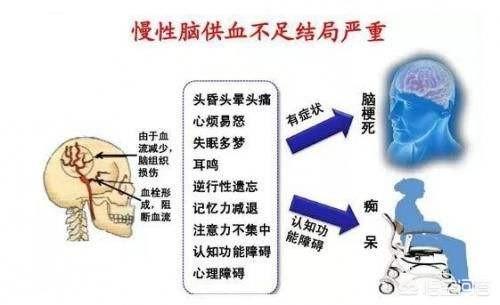
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, commonly known as chronic cerebral ischemia, is a clinical disease in which the blood supply to the brain is chronically and extensively insufficient for various reasons, leading to a series of cerebral dysfunctions caused by cerebral ischemia and hypoxia. Chronic cerebral ischemia was originally a common disease among middle-aged and elderly people. According to statistics, 2/3 of middle-aged and elderly people suffer from chronic cerebral ischemia, which is a frequent disease among middle-aged and elderly people. However, in recent years, there has been a trend of rejuvenation and aging, which is closely related to the unhealthy lifestyle of young people.

Chronic cerebral insufficiency has many clinical manifestations, mostly insidious and gradual.
The most common and easily overlooked clinical symptoms are:
① Dizziness and headache.Such as dizziness and dullness of the head, unclearness of the mind, swelling and pain in the head, dullness and pain in the head, dizziness and dizziness, dizziness and deafness.
② Insomnia or drowsiness.Such as insomnia and dreaminess, sleep shallow and easy to wake up, or all day drowsiness, sleepy after meals.
③ Memory loss.For example, you can't remember things that have happened recently, and you can't remember commonly used phone numbers or familiar names. ④ Eye symptoms. Eye swelling and pain, laziness in opening the eyes, foggy vision, etc.
(5) Ear symptoms.Tinnitus, ear "shut-in" and hearing loss.
(vi) Balance disorders.It is characterized by an unsteady gait, slow walking, and a weak demeanor.
⑦ Character change.For example, they become withdrawn, silent or have an indifferent expression, or they are talkative, irritable, stubborn and selfish. Some may experience a transient loss of consciousness or mental deterioration, or even loss of normal judgment, all of which are related to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
Middle-aged and elderly people should be alerted if the symptoms listed above occur fluctuatingly or progressively.

Chronic cerebral insufficiency of blood supply can be caused by a variety of reasons, which are summarized in the following four aspects:
① Vascular causes.Such as damage to the vessel wall, narrowing of the lumen or vasospasm. Cerebral arteriosclerosis, the formation of hardened plaque on the wall, lumen narrowing, thinning, increased vascular resistance resulting in reduced blood flow, especially after prolonged periods of continuous overuse of the brain, often occurs relative cerebral insufficient blood supply.
② Hemodynamic causes.Decreased blood pressure and slow blood flow. Common in people with low blood pressure or cardiac insufficiency. Decreased heart output causes insufficient blood supply to the brain. In people with arteriosclerosis, blood pressure drops during sleep at night compared to daytime, when blood flow is slow, and cerebral hypoperfusion occurs when they wake up in the early morning.
③ Blood-related causes.Changes in blood chemistry, increased viscosity. such as erythrocytosis, hyperlipidemia, dehydration, and decreased blood volume, which stagnate blood flow, all predispose the brain to inadequate blood supply.
④ Cervical spondylosis.The vertebral artery is an important blood vessel supplying the brain, which penetrates the transverse foramen on both sides of the cervical spine and travels upward to the skull. When the patient has obvious hyperplastic cervical spondylosis with intervertebral foraminal stenosis, especially when violently turning the neck, the vertebral artery can be compressed, causing temporary insufficient cerebral blood supply, followed by vertigo.
For chronic cerebral insufficiency of blood supply, timely diagnosis and treatment should be made to assess the degree of cerebral ischemia, search for the main causes of the disease, and carry out targeted treatment. Practice has proved that cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is reversible in the early stage, and correct treatment will often get good results. Some people think that these symptoms are a "normal phenomenon" of the elderly, and that they are "a trivial matter of no great importance". This is not the case, and it will be too late to regret if the best time for treatment is missed because of this "taking it easy".
(Duty Editor: Tomomi)
Cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is relatively common. According to statistics, 80% of people over 80 years old have cerebral insufficiency of blood supply, and 70% of people over 60 years old have cerebral insufficiency of varying degrees. This disease used to occur mostly in middle-aged and old people, but in recent years, cerebral insufficiency of blood supply also occurs in young people.

