What tests are done to detect coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia?
What tests are done to detect coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia? 
Whatever the cause of chest tightness, chest pain, and breathlessness, it is always a jittery experience. Because I've seen too many characters in movies and on TV, collapsing with their chests covered.
Let's talk about the most common cardiology tests.
1. Electrocardiogram:
The electrical signals from the heart are converted into a waveform pattern through a collection device on the surface of the body, and this is what we see as an electrocardiogram (ECG). Just like a telephone, a regular electromagnetic signal is received and converted into speech so that you can understand what the other party is saying. This test is used for basically all diseases in cardiology, and it is one of the basic tests that are indispensable, whether it is a problem with the heart's rhythm or a problem with the blood supply. If you come across a doctor who says that you are suffering from myocardial ischemia and prescribes medication without looking at the ECG, you can ask him to his face: "How can you conclude that I am suffering from ischemia when the heart is not in the right place? You think you're an electrocardiogram machine!"
The drawback of the EKG is that it can only reflect what is happening to your heart during the few minutes you are lying on the examining bed. If you are not uncomfortable when the EKG is done, the EKG may be a normal indication, so how can it reflect what is happening at other times. The following test is an upgraded version of an EKG.
2. Dynamic electrocardiography:
If 24 hours for the doctor to keep an eye on your electrocardiogram is not very realistic, the tiger has napping time, but the 24-hour electrocardiogram is like a 24-hour never annoying, conscientious doctor, complete record of your electrocardiogram changes, record your heart want to tell the doctor things. This test is for 24 hours of the heart beat regularly ah, there is no ischemia and other issues, if you back 24-hour dynamic electrocardiogram test at the same time, can do a climbing exercise, he can also be used as an exercise load experiment to assess your activities after the blood supply of the heart muscle. If you have a sensation of falling out of the precordial area, a sensation of a chaotic beat, self-consciousness of a fast or slow heart rhythm, chest tightness at night, waking up with suffocation, chest tightness and chest pain after activity. This 24-hour EKG is an essential tool to confirm your diagnosis.
Of course, the dynamic ECG is not foolproof, if you are episodic discomfort in the precordial region, on the day of the dynamic ECG, there is no attack, then the dynamic ECG can not reflect your problem, and the previous can only rely on repeated many times to improve the dynamic ECG, in order to be able to catch the changes in the ECG during the attack. How to get rid of this limitation and check your heart condition at any time, then it is the following test.
3. Coronary CT examination:
The birth of 64-row CT and the development of dynamic tracking technology have allowed us to examine the blood vessels of the heart in a non-invasive way to clarify the presence and extent of stenosis in the coronary vessels. This technique has benefited many patients with chest tightness and chest pain who are afraid of needles and the operating room. The main principle of this test is that a contrast agent is injected intravenously and the contrast-filled coronary vessels are scanned helically by CT, and then each scanned slice of the coronary artery is combined to form a picture of the coronary artery by image combination technology.
This test is non-invasive, safe, but there are a number of shortcomings, ① rhythm control 64-row CT requires the heart rate to be controlled at 60 beats / min or less, faster 128-row and dual-source CT also requires the heart rate to be controlled at 70 beats / min or less as far as possible; ② coronary CT between the heart of the ordinary examination and coronary angiography, but also and coronary angiography, as the same as the radiation and contrast damage, if the symptom If the symptoms are very clear, it is not as good as to do the imaging test in addition to the examination can also be directly treated; ③ remember this sentence, if the coronary CT examination that you do not have coronary heart disease, the credibility of this sentence is as high as 99%, but if the coronary CT examination that you have coronary heart disease, the credibility of this sentence is only 70%.
4. Coronary angiography:
Finally, it's time to talk about the king of cardiac vascular tests. Coronary angiography is much older than I am, and it has a history of nearly 56 years since Dr. Sones of the Cleveland Medical Center completed the first coronary angiography in 1959. Since its inception, coronary angiography has become the gold standard for coronary artery disease because of its visual and objective characteristics.
The significance of the gold index for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease is a bit like the emperor's will, saying yes or no. Regardless of what tests have been done on the coronary arteries, as long as a coronary angiogram has been done, everything will be based on the results of the coronary angiogram. Coronary angiography is to insert a ball-point pen core thick catheter from the femoral artery or radial artery, place it into the opening of the coronary artery, and through the method of injecting contrast medium and developing the image, observe the traveling of coronary artery vessels, the number of coronary artery vessels and deformities under the contrast medium; evaluate the presence or absence of coronary artery lesions, their severity and the scope of the lesions; evaluate the functional changes of coronary arteries, including spasm of coronary arteries and the presence or absence of side circulation; at the same time, it can also take into account the left side of the coronary artery. Evaluation of functional changes in the coronary arteries, including coronary artery spasm and collateral circulation; at the same time, it can take into account the evaluation of left heart function. It can be said that this examination basically covers all cardiac related examinations except electrophysiology.
The risks of coronary angiography are centered on: (1) intrusion of arterial plaque during puncture, which can lead to coronary plaque dislodgement and coronary spasm; (2) post-procedure hematoma at the puncture site; and (3) the effect of contrast media on renal function. It should be noted that these risks, although present, can be avoided by preoperative vascular assessment, adequate postoperative hemostasis with compression, and adequate hydration.
All in all, if performed by an experienced interventionalist and team, the safety of coronary angiography is still very much guaranteed and there is no need to worry too much. The benefits of coronary angiography outweigh the drawbacks when compared to the diagnostic utility for patients with coronary artery disease.
Well, here you are introduced to the most important 4 tests for diagnosis of coronary heart disease examination, with these four tests, basically, the lesions of coronary blood vessels have nothing to hide.
So dear friends, if you have paroxysms of chest tightness, chest pain, and all sorts of suspected heart problems found on Baidu, don't be too busy to ask your doctor: is this coronary heart disease I have.
Without the support of these tests, a responsible cardiologist in Western medicine would never blindly tell you his judgment.
This is because once a diagnosis of coronary heart disease is made, the cost of lifelong medication will be countless times the cost of these definitive coronary heart disease tests.
最后,对于那些实在觉得医生开检查就是在骗钱的亲们,我啰嗦最后一句:知己知彼百战不殆、工欲善其事必先利其器、战略上要藐视对手战术上要重视对手、目的正确要比跑的快更重要...........!
Welcome to follow and give you a different view of medicine!
Thanks for the question invitation!
