What are the symptoms of HIV infection?
What are the symptoms of HIV infection? 
Symptoms of AIDS are different at different periods of infection. Some time ago, I admitted a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus combined with rheumatoid arthritis, who had lung infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections that had been so bad that I couldn't explain the condition, and then I found out that it was AIDS. This disease is encountered almost every month or two. They are infected through sexually transmitted, men who have sex with men, blood sales, drug use, and so on.
The next step is to talk in detail about what the symptoms of AIDS look like at different times:
asymptomatic infection
It is estimated that 10-60% of people with early HIV infection are asymptomatic, but the exact percentage is difficult to estimate due to the fact that patients often present to the doctor with symptoms, so asymptomatic infections usually remain undiagnosed.
time course
In acutely symptomatic infections, the interval between HIV exposure and the onset of symptoms is often 2-4 weeks, but incubation periods of up to 10 months have been found.
The most common manifestations include fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, rash, myalgia/arthralgia, diarrhea, weight loss, and headache. Certain features are suggestive of HIV infection, especially the prolonged duration of symptoms and the presence of skin and mucosal ulcers.
systemic symptom
The most commonly reported symptoms in people with acute HIV infection are fever, malaise, and myalgia. The vast majority of symptomatic acutely HIV-infected patients with fever have a temperature of 38-40 degrees Celsius.
lymph node enlargement
Non-palpable lymph node enlargement is also common, mainly involving the axillary, cervical and occipital lymph nodes. Lymph node enlargement usually occurs in the 2nd week of the disease course and is accompanied by an HIV-specific immune response. After the acute presentation, the lymph nodes decrease in size, but mild lymph node enlargement usually remains. Enlargement of the liver and spleen may also occur.
Oropharyngeal manifestations
Sore throat is a common presentation of acute HIV infection. Investigation reveals pharyngeal edema and congestion, usually without enlarged tonsils or exudate.
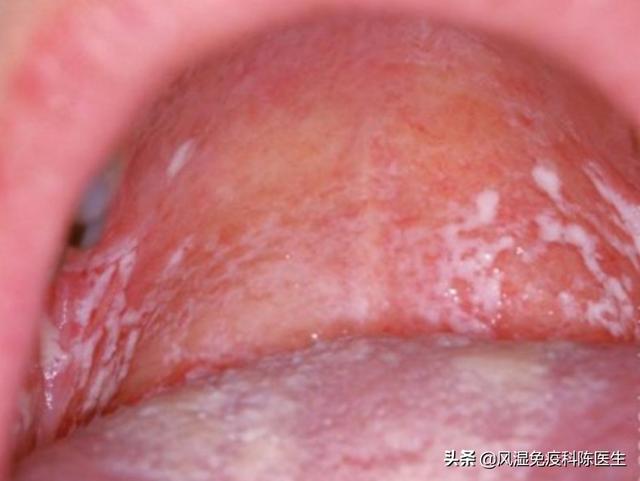
a rash
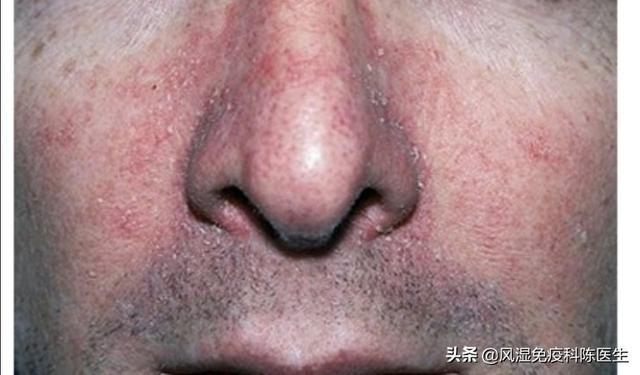
Gastrointestinal symptoms
As the gastrointestinal tract manifests itself in the acute infection phase with nausea, diarrhea, anorexia and weight loss of more than 10 pounds. Even pancreatitis and hepatitis.
opportunistic infection
What does opportunistic infection mean? It means that normally when your immunity is normal, you don't have a chance to get these viruses, bacteria, fungi, and so on, but people with AIDS have very low immune function, and these bacteria that don't infect normal people have a chance to infect them.