Under normal circumstances, the blood supply of the human brain is very rich, in a quiet state, if the heart beats 70 times per minute, each time the heart contracts, from the left ventricle into the aorta of the blood has about 70 milliliters, the left ventricle of the left ventricle of 5000 milliliters of blood per minute, of which the blood supplied to the brain has 800 ~ 1200 milliliters, accounting for 20% of the total body's blood supply, but the weight of the brain is only 1,300 ~ 1,500 grams accounted for only 2% of the body's weight. But the weight of human brain is only 1300~1500 grams, which is only about 2% of the whole body weight, so the blood supply of human brain is quite rich compared with the human body organs.
Symptoms of cerebral insufficiency of blood supply are not exactly the same because of individual differences in each person, but some of the more common symptoms are as follows.
I. Common manifestations of cerebral hypoperfusion.
1,Sensory symptoms: The most common are headache, dizziness, vertigo, some patients are prone to drowsiness, fatigue, poor mental status, daytime lethargy, nighttime sleep disorders insomnia, dreamy and easy to wake up, temper becomes irritable, sometimes inattentiveness, some patients have anxiety and depression, and some have unilateral numbness of the face, hands and feet. Long-term severe cerebral insufficiency of blood supply can lead to recurrent and significant headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, accompanied by a strong sense of vertigo.

2,Symptoms in sportsThese symptoms are relatively rare compared to the sensory symptoms, which may be manifested as limb weakness or stiffness, unilateral uncontrollable spasms in a certain part of the limb, and in some patients, transient ischemic attack, resulting in cranial nerve dysfunction, such as sudden aphasia, slurred speech, unfavorable speech, drooling, and weakness of one side of the limb, resulting in unsteady walking and easy to fall. Severe cerebral insufficiency of blood supply can appear facial nerve paralysis, manifested as numbness around the mouth and lips, pain, pinprick sensation, and even a transient black blindness with limb sensory abnormality, or sudden and transient blindness.
3,concomitant symptom: Memory loss, reduced social and work skills, slow to acquire information about new things, communication difficulties, etc.

Second, why does it cause cerebral hypoperfusion?
The following four are the most common causes of insufficient blood supply to the brain:
1,high blood pressureIn general, patients with high blood pressure are 4-8 times more likely to have insufficient cerebral blood supply and cerebral atherosclerosis than normal people. High blood pressure is one of the "main culprits" of atherosclerosis, and when high blood pressure and high blood sugar coexist, the "power" will be more significant!
2,excessive fat in bloodThe most important danger of hyperlipidemia, especially in patients with high LDL and high cholesterol, is that it causes atherosclerosis and the formation of plaque on the inner walls of the blood vessels, on top of which it causes narrowing of the blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood supply to the brain.
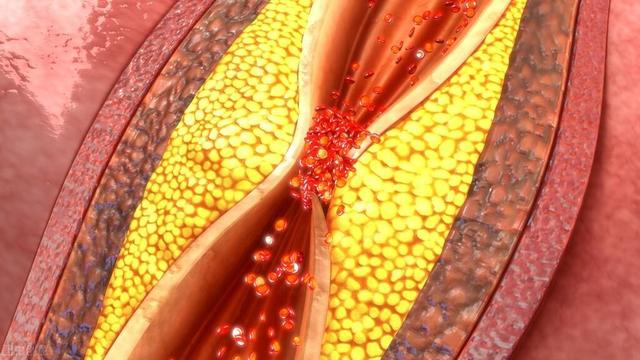
3,diabetesDiabetes mellitus causes small blood vessels and microvascular lesions, which are also the basis of insufficient cerebral blood supply. Diabetic patients not only have disorders of glucose metabolism, but also have disorders of lipid metabolism, which are manifested as dyslipidemia, resulting in atherosclerosis, which further causes the lumen of blood vessels to become smaller, the wall elasticity to decrease, and the ability to supply blood to the brain to decrease. Diabetic patients often also have platelet hyperfunction and coagulation abnormalities, which promote platelet aggregation and thrombosis, further aggravating atherosclerosis.
4,cigarette smokingSmoking damages the endothelial cells of the blood vessels, which, together with other risk factors, makes it easy to develop atherosclerosis, insufficient blood supply and even cerebral infarction.
The above four causes often play a role in each other, each other's influence, such as high blood pressure patients with diabetes, the two can be said to be the relationship between the fuel on the fire, high blood lipids can make the blood pressure further increase, accelerate the hardening of blood vessels, the end result is to cause the narrowing of the cerebral blood vessels, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the brain.
There is also a part of the cause of insufficient blood supply to the brain is out of the heart, commonly found in patients with chronic heart failure, because the heart pumping function is reduced, the heart output is reduced, resulting in cerebral ischemia.
In addition, irregular life, especially now obese people are increasing, obesity, smoking, irregular life, etc. will induce or aggravate the degree of atherosclerosis. Young and middle-aged people, the incidence of cerebral blood supply insufficiency of the population is mainly brain workers, some work overtime for many years, work and life is not regular, overworked, very easy to lead to coronary artery spasm, thus inducing cerebral blood supply insufficiency. In addition, sedentary lifestyle and poor sitting posture will lead to cervical spondylosis, which will induce insufficient blood supply to the brain.