There is a strong connection between coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia. Coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction are the names of diseases. The former refers to the narrowing of the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart due to atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle, which in turn can produce symptoms such as chest tightness and chest pain. Myocardial infarction, on the other hand, is a severe myocardial ischemia that ultimately leads to the necrosis of heart muscle cells. From these two processes, it can be seen that myocardial ischemia refers to a state rather than a disease. From the perspective of disease classification, all three can be categorized as coronary heart disease. There are many tests for coronary artery disease, and Dr. Elf describes some of the more important ones below:
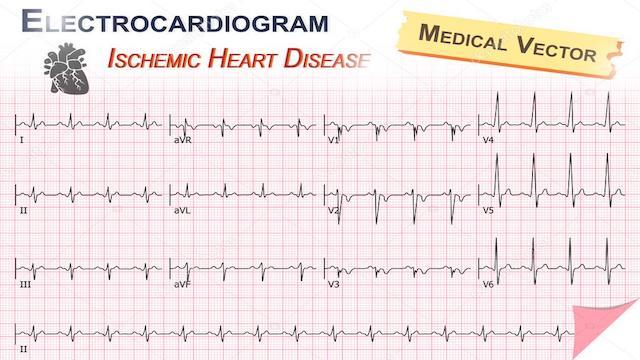
1、Electrocardiogram (ECG): when myocardial ischemia or necrosis occurs, ECG can often see some changes, and it shows dynamic changes, in addition, according to the abnormalities of different leads, it can be judged which wall of the heart ischemia or infarction occurs, and then further deduce which blood vessel may be ischemia; this test can be said to be the most convenient and cheap, but the beauty of the shortcomings is that the electrocardiogram cannot directly observe the condition of blood vessels, so it is not the golden index for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease; this examination can be said to be the most convenient and cheap. However, the drawback is that ECG does not directly observe the condition of the blood vessels, and is therefore not a golden indicator for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease;
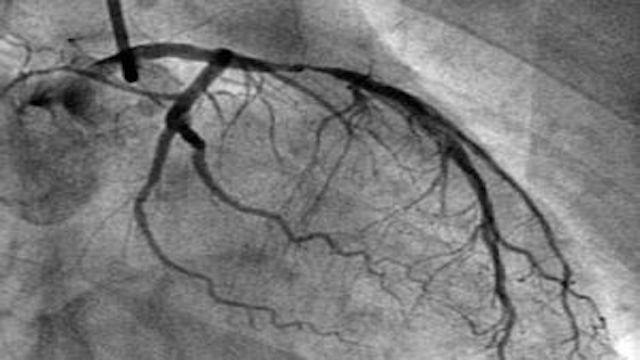
2, coronary angiography: this is a kind of invasive examination, through the arterial puncture, the catheter will be put into the opening of coronary artery, injecting the contrast agent into it, and observing the filling situation and blood flow speed inside the blood vessel under the X-ray; this kind of examination can directly see the situation inside the blood vessel, so it is the golden index for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, but the disadvantage is that this kind of examination is an invasive examination;
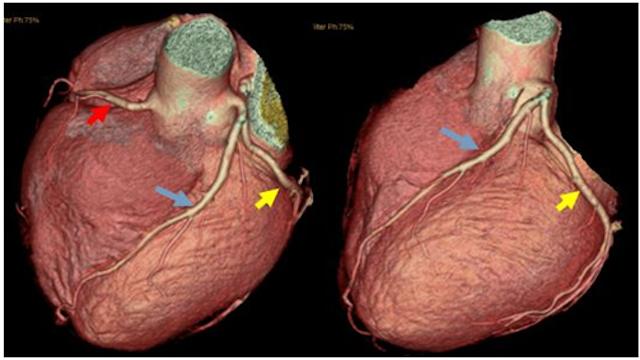
3、Coronary CT: It injects contrast agent through superficial vein and utilizes CT imaging, so the safety is higher than direct arteriography, but the diagnostic efficiency is weaker than coronary arteriography due to the image is synthesized and there are certain requirements on the heart rhythm;
4, plate test: this test is somewhat similar to walking on a treadmill, through different amounts of exercise, to observe the changes in the electrocardiogram, the difference between it and the ordinary electrocardiogram is that it can actively observe the performance of ischemia under the load of the heart to do the work; this test is not suitable for those patients with unstable conditions;
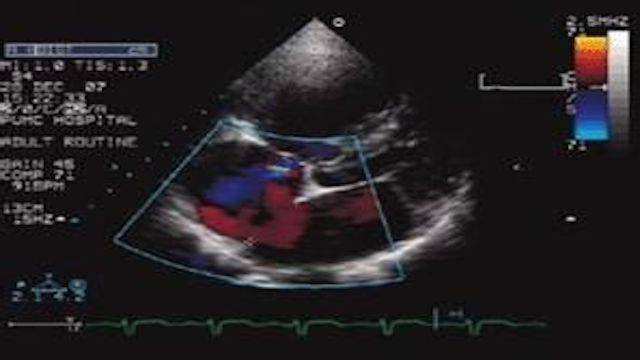
5, cardiac ultrasound: cardiac ultrasound is to look at the heart muscle and internal anatomy of the examination, it can not directly see the coronary arteries, but if there is myocardial ischemia or necrosis, it will affect the myocardial movement, so as to indirectly respond to the situation of the heart blood supply;
The above introduces several commonly used coronary heart disease examination methods, for the general public to understand on the good, in the end when to use what examination is best to listen to the advice of a professional doctor is better.
Thanks for the invite! This question has been asked several times, but the topic is so big that I can only give a brief overview.
Coronary heart disease is the abbreviation of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, of course, caused by insufficient blood supply to the coronary arteries or myocardial infarction is not only atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, there are other reasons, but the most important, the most common, more than 95% are because of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, the stenosis of the coronary arteries caused. Therefore, when we say coronary heart disease, we mean coronary atherosclerotic heart disease.

Coronary heart disease can cause myocardial ischemia if the blood supply is only insufficient, and myocardial ischemic necrosis, which is myocardial infarction, if the ischemia is severe or completely interrupted. Therefore, both myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction can be caused by coronary artery disease, just to a different extent.
Introduces some commonly used screening methods.
1. Electrocardiogram. Myocardial ischemia has a relatively low detection rate (usually less than 50%), unless one is having an angina attack, because the ECG changes during ischemia and recovers after ischemia. Myocardial infarction has a higher detection rate, but sometimes the timing of the test is wrong (pseudo-improvement period) and it can be missed.
2. Ambulatory electrocardiogram.. It is the examination and recording of the ECG for 24 hours or even longer. In this way, it is possible to record the ECG changes during an episode of myocardial ischemia, to make up for the lack of a general ECG, and to detect some patients with painless (asymptomatic) myocardial ischemia.
3. Exercise (load) test.. There are flatbed (running) or pedaling (cycling) methods, and the newest ones also monitor respiratory function at the same time. Exercise should be run to sub-extreme levels (heart rate levels based on age, and metabolic value criteria). This is because when the coronary arteries are narrowed to a certain degree (75% or more), the ability to compensate (dilate when the demand for blood supply increases to ensure blood supply) is significantly reduced, and when exercise increases the load on the heart and requires an increase in blood supply, myocardial ischemia occurs, and the electrocardiogram will change accordingly. This method can probably detect about 70% of patients.