Opportunistic infections usually occur in the late stages of HIV infection, but can occasionally occur in the early stages of HIV infection when CD4 lymphocytopenia is present.
The most common opportunistic infections are oral and esophageal pseudomycosis.
Other opportunistic infections during acute HIV infection include cytomegalovirus, infections (proctitis, colitis and hepatitis),Pneumocystis jiroveci, pneumonia, and chronic, severe cryptosporidiosis.
There are a lot of people who just get too many infections before they are found to have AIDS. I remember I used to search a young guy who had a big soft growth on his neck, and would give him an ultrasound, and it was full of fluid, so I drew it out of him with a syringe and sent it over for a test, which came back with tuberculosis, and later on this patient was also diagnosed with AIDS.
Detectable viremia does not occur until 10-15 days after infection, and even the most sensitive immunoassays do not react positively until 5 days after infection. Therefore, if exposure occurs during this window period, HIV infection may be missed. If the initial immunologic and virologic tests are negative and there is a high suspicion of recent HIV exposure, retesting can be done 1-2 weeks later.
Acute and early HIV infection is not often diagnosed for these reasons:
- Symptoms are not specific (especially in mild cases) and may resolve on their own without treatment. In addition, many patients may be asymptomatic.
- Patients may not be aware of their risk, for example, many people do not know that oral sex can transmit HIV.
communicability
People with early HIV infection have temporarily elevated viral loads, and the ability to transmit to others is high at this time. In acutely HIV-infected men, the highest level of viral load in semen occurs at about 20 days after infection or on day 6 after the onset of symptoms of acute retroviral syndrome.
Most of my clinical encounters are sexually transmitted. I remember that a very bright girl at school fell in love with a black man and was infected, then she went to graduate school and infected a professor at a very famous hospital. Then she went to graduate school and infected a professor at a very famous hospital. She went on to get a PhD in Shanghai, and it's hard to say if she's infecting other people. So please be sure to clean up your act to avoid these risks.
Now that AIDS is becoming more widespread, appropriate measures should be taken to prevent HIV transmission, including consistent and proper condom use and avoiding the sharing of injecting drug paraphernalia.
AIDS is a silent and colorless manifestation early on. If the patient is carrying HIV, in the absence of clinical manifestations, the disease can not be seen from the surface alone. Therefore, the main way to prevent AIDS is through clean living habits. I am an AIDS publicizer, and I have to report the situation in my district every month. A week ago, a person with AIDS died in my district. What are the symptoms of AIDS? Let me talk about this.

What is AIDS?
AIDS, an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), is a disease that has the human immunodeficiency virus ((HlV for short), after being infected by the virus -, within days the immune system is disrupted and gradually becomes the target of many candidate diseases, contributing to a variety of clinical symptoms called syndromes. Rather than a simple disease, the syndrome can be transmitted through contact with mucosal tissue of the mouth, genitals, anus, or blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk with the virus.
How AIDS is transmitted
HIV is found primarily in the blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk of infected and sick people. ❶ Sexual transmission: The possibility of being infected through unprotected sexual intercourse with a person already infected with HIV, including homosexual, heterosexual, and bisexual contact. ❷ Intravenous drug use: Sharing infected syringes with others is a high-risk route to HIV infection. ❸ Mother-to-child transmission: HlV-infected mothers may transmit HlV to their fetuses and infants during pregnancy, labor, and breastfeeding. ❹ Blood-to-blood transmission: including blood products and artificial insemination, skin grafts and organ transplants are high-risk routes of infection.

susceptible population:The population is generally susceptible to infection. High-risk susceptible groups include: gay men, intravenous drug users, frequent sexual contact with HlV carriers, frequent blood and blood product transfusions, and babies born to HlV-infected mothers.