Nowadays, people, generally too much pressure, the pace of life is too fast, the pressure of work and life tends to be concentrated together, when people are nervous, it will be a large amount of secretion of adrenaline, resulting in blood vessel constriction, heartbeat acceleration, blood pressure rises, and sympathetic nerve excitation, all of which can easily lead to cerebral insufficiency of blood supply occurs.
Third, how to prevent cerebral hypoperfusion.
Cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is not an independent disease, it occurs on the basis of other diseases, so in order to prevent it, you need to actively treat the original disease, usually need to actively improve the lifestyle, maintain a regular work and rest time, a reasonable diet and a good mood will help to prevent the further development of the disease.
1,Management of daily life
Maintain a healthy routine: avoid late nights, get good rest and sleep, and go to bed early and get up early.

Change bad habits: stop smoking, stop drinking, lose weight, etc. Avoid being sedentary. Increase socialization, improve your mood, and keep your mood happy, which can reduce the occurrence of cerebral insufficient blood supply. Squatting down and getting up suddenly, or getting up suddenly to change your position, should be slower.
Maintain a healthy diet: eat more dietary fiber and fish and other high-quality protein, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, don't eat too much at dinner, and drink a small glass of warm boiled water before going to bed to reduce the viscosity of the blood.
Active physical exercise: more aerobic exercise: such as swimming, walking, jogging, playing tai chi, etc., according to the amount of strength, daily adherence.
2,Daily home care
Attention should be paid to preventing the patient from falling and bruising. The bathroom at home should not be wet and have anti-slip measures, shoes should be worn comfortably and non-slip, the patient's family members need to actively learn the symptoms of acute stroke and first aid knowledge, such as patients with acute ischemic stroke, you need to undo the patient's collar, to keep the patient's airway open and call the emergency number in a timely manner.

Written in the end: Chronic cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is very common, known as the invisible killer jeopardizing the health of middle-aged and elderly people, so we must not take it seriously. At present, there is no clear understanding of cerebral blood supply insufficiency in the medical field, and there is no classification of this disease in the international diagnostic standards. If you are diagnosed with this disease, you don't have to be in too much of a hurry, and it is key to actively search for the primary cause of the disease, and you have to be careful to comply with the doctor's prescription of medicines in treating the disease. Do not believe in the so-called "biased prescription", "secret recipe", so as not to be deceived and delay the condition.
This content is for the use of medical knowledge science only, not as a specific diagnosis and treatment of the opinion, specific decision-making please follow the doctor's advice.