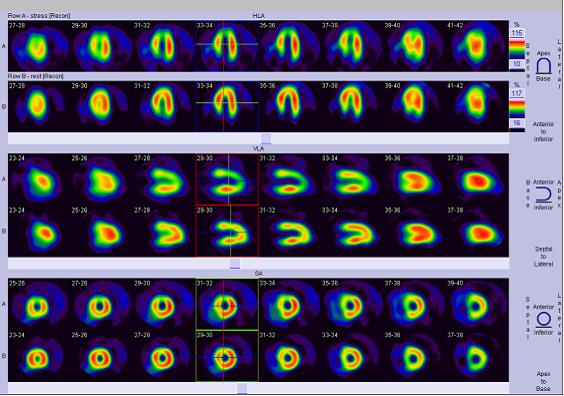
4. Exercise Nuclide Myocardial Perfusion ImagingIt's the exercise test plus the nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging. It is an exercise test coupled with radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging. This is done by injecting radionuclides (isotopes) intravenously that can be taken up by the heart muscle cells, and these are pumped through the blood vessels to the heart to be taken up by the heart muscle cells; if there is no blood supply, the heart muscle cannot take up the radionuclides. In this way, the blood supply is determined by how much radionuclide is in the myocardium (concentrated, sparse). Exercise is then used to identify ischemia or infarction. If the examination is fine during exercise, then there is no ischemia or infarction; if the nuclide perfusion decreases during exercise and is normal during quiet, then there is ischemia; if there is no perfusion during exercise or quiet, it means that the blood vessels supplying blood are blocked.
5. Coronary CTA (CT coronary angiography)The procedure is to inject an iodine contrast agent into a blood vessel. It involves injecting an iodine contrast agent into a blood vessel and using CT (computed tomography) to look at the coronary arteries to see if there are any malformations, bridges in the myocardium, and plaque and stenosis in the coronary arteries. The advantage of this method is that it is "non-invasive" and does not require a catheter to be inserted into the coronary arteries. However, because it is an X-ray, it is better to look at calcification, but there are limitations in looking at stenosis, which is not so accurate (it has to do with the instrument and the examiner's skill level), and in addition, a fast or irregular heartbeat will also affect the imaging effect. Therefore, this method is best for ruling out coronary artery disease and less accurate for diagnosing stenosis. In addition, during the examination, 80-100 ml of iodine contrast agent is injected intravenously. First, there is a possibility of allergy (skin test may not be detected), and second, the contrast agent has to be excreted through the kidneys, which is damaging to the kidneys, and a few patients may develop "contrast nephropathy" (contrast nephropathy), with renal impairment or insufficiency, so it is necessary to "hydrate" before and after the examination. Therefore, it is necessary to "hydrate" before and after the examination.
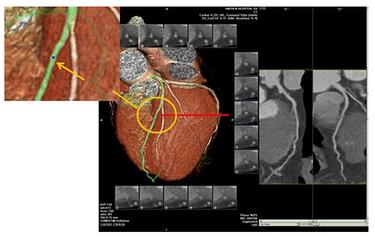
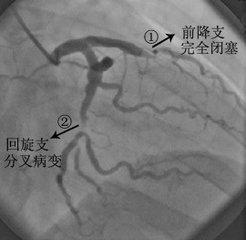
6. Coronary angiography (percutaneous transarterial coronary angiography)The procedure. This is done by arterial puncture (radial artery in the wrist or femoral artery at the base of the thigh) to deliver a catheter to the opening of the coronary artery, injecting an iodine contrast medium to look at the morphology of the coronary arteries and the blood flow, and generally diagnosing coronary artery disease when there is a narrowing of more than 50 percent. This method is currently the "gold standard" for diagnosing coronary artery disease. The advantage is that it is accurate (of course, there are also inaccuracies, due to the angle of illumination, the doctor's experience, vascular deformities, etc.), and can be treated immediately after the problem is detected, with the use of balloon dilatation or stenting (and other techniques) to open the coronary arteries and improve the supply of blood, checking and treating at the same time. This method is a minimally invasive procedure with proven technology and excellent safety. But since it is a procedure, there is injury, risk, and the same problem with contrast media.
When coronary angiography is done, it is also doneintravascular ultrasoundExamination to determine atherosclerotic plaque
7. EchocardiographyThis is a non-invasive test that looks at the structure and function of the heart. This is a non-invasive test that looks at the structure and function of the heart. Ischemia or infarction is determined by looking at the movement, thickness, etc. of the ventricular wall. When ischemia occurs, the ventricular wall movement will be weakened and uncoordinated, and the infarcted myocardium will be thinned, or even not moving (contracting), or even moving in the opposite direction (contracting), which is medically referred to as "ventricular wall tumors", and there can also be "wall thrombi". In patients with large infarcts, cardiac function measured by ultrasound may be reduced.
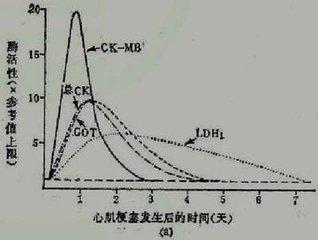
8. cardiac muscle enzymes (CK-MB) and markers of myocardial injury(TnI, troponin), blood troponin can be elevated in myocardial ischemic injury; in myocardial infarction, both troponin and cardiac enzymes can be elevated.
These are all ancillary screening modalities for myocardial ischemia and infarction. In factAngina pectoris and myocardial infarction during myocardial ischemia是Have their own clinical manifestations and patternsThe.surgeon要Based on medical historyThe patient'sSymptoms and signs to make a preliminary diagnosis and determine which tests to doAnd thenSynthesize clinical and examination findings to determine diagnosis and management. Therefore, the symptoms of clinical episodes, the pattern of episodes, the mode of relief, and the response to medication can provide good help to the doctor's diagnosis, and are also important and should not be ignored.

(Image from the Internet)
Hello, I'm Dr. Knowles Blue.
First of all, the answer, the full name of coronary heart disease is called coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, with the progression of the disease, there will be different pathological states, including stable angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, commonly used in the diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease means, including there is an electrocardiogram, cardiac ultrasound, coronary CTA, coronary angiogram, blood tests (cardiac enzymes, troponin), each kind of examination has its Each of these tests has its own characteristics and role, and can complement and corroborate each other, but not replace each other. Let's take a look at these tests.
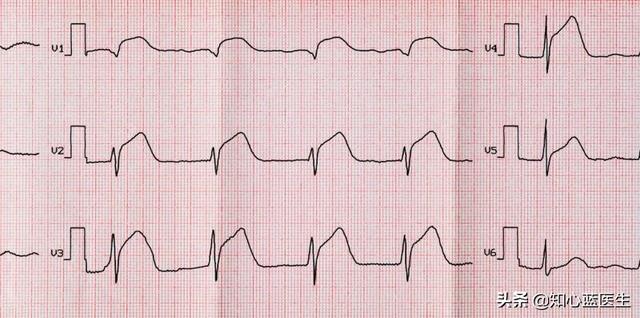
An electrocardiogram is like an electric pen that measures the heart's electricity to determine the condition of the heart muscle.
The reason why the heart can keep beating relies on the bioelectricity inside the heart, when ischemia occurs in the myocardium, these bioelectricities will also have specific changes, the electrocardiogram (ECG) is like an electric pen, by depicting the integrated vectors of these bioelectricities, there are three types of electrocardiograms commonly used at present: ordinary electrocardiograms, 24-hour ambulatory electrocardiograms, and exercise suits and electrocardiograms.
- General electrocardiogram:Almost everyone who has had a routine health checkup has had one of these ECGs, the kind where you lie down on a bed with electrodes affixed to your hands and feet as well as your chest, and it's over in a couple of seconds, and then a printout of the ECG waveform is made. This kind of examination is very convenient, quick and relatively inexpensive, usually costing only 20 to 30 dollars.In coronary heart disease myocardial ischemic attack can be seen, no ischemia is not visible, in fact, it is also the occurrence of angina pectoris or myocardial infarction, can be seen. But then, even when the coronary stenosis reaches 75%, which is well on its way to a diagnosis of coronary artery disease, there is no way to see it if there is no activity and the myocardial blood oxygen is still sufficient.In the other case, if there has been a myocardial infarction, then the ECG will show a "scar" like ECG changes, which is a pathologic Q wave.