What are the symptoms of HlV infection?
Clinically, HlV infection is generally categorized into 3 stages: acute, asymptomatic and AIDS.
Ⅰ acute stage:
It usually occurs about 2 to 4 weeks after the initial HlV infection. Clinical symptoms include fever, sore throat, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, arthralgia, swollen lymph nodes and neurological symptoms. Most patients have mild clinical symptoms that last for 1~3 weeks and then resolve.
II Asymptomatic period
It is usually entered into this phase from the acute phase, or directly into this phase without significant acute phase symptoms.
The duration of this phase is usually 6 to 8 years. However, there are also patients with rapid progression and long periods without disease. The length of this period is related to a number of factors such as the number of infected viruses, the route of infection, and the immune status of the body.
III Period of AIDS
This stage is the final stage after HIV infection. This stage mainly shows associated symptoms, various infections and tumors.
The main manifestations are: patients with fever, night sweats, diarrhea, weight loss, etc., lasting for more than one month; some patients show neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as: memory loss, apathy, personality changes, headache, epilepsy and dementia. Some patients also present with persistent generalized lymph node enlargement, which is mainly manifested in two or more parts of the lymph nodes outside the groin; and the lymph nodes are ≥1 cm in diameter, with no pressure and pain, and no adhesion; usually such symptoms last for more than 3 months.

Common symptoms of HIV infection areSymptoms include fever, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, coughing up phlegm and blood, dyspnea, headache, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea, gastrointestinal bleeding, dysphagia, loss of appetite, white spots and ulcers in the mouth, rashes of all kinds, loss of vision, blindness, dementia, epilepsy, paralysis of the limbs, lethargy, anemia, diarrhea, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, and intestinal obstruction.
Common tumors: cervical cancer, malignant lymphoma, and Dr. Kahl's sarcoma are common comorbidities in patients with late-stage AIDS.
What are the dangers of being infected with HIV?
HIV infection is a high-risk disease in which systemic immune organs are destroyed. It can cause the following harm.
- Harm to the patient himselfAfter infection, the organs of the whole body of the patient are invaded and destroyed with the spread of the virus, resulting in the decline of the immune function of the whole body organs, leading to the occurrence of a variety of diseases, and to the eventual failure of the organs, leading to the death or disability of the person, which often creates a kind of strong psychological and spiritual pressure on the AIDS patient.
- Harm to others: Infected persons can transmit HlV to others through unprotected sex, intravenous drug use with shared needles, or through mother-to-child transmission.
- Harm to the family and society: People living with AIDS can place a heavy financial burden on their families and create a problem of dangerous insecurity for society.
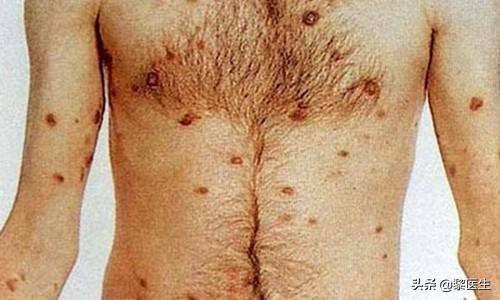
To summarize: The main way to prevent AIDS is to stop being infected by it through cleanliness and self-care. Don't share intravenous drug paraphernalia and minimize the use of blood products.
Hi everyone, I'm Dr. Bobo and I specialize in HIV prevention and treatment at the CDC, so I'm not invited haha, let me answer.
The incubation period of AIDS after infection is 2-10 years on average, with the shortest period being half a month and the longest period being as long as 25 years. Therefore, it is a long process from infection to the onset of AIDS, with different clinical manifestations at different stages.

To talk about the symptoms of AIDS, you have to talk about the staging of AIDS, after the infection of AIDS will be divided into three stages: acute stage, asymptomatic stage and AIDS stage, the symptoms of each stage are different haha.