Hello, I am glad to answer your question. Cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is mostly seen in the middle-aged and elderly population, and the symptoms are different for each person, but all of them don't care about the following kinds of symptoms. Because chronic cerebral insufficiency can lead to so many negative consequences, I'd like to share them with you today!
First, headache and dizziness, the most common. Dizziness, mental depression, can appear in the back of the head swelling pain, migraine, head is like wearing a helmet, serious cases can appear vertigo, nausea and vomiting.
Second, it can lead to eye and ear discomfort, such as blurred vision, vision loss, dry and swollen eyes, tinnitus and dull ears, and hearing loss.
Third, it causes weakness, numbness and pain in the limbs, poor peripheral circulation, cold hands and feet, and abnormal sensation in the peripheral joints.
Fourth, transient ischemic attacks are more common, with transient dizziness and lightheadedness, or blackness in front of the eyes, and in severe cases, sudden collapse and loss of consciousness, usually lasting less than half an hour.
Fifth, the heart and brain are not separated, the brain blood supply is not enough with myocardial ischemia close relationship, so that the panic chest tightness and shortness of breath, more common.
Sixth, abnormal blood pressure, which can cause hypertension and low blood pressure.
Seventh, unsteady walking, severe cases can appear to be unable to walk in a straight line, walking on cotton well, poor balance function.
Eighth, mental changes, insomnia, dreaminess, irritability, memory loss, poor sleep quality.
Ninth, drowsiness, whether it is day or night, always sleepy, sleepy, drowsy, dizzy, eyes can not open.
Tenth, long-term insufficient cerebral blood supply can cause cerebral infarction, cavernous infarction, and even other cerebrovascular diseases, which is a more serious reaction.
As long as the chronic cerebral blood supply insufficiency, must be enough to pay attention to, otherwise, over time the impact on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular will be more and more large, many serious diseases is formed in the unknowing, for the sake of health, early prevention and early treatment, is always good!
What is the brain? It is the "headquarters" of the human body. It is born with its own "helmet", the skull, which is superior to the heart and lungs, which are also protected by ribs. The importance of the brain is self-evident, and any disease will affect the whole body.
The total blood flow circulating in the brain per minute is about 750 milliliters, which is equivalent to 15% of the cardiac output, while the weight of the brain only accounts for about 2% of the body weight. The metabolic level is high, and the energy consumed is the aerobic oxidation of glucose, so the oxygen consumption is also high, about 50 milliliters per minute when quiet, accounting for about 20% of the whole body's oxygen consumption.
Brain tissue is sensitive to ischemia and hypoxia, and symptoms of cerebral ischemia can occur if blood flow per 100 g of brain tissue is less than 40 ml/min.
The blood supply to the brain comes from the internal carotid and vertebral arteries, with varying symptoms of ischemia
I. Inadequate blood supply to the internal carotid artery
The main symptom is visual impairment or cerebral hemispheric lesions.
For example, if the ischemia is on the left side, the visual impairment is in the left eye, and the motor and sensory impairment (or hemiparesis) is in the right hand or foot. Rarely, both symptoms are present at the same time, mostly alone.
Transient monocular blindness or transient blackouts are most common. Blackouts consist of a gradual decrease (or increase) in lightness and darkness in the visual field that progresses to complete, painless blindness in one eye. It is also sometimes characterized by incomplete visual fields, total blurring of vision, or gray or bright blurring of vision. Some people consult the ophthalmologist for blackouts, which can be easily missed.

II. Inadequate blood supply to the vertebral artery
Symptoms are varied and often include vertigo, diplopia, dysarthria, bilateral facial numbness, ataxia, and weakness or numbness of the arms and legs unilaterally or bilaterally.
Less common symptoms include hemiparesis, head or ear ringing, head pain or other specific head sensations, vomiting, eructation, tilting sensations, memory loss, behavioral disturbances, sleepiness, impaired hearing, deafness, unilateral limb twitching, hallucinations, and eyeballs that do not conjugate.
What are the consequences of chronic insufficient blood supply leading to chronic brain insufficiency - cognitive impairment
Cognitive impairment manifests itself in a variety of ways, including learning, memory, language, motor, thinking, creativity, mental, and emotional.
I. Learning and memory disorders
The process of memory involves: sensory input → sensory memory → short-term memory → long-term memory → stored information.
Short-term and long-term memory are associated with the phosphorylation of specific proteins, and in different parts of the cerebral cortex during ischemic injury, then different memory deficits occur.
For example, damage to the hippocampal region of the temporal lobe can cause spatial memory impairment, and damage to the amygdala region can cause emotional memory impairment.