- 24-hour ambulatory electrocardiogram:A normal ECG can only be seen when a patient is having an ischemic attack, but patients are often out of the hospital at the time of the ischemic attack, and by the time they get to the hospital they may already be in remission. the advantage of a 24-hour ambulatory ECG is that it can monitor the patient's cardiac changes over a 24-hour period.As long as the patient has an episode of myocardial ischemia within the 24 hours of the test, the ischemic electrocardiogram will be able to be captured。

- Exercise stress electrocardiogram: In fact, if there was no more strenuous activity during the entire 24 hours that the 24-hour ambulatory electrocardiogram was worn, it's possible that there was no ischemic attack during that 24 hours, and then another type of electrocardiogram called an exercise stress electrocardiogram can make up for that.The patient is asked to stand on a treadmill-like machine and run while the ECG is monitored. When the exercise reaches a certain intensity it is possible to induce an ischemic attack, at which point an ECG of ischemia is traced, which is also able to diagnose myocardial ischemia.Of course this type of exercise-loaded ECG carries certain risks and should only be performed under the protection of an experienced physician.

Cardiac ultrasound is like a ruler that allows the heart's size, mobility, contractility
- Cardiac ultrasound is based on the principle of sound wavesIt receives sound waves reflected from the heart and converts them into images on a cardiac ultrasound machine, allowing direct measurement of the size of each atrium and ventricle of the heart, the contractility of the heart, the condition of the valves, and the activity of the heart.However, a heart ultrasound is usually not able to directly see if there is a narrowing and blockage of the coronary arteries.
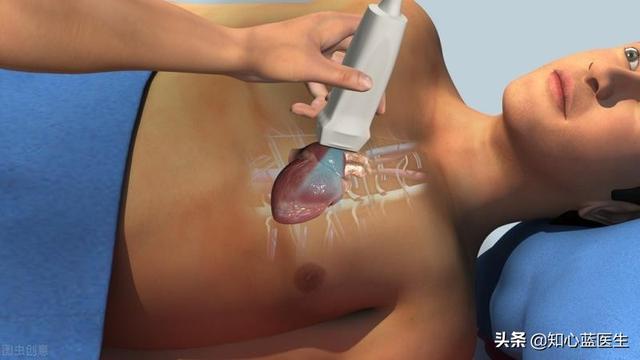
- More mild forms of myocardial ischemia and coronary artery disease do not usually show changes in heart size, changes in heart contractility, or changes in heart activity.So if the heart ultrasound suggests normal or essentially normal, it does not prove the absence of myocardial ischemia or coronary artery disease.

- Severe myocardial ischemia coronary artery disease, or even a relatively large myocardial infarction, can be clearly seen on cardiac ultrasound changes in cardiac contractility, changes in myocardial mobility, and even abnormalities in the functioning of the heart valves. In this way it can be indirectly inferred that the myocardium is severely ischemic.
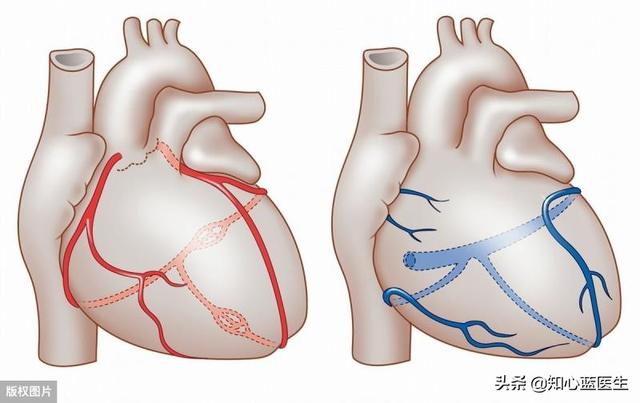
Coronary CTA and coronary angiography are like a plumber who can inspect pipes and fix them
The coronary arteries are used to supply blood to the heart itself, so they are like the plumbing that supplies water to the inside of a house. Coronary CTA and coronary angiography are the plumbers who can see directly into the coronary arteries.
- 冠Pulse CTA is a junior plumberCoronary CTA is actually a kind of CT examination. When doing this kind of CT, a kind of drug is injected through a vein in the hand, this kind of drug is the contrast agent, when the contrast agent flows to the coronary artery, it will show the shadow of this coronary artery, and it can determine whether there is any blockage or narrowing of the coronary artery.The main trunks of the coronary arteries and some of the larger branches are better seen, while the smaller branches are poorly visualized.
- Coronary angiography is advanced plumbing: The principle of coronary angiography is similar to coronary CTA, but coronary angiography is an invasive test in which a tube is sent through an artery in the hand or thigh to the coronary arteries of the heart, where a contrast agent is injected directly into the coronary arteries, and the morphology of the coronary arteries is visualized by means of a DSA (digital radiography) machine.This test is the gold standard for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, and is able to see not only the main trunk and large branches of the coronary arteries, but also some of the smaller branches. It is said to be an advanced plumber, most importantly because it can not only be used as a means of diagnosing coronary artery disease, but it can also be used as a catheter to send in balloons or stents, etc. for treatment, which is called coronary intervention.
Blood tests (cardiac enzymes, troponin) act like a guard dog with a keen sense of smell to detect myocardial ischemia products
Hematological tests used for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease mainly include cardiac enzymes and troponin, which are originally found in normal cardiac muscle cells and do not run into the bloodstream. However, when severe ischemia occurs in the myocardium and myocardial infarction occurs, the myocardial cells become necrotic, and these substances run out of the myocardial cells and into the bloodstream.We are able to detect these substances by drawing blood from a vein, indirectly inferring that the heart muscle is severely damaged or necrotic at this time.
To summarize, coronary artery disease is the general term for this disease, myocardial ischemia is the pathophysiological change of this disease, stable angina, unstable angina, and myocardial infarction are the ischemic conditions of different severity of this disease. Electrocardiography, cardiac ultrasound, and hematology are all indirect means of inferring whether the myocardium is ischemic and necrotic. Coronary CTA and coronary angiography are both used to directly observe coronary artery lesions through contrast media. Coronary CTA is non-invasive, convenient, relatively inexpensive, and can observe the larger coronary arteries and their branches; coronary angiography is invasive, relatively expensive, and can observe the various large and small branches of the coronary arteries, and it is the gold standard for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, and it can be used to perform coronary interventional treatments such as balloon dilatation or stent implantation in cases of severe coronary artery disease. It is the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease, and for severe coronary artery disease, balloon dilation or stent implantation can be performed.
Follow Dr. Know Your Heart Blue to learn more about the heart.
To answer this question, we first need to clarify the differences and overlapping parts between the three concepts of coronary heart disease, heart attack and myocardial ischemia.