I mainly combined with my case in the course of work to answer the acute stage symptoms, the symptoms of AIDS stage can be Baidu or read other answers, they write very detailed haha.
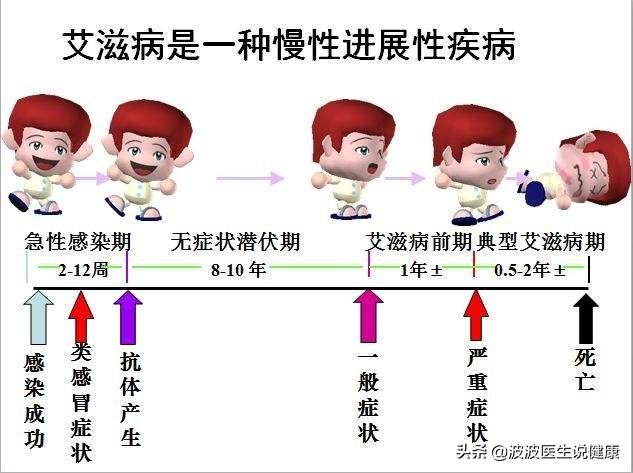
Symptoms in the acute phase generally appear 2-4 weeks after infection, with some infected individuals experiencing clinical symptoms resulting from HIV viremia and acute damage to the immune system. In most infected patients, clinical symptoms are mild and resolve spontaneously in 1-3 weeks. Fever is the most common clinical manifestation, which may be accompanied by general malaise, headache, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, arthralgia, skin rash, and enlarged lymph nodes.
These symptoms are similar to those of a cold. In the course of my work, I have encountered many counselors who have had high-risk behaviors but have the above symptoms caused by a cold, and they are extremely worried about contracting AIDS, and they are very scared and fearful. Usually when I encounter such counselors, I patiently explain to them that the probability of contracting AIDS is not actually high. Although we have the corresponding symptoms, we should not approach the symptoms towards AIDS, if we think so, then any symptoms on your body are applicable to AIDS. So when we have had high-risk behaviors, we should go to the CDC or hospitals or certain community health centers for free counseling and testing, and we should trust science, shouldn't we? There is no problem with the test, we should trust it, right? However, in the course of my work, I did come across the kind of people who had the above symptoms after having high-risk behaviors. We tested him three times, and all three times were negative, but he just didn't believe that he didn't have any problem, and he still wanted us to test him, which increased our workload and wasted a lot of resources.

AIDS is a preventable but incurable chronic disease, so we healthy people should prevent it by avoiding high-risk behaviors as much as possible, always insisting on the use of condoms during sex, and eliminating drug use in any way.
For those who are infected, you should have confidence that the treatment of AIDS is becoming more and more mature, more and more new drugs are on the market, and we should believe that one day in the future, AIDS can be cured.
I am specialized in AIDS prevention and treatment at the CDC, please follow the private message for any questions. Please forward it to let more people know about HIV and AIDS prevention and treatment, thank you.
Many people say that AIDS is really too scary, I have to do a good job of preparation to prevent themselves from being infected, even if they accidentally suffer from AIDS, but also have to know the symptoms of AIDS as early as possible to detect, and perhaps early treatment can also live longer. Indeed, understanding the symptoms of AIDS is very important for treatment, the following are the main symptoms of AIDS.
1、Widespread generalized lymph node enlargement
Widespread lymph node swelling is one of the most characteristic symptoms of AIDS. When a person with AIDS reaches the middle to late stages of the disease, because most of the body is parasitized by the virus, that is, almost every part of the body contains a large amount of the HIV virus, the immune system will then attack the virus, and the phenomenon of swollen lymph nodes occurs, especially the lymph nodes in the neck and armpits.
2. Systemic symptoms
AIDS patients will experience generalized symptoms such as generalized pain and weakness, persistent high fever, decreased meal intake or anorexia, dramatic weight loss, and frequent night sweats at night while sleeping, and at the initial stage, they may also have flu-like manifestations.