II. Language - Aphasia
If the lack of blood supply to the brain is in the area of the thalamus and basal ganglia, it can cause aphasia.
Aphasia is a disorder of verbal communication. It means that you cannot understand what others or yourself are saying, you cannot say what you want to say, you cannot understand or write what you could read or write before the onset of the disease, and so on.
III. Loss of Recognition
Inability to recognize previously familiar objects through one sense, but can do so through other sensory channels.
If you see a watch and don't know what it is, you can perceive it as a watch by touching the shape of the watch or listening to the sound of the watch moving.
IV. Misuse
Inability to use some of the limb functions correctly in conjunction with whole body movements to accomplish movements that would otherwise be habit-forming.
Such as not being able to perform simple actions such as sticking out the tongue, swallowing, brushing the teeth, washing the face, etc., as required, but being able to do these actions spontaneously without thinking about it.
V. Other changes in mental and nervous activity
It is characterized by abnormal changes in mental and nervous activity such as talkativeness and nagging, mood changes, anxiety, depression, agitation, and euphoria.
VI. Dementia
It is the most severe form of cognitive impairment.

Prevention of Cerebral Hypoperfusion
The focus of prevention is to identify the cause of the disease, the elimination of the cause of the disease will achieve the purpose of prevention; the cause of the disease can not be eliminated, can better control its progress is also a preventive measure.
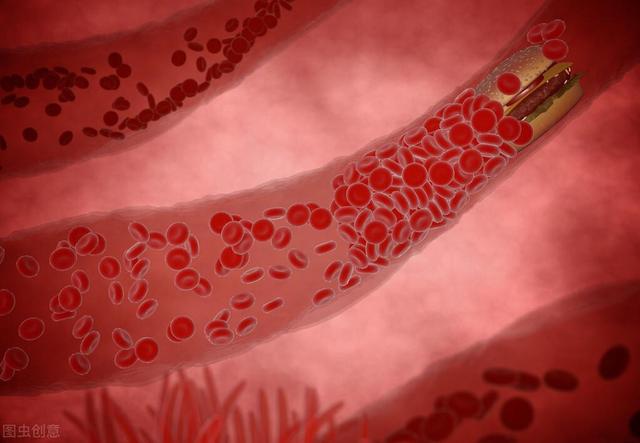
I. Ischemia
Ischemia generally occurs when there are changes in the blood vessels, such as plaque and hardening of the blood vessels, that result in altered blood flow.
Plaque, such as that in the carotid arteries, leads to insufficient blood supply to the brain as blood flow becomes smaller as it passes through. This lesion can be detected by ultrasound, and the general treatment plan is to control blood pressure and lower blood lipids, aiming at preventing plaque from getting bigger and new plaque, but not eliminating plaque. For plaques that are too large and seriously affect the blood supply to the brain, surgical removal is an option.
II. Hypoxia
The brain has an adequate blood supply, but is deprived of oxygen, which can also be counted as an inadequate blood supply.
Brain tissue relies on the aerobic oxidation of glucose for energy, and anaerobic digestion occurs in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic digestion produces less energy and can cause lactic acidosis and damage to brain tissue.
The etiology of hypoxia is twofold: inadequate oxygen supply and the presence of barriers to oxygen utilization.
① Insufficient oxygen
Commonly for chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, etc.; prevention lies in the active administration of oxygen therapy, such as home oxygen therapy.