Coronary heart disease refers to the degree of coronary artery stenosis of more than 50%, based on coronary atherosclerosis, a series of cardiovascular diseases collectively, chronic coronary heart disease accompanied by stable angina pectoris problem is called coronary heart disease, due to coronary artery stenosis or blockage caused by acute coronary syndrome, also belongs to the coronary heart disease, therefore, if from the scope of the disease, acute infarction occurs in the category of coronary heart disease is included in the scope of the coronary heart disease, and the Coronary heart disease patients, how to recognize the risk of sudden acute heart attack, is very important thing.

About myocardial ischemia, there are more misunderstandings, some friends often appear chest tightness, palpitations and other uncomfortable symptoms, it is recognized that they have myocardial ischemia, but in fact, the blood supply to the myocardium is mainly through the coronary arteries, and the coronary arteries are generally narrowed if the degree of stenosis is not more than 50%, basically does not affect the blood supply to the myocardium, and there is no myocardial ischemia, therefore, usually only the diagnosis of coronary heart disease patients may exist in the situation of myocardial ischemia. Therefore, usually only patients with diagnosed coronary heart disease may have myocardial ischemia, and if chest tightness, palpitations and other discomfort, in addition to myocardial ischemia, there may also be due to menopausal syndrome, vegetative nerve disorders and other problems caused by, be sure to pay attention to identify.

Exactly how do you determine coronary heart disease, heart attack and myocardial ischemia? The following tests are often essential.
electrocardiography
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is an important test for myocardial ischemia, which is characterized by non-invasive, simple and direct interpretation of the results. Generally speaking, if the myocardial blood supply is insufficient in patients with coronary artery disease, it can be fully characterized by electrocardiogram without the symptom of chest tightness and angina pectoris. For patients suspected of sudden infarction, a standard 12-lead electrocardiogram should be completed within 10 minutes after the patient is seen, and the electrocardiogram can be used to initially determine whether it is a problem of infarction, and whether there is any problem of posterior wall infarction, etc. However, it is important to note that If the ECG is normal but the chest pain persists without relief, the infarction problem cannot be excluded, and the ECG should be reviewed again after an interval of 5 to 10 minutes.

The disadvantage of ECG examination is that it mainly reflects the electrocardiographic situation during the examination time, if it happens to be examined at the time when there is no ischemia in the myocardium and all other aspects of the heart's performance are normal, then some potential cardiovascular disease problems may not be accurately reflected, but it is also very difficult for us to do the ECG examination in a timely manner when there is chest tightness in our body, so that this kind of examination, which is a kind of preliminary judgment of the examination, but also has certain limitations.
Myocardial Injury Marker Screening
If the myocardium develops ischemic problems, the long-term effects down the road or short-term severe effects (such as the effects of an acute heart attack) can result in chronic or acute damage to the myocardium, and there are some hallmark tests to characterize myocardial damage when it occurs.

Cardiac troponin is a marker of myocardial injury in acute infarction and unstable angina pectoris, if the test result is negative, most of the infarction can be excluded, but in the absence of such a test, it can also be used as an alternative marker of myocardial injury by creatine kinase isoforms, and in the early stage of the examination of cardiac troponin-negative patients with chest pain, it can be repeated after an interval of 4-6 hours, if it is still negative, then it can be initially excluded from infarction. Exclusion of infarction, but it is important to note that for patients who present with ischemic chest pain and those who present with electrocardiographic changes, do not miss treatment because of waiting for the results of the marker test.
Cardiac Stress Test Examination
As we mentioned earlier, the ECG only reflects the health of the heart at the time of testing and not the ischemic condition of the heart after certain exertions, and cardiac stress testing is a useful addition to troubleshooting myocardial ischemia in stable coronary artery disease. Cardiac stress testing, including plate exercise testing, stress echocardiography, stress myocardial nuclear perfusion imaging, and stress magnetic resonance imaging, can be useful in identifying ischemic chest pain.
Coronary CTA
Coronary CTA examination is a kind of examination means combined with CT examination of coronary artery by contrast, through which it can diagnose coronary artery disease, examine and judge the location of coronary plaques, especially the degree of calcified plaques, etc. Coronary CTA examination is also able to assess whether the blood flow is smooth at the stent site of coronary artery disease patients with stent implantation, and at the same time, for the patients who suffer from chest pains, the coronary CTA examination is used to detect problems such as aorta, pulmonary artery and pneumothorax. At the same time, for patients with chest pain, coronary CTA can be used to detect aortic, pulmonary, and pneumothorax problems, but it is not recommended for patients with highly suspected acute infarction problems to prefer coronary CTA for confirmation of infarction.
coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is still the gold standard for clinical diagnosis of coronary artery disease, with the disadvantage that it requires the use of contrast medium and invasive interventional procedures. For assessing the degree of coronary artery stenosis, coronary angiography can evaluate the functional changes of the coronary arteries, including coronary artery spasm and the presence or absence of collateral circulation; at the same time, it can also take into account the evaluation of the left heart function, etc. In addition, for patients with sudden chest pain and highly suspected acute infarction, if contraindicated, it should be implanted as early as possible. In addition, for patients with sudden onset of chest pain and highly suspected acute infarction, coronary angiography should be performed as early as possible if there is no contraindication. If it is confirmed that a stent can be placed in the infarcted area to reconstruct the blood flow, a stent should be implanted directly to open up the blood flow as soon as possible, so as to minimize myocardial damage brought by the acute infarction.
Coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction or myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia, these concepts are very familiar to everyone. However, careful friends will find that often encounter such a situation: the doctor to get the results of electrocardiograms, after reading that "there is myocardial ischemia performance", but when you ask the doctor, this is not coronary heart disease, the doctor will say, "is not coronary heart disease, can not be determined! "......
From here, we can see that myocardial ischemia, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction are actually different clinical concepts, the criteria for making a diagnosis and the clinical techniques required are also different, and we will look at each one of them next.
Lowest diagnostic threshold and most common - myocardial ischemia
If we were to categorize the three concepts mentioned above according to how common they are in clinical practice, myocardial ischemia would be the most common, due to the fact that it has the lowest diagnostic threshold.Conclusion of "myocardial ischemia" based on a routine 12-lead electrocardiogram alone。
According to the definition of coronary heart disease in the textbook of internal medicine, coronary heart disease is a heart condition caused by atherosclerotic stenosis or occlusion of the coronary arteries (coronary arteries) that supply blood to myocardial tissues, resulting in myocardial ischemia, hypoxia, or necrosis. Strictly speaking.Myocardial ischemia is a common manifestation of coronary artery disease, and patients with coronary artery disease are generally certain to have myocardial ischemia; however, not necessarily all people with myocardial ischemia manifestations are sufficient to meet the diagnostic criteria for coronary artery disease.
The concept of myocardial ischemia first appeared in diagnostic textbooks as a common ECG change. Medical experts first discovered the "signs" of myocardial ischemia on the graph of the electrocardiogram; when ischemia occurs in a part of the myocardium, this affects the electrical repolarization of the heart, which in turn leads to an increased risk of ischemia in theST-segment depression or T-wave inversion in the corresponding leadsThis is the most basic basis on which physicians determine myocardial ischemia in the clinical setting.
There are several things you should know about myocardial ischemia:
- Myocardial ischemia is not always caused by coronary artery disease; spasm of the coronary arteries can also cause myocardial ischemia to manifest;
- Myocardial ischemia is not always persistent, and a number of patients have intermittent ECG manifestations of myocardial ischemia;
- Myocardial ischemia does not always present with obvious symptoms such as chest pain and chest tightness, and asymptomatic myocardial ischemia is common.