3. Multiple tumor infections
With the deterioration of the disease, in the late stage and advanced stage, the HIV virus will invade and damage the T-cells of the immune lymphocytes in the whole body of the patient, resulting in the complete loss of cellular immune function of the organism. At this time, the patient will be infected by other pathogenic microorganisms and some carcinogens, because the body has lost most of the immune ability and lead to multiple tumor infections, in the end, most of the AIDS patients are also due to the onset of tumors and towards death.
In fact, the symptoms of HIV are quite diverse, after all, each HIV patient's physical condition and the tumors or diseases that he or she suffers from as a result of the infection at a later stage are also different. But no matter what the symptoms are, they are closely related to the HIV virus in the patient's body.
Instructor: Zhou Lijun, Deputy Chief Physician, Department of Infection, General Hospital of Tong Coal Group Company.
He specializes in the treatment of chronic liver disease, bacillary dysentery, typhoid fever, brucellosis, and infectious diseases such as chickenpox, hand-foot-mouth disease, mumps, scarlet fever and measles in children.
If you find this article useful, please feel free to like or recommend it to your friends and follow [Medlink Media].
With regard to AIDS, because of its rapid spread and high morbidity and mortality rates, there is currently no fundamental cure. In addition, there are no obvious symptoms in the early stage, but as the disease progresses, it can show diverse manifestations and eventually complicate various serious opportunistic infections and malignant tumors. With the world's attention to the disease and the popularization of science and the dissemination of preventive knowledge, the disease is now well under control in our country.

AIDS (loanword)
AIDS, also known as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, is a serious, chronic and fatal infectious disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which primarily attacks and destroys helper T-lymphocytes.
People infected with HIV are the only source of infection for the disease, including patients and asymptomatic carriers of the virus, who can be more at risk due to long-term carriage of the virus, but regardless of stage, HIV-infected people will be infectious for life.
HIV-infected people's blood and semen, vaginal secretions, breast milk and other body fluids carry the virus. The main ways of transmission are: ① sexual contact transmission; ② blood and blood products transmission; ③ mother-to-child transmission.
There is no need to worry too much about the following: daily life contact (e.g., air, water, food, or insect bites) with a person with AIDS will not transmit HIV, and general social contact such as shaking hands, sharing meals, recreational facilities, common office supplies, and sharing toilets or bathrooms (swimming pools) will not infect the person.
What are the symptoms of HIV infection?
AIDS does not usually develop immediately after infection, and the incubation period can be quite long, which is one of the reasons for its wide spread. The length of the incubation period and the length of the infection are related to the number and type of viruses infected, the route of infection, the immune status of the body, the nutritional status, living habits and medical conditions. It usually takes 2 to 10 years before the disease develops into AIDS. There are great individual differences in the manifestation of symptoms, which are generally categorized into four stages.
Acute Infection Stage (Stage I)
In the first 2 to 4 weeks after infection, a small number of people will experience serum sickness-like symptoms such as fever, general malaise, sore throat, rash, anorexia, myalgia and arthralgia, and enlarged lymph nodes, which usually last for 1 to 2 weeks and then disappear naturally. Uninformed infected people can easily mistake it for an unusual common cold.
Asymptomatic infection stage (stage II)
This stage of the disease can last 2 to 10 years or longer. There will not be any manifestations or signs, but it is contagious and HIV and anti-HIV antibodies can be detected in the serum. These people are difficult to detect if not for the progression of the disease into the next period or physical examination tests.
Persistent generalized lymph node enlargement syndrome (stage III)
Also known as the pre-AIDS stage, one of the main characteristics of this stage is that the lymph nodes are enlarged and >1cm in diameter, tough, non-pressure, mobile, and can last for more than 3 months. The enlarged lymph nodes may be located in two or more places. It is accompanied by persistent or intermittent fever, fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, chronic cough and diarrhea.
AIDS stage (IV)
This is the terminal stage of AIDS, as HIV attacks the body and causes problems to begin to manifest themselves in all areas of the body, which can be categorized into five main groups.