②Oxygen use disorder
Anemia and carbon monoxide poisoning are common.
In anemia the amount of hemoglobin decreases resulting in insufficient ability to transport oxygen, and carbon monoxide poisoning results in a decrease in the ability of hemoglobin to transport oxygen. Prevention lies in correcting the anemia and quitting smoking or staying out of second-hand smoke environments.
Cerebral insufficiency of blood supply can be said not to be a disease, but a series of symptoms appearing after various etiological factors lead to cerebral ischemia. Therefore, the root of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention lies in the search for various existing etiological factors, and elimination of the etiological factors eliminates insufficiency of blood supply; some irreversible etiological factors, such as atherosclerosis and plaque, can be targeted for treatment, prevention of their progression, and prevention of the emergence of serious complications.
Hi, thanks for the invite!
Cerebral hypoperfusion is a cerebral dysfunction caused by insufficient localized blood supply to the human brain, mostly related to cerebral atherosclerosis, cervical vertebrae, carotid artery plaques, blood viscosity and so on.
When the cerebral blood supply is insufficient for a long time, or when the treatment is not timely, it will lead to cerebral infarction or dementia. Therefore, insufficient blood supply to the brain should be taken seriously and not be sloppy.
When there is insufficient blood supply to the brain, our body will show symptoms such as.
1、Drowsiness
Always wanting to sleep and being groggy, this drowsiness is not caused by fatigue, but by insufficient blood supply to the brain.
2. Indifference in expression and reticence
When the blood supply to the brain is insufficient it can lead to abnormal mental awareness, such as withdrawn, silent, or apathetic expressions.
3. Transient loss of consciousness or mental deterioration
4. Crooked mouth, drooling, slurred speech, difficulty in swallowing
5. Loss of balance, unsteady walking, or sudden falls (insufficient blood supply to the brain affects motor nerve function)
6. Weakness or inactivity of one side of the limb, and unconscious dropping of things picked up
7. Numbness of the face and one side of the limb
8. Blurred vision or transient blackness before the eyes
9. Vertigo, headaches, limb pains
10, insufficient blood supply to the brain, but also cause tinnitus and deafness

Therefore, in daily life, we must do a good job of prevention and timely treatment of cerebral blood supply insufficiency. The main measures stomach reasonable diet, prevention of high blood fat, daily physical activity, sleep enough, etc., once the phenomenon of cerebral blood supply insufficiency, should be timely under the guidance of the doctor to give medication to improve the cerebral blood circulation.
What are the symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion?
Cerebral hypoperfusion is actually the main clinical term for cerebral ischemia.
Cerebral ischemia can also be categorized into a variety of/
(1) There is a transient, also known as transient cerebral hypoperfusion.
(ii) There is chronic cerebral ischemia, which exists to varying degrees in most people over the age of 60.
③There is also acute cerebral ischemia, which is very familiar as cerebral infarction, and commonly includes cerebral thrombosis, cerebral embolism, cavernous cerebral infarction, and cerebral infarction caused by shock, overdose of antihypertensive medication, or anesthesia medication resulting in a severe drop in blood pressure.
What are the causes of cerebral hypoperfusion?
The cervical artery is compressed by hyperplastic cervical bone or the cerebral blood vessels go into spasm; spasm and cramp are one and the same.
Atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc., can cause narrowing of the lumen of the internal carotid artery, poor elasticity, lipid deposition in the blood vessel wall to form atherosclerotic plaques, atherosclerotic plaques can rupture and bleed or form a thrombus leading to cerebral ischemia.
Cardiac lesions cause cardiogenic blood clots, blood clots will accompany the blood pumped out of the heart to land in the brain, causing the cerebral blood vessels to be partially blocked or completely blocked, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the brain, common lesions include heart failure, hyperthyroidism and other diseases caused by atrial fibrillation, pre-coronary artery disease, heart valve diseases such as rheumatoid artery disease, cardiac surgery, myocardial infarction, and infective endocarditis.
Various causes of blood viscosity and hypercoagulation, and various causes of low blood pressure.

What are the symptoms of cerebral insufficiency?
Dizziness, headache, neck and shoulder pain, spinning, nausea and vomiting, loss of vision or blurred vision, nausea or vomiting, mental and behavioral abnormalities, and sleepiness.
Anxiety, insomnia, depression, decreased concentration, easy to be distracted, talk too much, forgetfulness, anger, or silent, withdrawn, expression of indifference, emotional instability, tinnitus, insomnia, sleeplessness and dreaminess, hearing loss, decreased judgment, and slow decline in intelligence and other manifestations of dementia.
Weakness of one side of the limbs, inability to move well, loss of holding objects, unsteady walking or sudden fall and get up on their own, numbness of one side of the arms and legs or one side of the face, one side of the tongue or one side of the mouth and lips or the sensation of a foreign body, one side of the eyes with transient haze or heavy shadows, or visual field defects.
Some patients have a crooked mouth, drooling, slurred speech, loss of or difficulty in speaking, or even aphasia or hemiparesis.
Acute cerebral infarction can be characterized by confusion, drowsiness, lethargy, coma in severe cases, and incontinence.
Clinically, transient cerebral insufficiency of blood supply or chronic insufficiency of cerebral blood supply requires vigilance and attention because it can develop into acute cerebral infarction (acute cerebral insufficiency of blood supply) or dementia, which is more harmful.