Coronary heart disease - it's not easy to put on this "hat"!
Coronary heart disease, the full name is coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, most people think that coronary heart disease is a disease, but in fact, coronary heart disease is a large class of diseases composed of many kinds of diseases.Different types of coronary heart disease have different principles of treatment, degree of urgency of treatment, and so on!
At the earliest, in 1979, the World Health Organization had classified coronary heart disease into five types: occult coronary heart disease; angina pectoris; myocardial infarction; ischemic cardiomyopathy; and sudden death. This classification is classic, but with gradual development, more and more experts advocate the division of coronary heart disease into two main categories:
- Chronic coronary artery disease: subdivided into stable angina, ischemic cardiomyopathy, and insidious coronary artery disease;
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): this would include unstable angina (UA), non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Previously, we were under the impression that stable coronary artery disease was more common, but clinically, acute coronary syndromes are now becoming more common.
The diagnosis and classification of coronary artery disease is often based on a combination of clinical symptom characteristics, risk factor assessment, electrocardiogram, laboratory tests, and imaging. However.Of all the tests, the one that can provide direct evidence of vascular disease is coronary angiography, which is therefore known as the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease.。
For most patients with suspected severe coronary artery disease, doctors will recommend coronary angiography to assess the degree of coronary artery stenosis in detail, and, on this basis, coronary artery disease can be treated directly with coronary stenting techniques.
However, for a portion of the population that is not at high risk for coronary artery disease, doctors sometimes recommend screening for coronary artery stenosis using coronary CTA technology.Although the accuracy of coronary CTA is still some way from that of coronary angiography, it is adequate for ruling out patients who are negative for coronary artery disease.
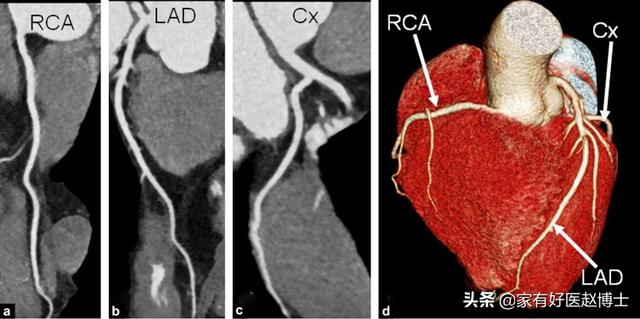
Myocardial infarction - a race to the bottom
Myocardial infarction is a fatal disease caused by acute occlusion of the coronary arteries resulting in acute necrosis of downstream blood-supplying myocardial tissue. Myocardial infarction is highly lethal in the acute phase and is a disease that requires urgent resuscitation.
In the emergency department.Any patient with sudden severe chest pain needs to be screened for myocardial infarction, and the most commonly used tools are electrocardiography and cardiac enzyme profiling.In general, myocardial infarction patients, myocardial enzyme spectrum related indicators will be significantly elevated, and when the electrocardiogram appears typical ST-segment elevation, this is the ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; and if there is no ST-segment elevation, then often belong to the non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Basically, the diagnosis of myocardial infarction is one that needs to be done in the emergency department in a race against time. After diagnosis, patients with acute myocardial infarction are immediately sent to the catheterization laboratory for coronary angiography if they are in a hospital that has the means to do so. The main purpose of the angiogram at this time is not to confirm the diagnosis of the disease, but to quickly help open the blocked blood vessels for endovascular treatment.
Okay, follow "Dr. Zhao, a good family doctor", please share this medical knowledge with friends who need it!

What is the relationship between coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia? Coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction are both diseases, and myocardial ischemia is a disease state; all three can be categorized as coronary heart disease.
Coronary heart disease refers to the narrowing of blood vessels due to atherosclerosis in the heart vessels, which further leads to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle, resulting in chest tightness and chest pain.
When the coronary arteries are completely occluded and the myocardium supplied by the blood vessels is not nourished and necrotic, it is called myocardial infarction. Generally, it is caused by severe myocardial ischemia, which ultimately leads to the necrosis of myocardial cells. Therefore, myocardial ischemia is a disease state that is closely related to the occurrence of myocardial infarction.
In summary: coronary heart disease is a very large category, myocardial ischemia is a disease state, and myocardial infarction is the most serious consequence of coronary heart disease.
What tests are done to detect coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia?
1. Physical examination
Generally the doctor will make an initial look at the patient to determine the basic condition of the patient, such as whether he or she is sitting up and breathing, whether there is cyanosis, jugular vein raging, edema, and so on. And by touching the patient to see if there are any abnormalities of the heart tip, capillary pulsation, abnormal changes of pulse, etc.. Finally, the stethoscope is used to observe the presence of abnormal changes in heart sounds, heart murmurs and pericardial friction sounds, and abnormal heart rate.
2. Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests include routine blood tests, routine urine tests, and a variety of biochemical tests, including the measurement of blood troponin, myoglobin, and cardiac enzymes, which are required to determine myocardial infarction.
3. Electrocardiogram
The electrocardiogram is a non-invasive, inexpensive, and practical test that is very useful in the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmias and in identifying the causes and nature of the various arrhythmias that occur.
Another very important clinical function of ECG is the diagnosis of myocardial ischemia. When myocardial ischemia occurs, it will be manifested in the ECG with the changes of injurious ECG, therefore, ECG is very significant for the preliminary judgment of myocardial ischemia site and area, the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction, including localization diagnosis, and judging the condition!
In addition, ECG can assist in the diagnosis of electrolyte metabolism disorders. Hypokalemia, hyperkalemia, and hypocalcemia are specifically altered on the ECG, which allows the doctor to determine if there is an electrolyte disorder.

4. Ambulatory electrocardiogram
Ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG): also known as Holter's test, can record ECG signals continuously for 24-72 hours, which improves the detection rate of non-sustained arrhythmias, especially transient arrhythmias and transient ischemic episodes, and is important for the diagnosis of various types of arrhythmias, causes of fainting, understanding of pacemaker functioning, and taking measures for the prevention of sudden death.
5. Cardiac ultrasound
Cardiac ultrasound is to reflect the changes in the structure of the heart. Through the examination of cardiac ultrasound, it can reflect whether there is any breakage or thickening of the atrial and ventricular walls, whether the atria and ventricles are enlarged, as well as whether there is any stenosis or incomplete closure of the heart's valves, and in addition, it can also reflect whether the heart's systolic and diastolic functions are normal, and whether the ejection fraction is normal, and so on.
6. Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is currently the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. The catheter is inserted into the opening of the coronary artery, and a small amount of contrast medium is injected to show the blood flow of the coronary artery. Dynamic observation of the coronary artery blood flow and anatomical conditions is used to understand the nature, location, extent and degree of coronary artery lesions, as well as to observe the presence of coronary artery malformations, calcifications, and formation of side-branch circulations.