①Somatic disorders: fever, malaise and discomfort, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia, chronic diarrhea, large liver and spleen. ② Neurological symptoms: headache, epilepsy, lower limb paralysis, progressive dementia. ③ Opportunistic infections: protozoa, fungi, antacid bacteria and viral infections. ④ Secondary tumors: Kaposi's sarcoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. ⑤ Secondary to other diseases, such as chronic lymphoid interstitial pneumonia.
summarize
Because the incubation period is so long, and because there are no specific manifestations in the first and middle stages of the disease other than a decrease in body resistance, the most convenient and fastest way to suspect infection is to undergo a serologic test at a relevant testing unit. If you are unfortunately infected, go to the relevant medical institutions for treatment, although it can not be cured, but symptomatic treatment can improve the quality of life, as well as the relevant disease education and guidance can better protect those around you. Reasonable arrangements for rest time after discharge from the hospital, avoid overwork, understand the implementation of the daily life of the disinfection of disposal, for asymptomatic HIV carriers, every 3 to 6 months to do a clinical and immunological examination, such as the emergence of symptoms in a timely manner with the isolation of the treatment, the pre-infection, to slow down the progression of the disease.
Thank you for reading and I hope my answer was helpful. If you think it's not bad, please give me a like! If you can also give me a follow, I think it must be the biggest support for me.
Article reference: human health edition of internal medicine nursing, second edition AIDS-related care
A friend's daughter, who worked as a hostess and had to have zero distance contact with different men every day, came back to recuperate after contracting AIDS five years later.
Friends of the daughter looks very beautiful, her face and body, the typical beauty billet, after dropping out of junior high school she went to the bar to do the desk lady, every day, zero distance and all kinds of men to deal with, but also earned a large sum of wealth.
But one day, five years later, she felt unwell with headaches, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, joint pain, skin rashes and swollen lymph nodes.
At that time, she thought she had a cold, but also casually went to the drugstore to buy some cold medicine to eat, and continue to work, but after taking medicine for more than a week has not improved, because every day and men contact, she is a little suspicious of whether it is AIDS.
Then went to the big hospital to check, really hit the jackpot, after she came back she began to grow a rash all over her body, red, swollen and ulcerated pus and blood, all are ulcerated, and all the body has no strength, the bed can't get down, the friend took her everywhere to see a doctor, and finally because of the seriousness of the disease, or in three years later died.
Only 23 years old, young and beautiful girls because of the love of vanity, want to get something for nothing to go astray and killed, really not worth it!

The full name of AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, and the full name suggests that AIDS is an immunodeficiency disease that is caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus.
We are all familiar with the main ways of HIV transmission, which are mainly through sexual contact (including heterosexual and homosexual), blood transmission, and vertical transmission from mother to child. However, it is generally not spread through food, respiratory tract, handshake, sharing swimming pools and public toilets.
The terrible thing about AIDS is that as it attacks the human body, it constantly kills and maims host cells and causes defects in the body's immune function, leading to a variety of opportunistic infectious diseases and tumors in the body.
What are the signs of HIV infection and progression to AIDS?
From the beginning of HIV infection until the patient's death, is a very long and torturous process, not once infected with AIDS can be immediately onset and symptoms, the fastest infected with AIDS will be a few months before the symptoms appear, some patients can be incubated for up to 15 to 20 years, from the statistical data, the incubation period for an average of 8 to 10 years. The specific manifestations are as follows:
1. Acute HIV infection
The onset of symptoms often occurs around 14 to 42 days after HIV infection, and about 50 to 70% of patients may develop acute impairment of the immune system and HIV viremia. However, the majority of patients have mild symptoms, which last from 7 to 60 days before disappearing and becoming invisible. Fever is the most common form of AIDS at this time, along with headache, sore throat, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, as well as a rash and swollen lymph nodes.