Thanks for the invite 😊!
In fact, the so-called cerebral blood supply is an organic state, that is to say, various causes of cerebral blood vessels, cerebral blood flow dysfunction, brain tissue can not get adequate blood supply and produce a variety ofManifestations of ischemia and hypoxia in brain tissue!
Clinically, insufficient cerebral blood supply, mostly due tohardening of the arteriescause, often appearing on imaging as multiple "ischemic focus"!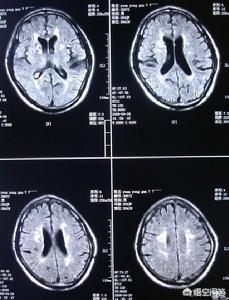
(Note: on the MRI image it appears as "white patch")
Chronic cerebral insufficiency is due to ischemia that has not yet reached the level that causes cerebral infarction:
Therefore, there are usually no particularly obvious clinical symptoms; they are mostly manifested asDizziness, heaviness of the head, lack of mental clarity, and long-term insufficient blood supply to the brain will also gradually show signs of memory and concentration loss!
Finally, understanding "cerebral hypoperfusion,"We need to know:
If we have symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the brain, we need to start paying attention to the prevention of "cerebrovascular disease" at an early stage!
I hope my answer is helpful to you!
Welcome to follow "Dr. Komai Shinouchi" for more health information!
Let's talk about the dangers first! Chronic cerebral insufficiency can be effectively controlled if timely and correct intervention is provided, otherwise, it may lead to stroke, vascular dementia and many other diseases. If there is no early treatment, it can lead to a person's cognitive and neurological functions, seriously affecting the health status and quality of life of middle-aged and elderly patients.
What are the symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion?
Chronic cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is a common clinical neurological disease in middle-aged and elderly patients, which manifests as recurrent dizziness, headache, insomnia, amnesia, and numbness of the limbs, etc., but there is no clear neurological organic lesion in the imaging examination. With the changes in people's living habits and dietary patterns in recent years, the incidence of this disease is increasing in the middle-aged population.
Insufficient cerebral blood supply type dizziness is a common disease in cerebrovascular internal medicine, often due to patients with aortic atherosclerosis or thrombosis leading to blood vessel blockage, affecting the normal blood supply, resulting in ischemic and hypoxic lesions in the brain, affecting the normal function of the patient's nerves or brain. The prognosis of these patients is poor and the clinical treatment is difficult.

Cerebral blood supply insufficiency can be categorized into acute and chronic, mainly due to insufficient blood supply to the brain triggering cerebral dysfunction, resulting in slurred speech, numbness of the limbs, generalized fatigue and so on, seriously affecting the normal life. Research has found that patients with cerebral blood supply insufficiency dizziness need comprehensive nursing interventions in order to promote the disappearance of symptoms and improve the psychological state.
How do I take good care of myself?
Dietary guidance can ensure adequate supply of nutrients to patients, but also avoid the increased risk of sequelae caused by overdiet; condition observation is a good basis for clinicians to the dynamic development of the patient's condition; psychological care is not only conducive to channeling negative psychology, but also improve the symptoms; medication care is the premise to ensure the rational and safe use of medication; and prognosis of complications can improve the patient's prognosis effectively.

Chronic cerebral insufficiency is closely related to hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, and even hemorrhagic cerebrovascular disease. It is the backup of cerebrovascular disease which is disabling and fatal. The efficacy of aspirin enteric-coated tablets combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of chronic cerebral insufficiency of blood supply is precise and obvious, and has clinical significance. If it can be included in the primary prevention of cerebrovascular disease, like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc., it will be conducive to health.
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! In addition, if your family members also have related troubles, please forward this article to them!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.