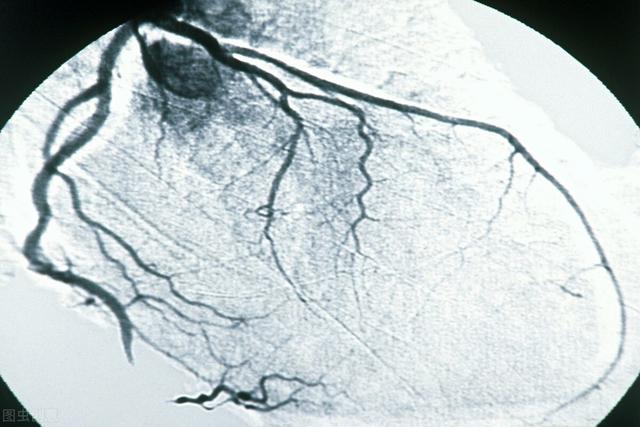
Coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia can generally be better determined by the above tests. Detection of heart disease is a very complex matter, so if you suspect any problem with your heart, you need to go to the hospital for confirmation!
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! In addition, if your family members also have related troubles, please forward this article to them!
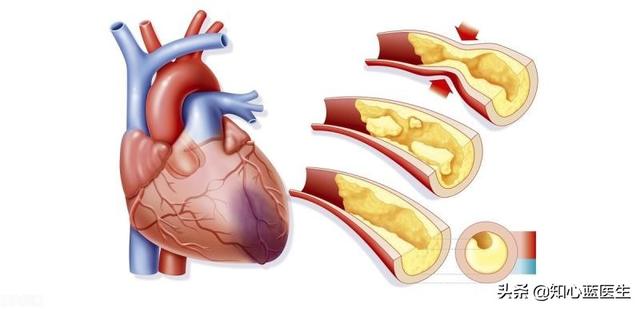
Coronary heart disease coronary heart disease (CHD), referred to as coronary heart disease, mostly caused by atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries, can also be caused by coronary artery spasm, one of the factors mentioned above or the two together, resulting in coronary artery lumen narrowing or obstruction, resulting in myocardial ischemia, hypoxia and heart disease, are called coronary heart disease, also known as ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Etiologies that can lead to myocardial ischemia and hypoxia include, in addition to coronary atherosclerosis, inflammation (e.g., rheumatic, syphilitic, Kawasaki's disease, vaso-occlusive vasculitis, etc.), embolism, spasms, connective tissue disorders, trauma, and congenital malformations.
Since coronary atherosclerosis is the predominant etiology, coronary artery disease is commonly used as a clinical alternative to coronary atherosclerotic heart disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
The etiology of coronary atherosclerosis is unknown, but it is generally believed to be closely related to the following risk factors
1, dyslipidemia: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL) and apolipoprotein (a) elevated, can lead to atherosclerosis.
2、Hypertension: aged between 40 and 70 years old, with blood pressure between 115/75mmHg and 185/115mmHg, if systolic blood pressure increases by 20mmHg or diastolic blood pressure increases by 10mmHg, the risk of coronary heart disease doubles.
Diabetes mellitus (DM): Atherosclerosis occurs earlier and is more common in DM patients.
4. Smoking: an average of 10 cigarettes per day can increase coronary heart disease mortality by 18% in men and 31% in women.
5. Genetic factors: e.g., family history of early-onset cardiovascular disease (onset at <50 years of age).
6. Age: Male > 50, Female > 55
7, other: poor lifestyle, such as physical activity, stay up late, mental stress, obesity, type A personality.
Clinical type
1. According to the 1979 WHO classification, coronary artery disease is divided into the following types:
① Asymptomatic myocardial ischemia (insidious type): there is objective evidence of myocardial ischemia, such as an electrocardiogram suggesting ischemic changes, but no symptoms.
② ischemic cardiomyopathy: after long-term chronic myocardial ischemia or myocardial infarction, myocardial fibrosis, gradual enlargement of the heart, heart failure and arrhythmia.
③ Angina pectoris: episodic retrosternal pain without myocardial necrosis. Including stable and unstable angina pectoris. Myocardial infarction: severe and persistent retrosternal pain with myocardial necrosis, including non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
⑤ Sudden death: Death from cardiac causes within 1 hour of the onset of acute symptoms. This is mainly due to severe ventricular arrhythmias.
2、According to the mechanism of myocardial ischemia occurrence typing
① Chronic myocardial ischemia syndrome: including insidious type, ischemic cardiomyopathy, stable angina. The main pathogenesis is increased oxygen demand myocardial ischemia.
② acute coronary syndrome (ACS): including unstable angina (UA), non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). In recent years, the former two are collectively referred to as non-ST-segment elevation ACS, which accounts for about 3/4 of the cases, and the latter is called ST-segment elevation ACS (including a small proportion of variant angina pectoris), which accounts for about 1/4 of the cases. The common pathophysiological basis is that, based on coronary atherosclerosis, plaque rupture, vesiculation, ulceration, and concomitant thrombosis, vasoconstriction, microvascular embolism, etc., which leads to acute or subacute reduction of the myocardial oxygen supply. Reduced oxygenation. The main pathogenesis is myocardial ischemia with reduced oxygen supply.
Coronary artery disease is examined in the following ways
1, ECG loading test: mainly including drug test (such as isoproterenol, pansentin test, etc.) and exercise loading test. The most commonly used simple method for clinical observation of myocardial ischemia is electrocardiogram. When angina attack occurs, ECG can record the abnormal ECG manifestations of myocardial ischemia. However, many patients with coronary artery disease have no signs of myocardial ischemia despite the fact that the maximal reserve capacity for coronary artery dilatation has been reduced, and usually coronary blood flow can be maintained at rest without signs of myocardial ischemia, and the electrocardiogram can be completely normal. To reveal relatively fixed or reduced blood flow, the presence of angina can be confirmed by other methods or exercise, which loads the heart and induces myocardial ischemia. Exercise testing is also essential for the evaluation of cardiac function after ischemic myocardial infarction or arrhythmia.
2. Ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG): A method of continuously recording and compiling and analyzing changes in the electrocardiogram of the heart in both active and quiet states over a long period of time. This technique was first used by Holter in 1947 to monitor electrical activity, so it is also known as Holter monitoring. Conventional electrocardiography can only record waveforms of a few tens of cardiac cycles in the resting state, whereas ambulatory electrocardiography can record up to 100,000 ECG signals in a 24-hour period, which increases the detection rate of nonsustained ectopic rhythms, especially transient episodes of myocardial ischemia and transient arrhythmias, and thus broadens the range of clinical applications of electrocardiography, and the time of occurrence can be correlated with the patient's activity and symptoms. The time of presentation corresponds to the patient's activity and symptoms.
3. Electrocardiogram (ECG): The most commonly used, basic and earliest diagnostic method in the diagnosis of coronary heart disease is ECG. Compared with other diagnostic methods, ECG is convenient to use, easy to popularize, and when the patient's condition changes, the changes can be captured in time, and continuous dynamic observation and various load tests can be performed to improve its diagnostic sensitivity. Whether it is myocardial infarction or angina pectoris, there are typical ECG changes, especially for the diagnosis of arrhythmia is more clinically valuable, but of course there are some limitations.
4. Coronary angiography: It is the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. It can clarify whether the coronary arteries are stenotic, the degree, extent and location of stenosis, and can further guide the measures to be taken for treatment. At the same time, left ventriculography can evaluate the heart function.
The main indications for coronary angiography are: 1) for those with chest pain resembling angina that cannot be diagnosed; and 2) for those with angina that remains severe despite medical treatment, to clarify arterial pathology in order to consider bypass graft surgery.
5. Ultrasound and intravascular ultrasound: cardiac ultrasound can examine the motion of the ventricular wall of the heart, the function and morphology of the left ventricle, and this method is one of the most commonly used means of examination at present. It has important diagnostic value for papillary muscle function, cardiac rupture, intracavitary thrombus, and ventricular wall tumor. Intravascular ultrasound can clarify the degree of stenosis and the morphology of the wall within the coronary arteries, which is a promising new technology.
6. Nuclide myocardial imaging: This test can be done when angina cannot be ruled out by electrocardiography according to the history. Nuclear myocardial imaging can show the ischemic area and clarify the location and extent of ischemia. Combined with exercise test and then imaging, it can improve the detection rate.
7, cardiac blood pool imaging: for determining ventricular wall movement and cardiac function has important reference value, can be used to observe the dynamic image of ventricular wall contraction and diastole.
8, myocardial enzymology examination: clinically, according to the specific isoenzymes of certain enzymatic changes and serum enzyme concentration of elevated sequence changes can be clearly diagnosed as acute myocardial infarction. It is one of the important means of differential diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
For cardiovascular doctors, the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, myocardial ischemia is as easy as eating with both hands and using chopsticks and bowls; however, it is different from eating because we have to be careful not to miss a true coronary heart disease, and not to wrongly accuse a false coronary heart disease.

One missed diagnosis could be a wrongful death;
A single case of wrongful conviction can cause patients to worry about long-term medication for a long time and even experience side effects from the medication.
Therefore, the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction must be made carefully and thoughtfully!
It's complicated to detail, and we need to combine symptoms, medical history, risk factors, and screening labs.
We will only briefly describe what ancillary tests are used to make the diagnosis today.
First, acute myocardial infarction
The most severe form of coronary heart disease, in which the blood vessels are completely blocked or nearly completely blocked.
1, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Usually we can basically confirm the diagnosis by symptoms + EKG, and the next step is to decide as soon as possible whether to thrombolyze or stent.
Typical ECG changes that facilitate the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
If the onset is prolonged, cardiac enzymes and troponin are also elevated.
Imaging can further validate the diagnosis.
2、Non ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
We need to combine the symptoms with the cardiac enzyme results, which need to be supported by cardiac enzymes, since the ECG is not significantly elevated, but rather a sign of depression.
Based on the risk stratification, the timing of the imaging was decided.
Second, coronary heart disease
In fact, coronary artery disease itself includes myocardial infarction, which we talked about independently above and will not repeat here.
Coronary heart disease diagnosis/
1. Electrocardiogram.The sensitivity is very high, and the evidence is strong enough to catch the ECG ischemic manifestations as soon as they develop. But the difficulty is that often when we do the ECG it is no longer difficult. But if dynamic changes in the ECG are detected, then it is very valuable for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease.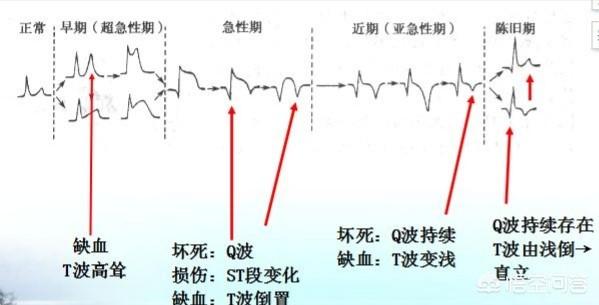
2. ambulatory electrocardiogram and exercise test.Changes in the 24-hour ECG can be caught, and if there happens to be an onset, the ECG is recorded. Exercise testing, which can determine the presence of myocardial ischemia by changes in exercise tolerance and post-exercise ECG.
3. Coronary CTAWhen coronary artery disease cannot be proved or ruled out from the ECG and clinical manifestations, coronary CTA can be used to visualize the presence of coronary artery stenosis in a more intuitive manner.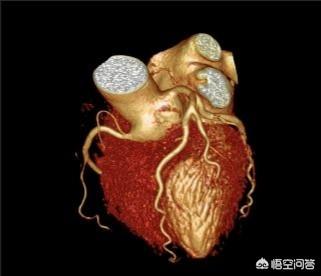
4、Coronary AngiographyIf severe coronary artery disease is suspected or cannot be diagnosed, coronary angiography is required for further investigation.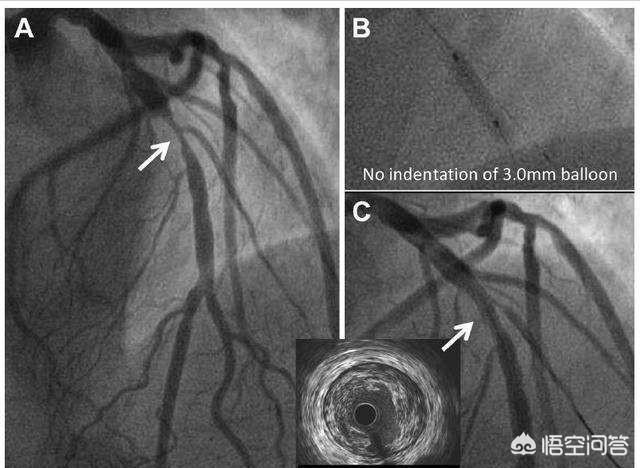
5. Microvascular lesionsThe coronary angiogram is normal, but the patient has typical angina pectoris, because coronary angiogram can only observe relatively large blood vessels, for the tiny blood vessels can not be seen, and can only be based on the clinical symptoms and special drug screening test comprehensive judgment.
In fact, it talks about the main means of examination, clinical symptoms are very valuable for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
We can't just look at the symptoms and we can't just look at the tests, we have to combine these two methods perfectly in order not to let a coronary heart disease go and not to wrongly accuse a coronary heart disease!
This is a good question and answer, and at first glance it is a concern of the general public. Dr. Zhang will talk about it today. First, let's talk about the relationship between coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and myocardial ischemia. Coronary heart disease is the abbreviation of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, myocardial infarction is the most serious type of coronary heart disease, but coronary heart disease includes not only myocardial infarction, but also other types, such as unstable angina, stable angina, and so on. Myocardial ischemia is a pathological state that occurs in all types of coronary heart disease and is used to describe the pathopathological basis of the disease.
It is not difficult to find out whether a patient has coronary heart disease. If it is a patient who has had a myocardial infarction, the diagnosis can be made by the patient's own symptoms, electrocardiogram and cardiac enzymes, which is very simple and can be diagnosed in general hospitals. If it is other types of coronary heart disease, for example, just suspected angina pectoris, this time to clarify the diagnosis, usually check the electrocardiogram at the onset of the disease can be. However, if you can't catch the ECG at the time of angina attack, what should you do? At this time, you can first screen the coronary CTA examination, usually can also clarify whether the coronary artery stenosis exists. As for how to clarify myocardial ischemia, it is not difficult, an ECG at the time of myocardial ischemia attack, or an exercise test can clarify the presence of ischemia.
Today, Dr. Zhang said these are very common, but real-life actionable, I hope to help you.

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.