2. Asymptomatic HIV infection: This period can extend from the disappearance of symptoms of acute infection, or patients with no obvious symptoms of acute HIV infection can enter this period directly. As mentioned earlier, this period can last from a few months to 20 years, with an average of 8 to 10 years. Patients in this phase usually have no symptoms. However, some patients may develop swollen lymph nodes that last for a long time.
3. Terminal AIDS stage, the main manifestations of which are as follows:
Fever, night sweats, and diarrhea that can last for more than a month without improvement.
②Weight loss
③Enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body
④ Various opportunistic infections and tumors, as described below:
Central nervous system lesions: Viral meningoencephalitis, toxoplasmosis, tuberculous or cryptococcal meningitis, dizziness, blurred vision and headache, and coma in severe cases.
Ocular: toxoplasmic retinitis and cytomegalovirus retinitis: presenting as flocculent white spots at the base of the eye.
Oral lesions: thrush, recurrent mouth ulcers, gingivitis, etc., manifesting as pain in the mouth after eating; the above lesions can recur.
Respiratory disease lesions: Pneumocystis pneumonia and Kaposi's sarcoma. Patients present with chronic cough and fever, shortness of breath, cyanosis of the nail beds of the lips and mouth, and failure to maintain normal oxygen saturation.
Digestive system lesions: esophagitis, gastroenteritis, perianal inflammation. Patients may present with painful swallowing, burning pain behind the sternum and associated diarrhea.
The danger of AIDS is so great that the emphasis is on prevention, and the focus of prevention is on cleanliness.

(Images from the Internet, not for commercial use! (The content of this article is for reference only, not as a basis for diagnosis and medication, and can not replace the diagnosis and treatment of doctors and other medical personnel and advice, if you are not feeling well, please seek medical attention in a timely manner.)

Unfortunately, three years of high risk and still no typical symptoms still does not rule out AIDS.
The incubation period of AIDS can reach about ten years, around 1990, because the single blood collection of people infected with AIDS, most of them have an incubation period of more than ten years, then in recent years our country's AIDS infected people infected with HIV is mainly the way of sexual behavior, well, we observed that homosexuals infected with HIV incubation period, probably only 4 to 5 years, but overall, a person if there are no symptoms for three years after the high risk But in general, a person who has no symptoms for three years after a high-risk exposure cannot be ruled out as being infected with AIDS.
In fact, the rate of clinical progression of HIV-infected patients is not the same, we generally categorized into three types, the first is the typical progression, the second is rapid progression, and the third is the long term slow progression, factors affecting the rate of clinical progression of HIV-infected patients, including the virus, host immunity, and the genetic background, and so on.
Considering that there is also a portion of the population that are slow progressors, then their asymptomatic period may be longer, so the absence of typical symptoms of AIDS within three years does not rule out HIV infection, as the person is most likely still in the asymptomatic period.
We judge whether we are infected with AIDS, in fact, there is another indicator is whether the acute phase symptoms appear two weeks to four weeks after the high risk, acute phase symptoms are mainly manifested in fever, sore throat, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, joint pains, swollen and painful lymph nodes, etc., and in some people there are also headaches.
Of course, if you do engage in high-risk behavior, it is still recommended that you take an HIV antibody test to determine whether you are infected or not. If you test negative for HIV antibodies six weeks after the high-risk behavior, then you can rule out HIV infection. 99% of HIV-infected patients can be detected within six weeks of infection. If a four-generation antigen-antibody combination test is used, then 99% of infected people are detected within four weeks.
So according to the question in the title, three years after a high risk with no symptoms cannot rule out AIDS, and it is recommended that an HIV antibody test be done to rule out HIV infection.
AIDS, that is, people infected with HIV (or carriers of the virus), will develop into AIDS only after a latent period of many years or even 10 years or more. A few years ago, when I was invited to write a documentary on a re-education through labor camp before the abolition of the re-education through labor system, the judicial police arranged an interview with a trainee. The young man just sat down and said, "Teacher, I'm an AIDS patient." You wouldn't have known he was an AIDS patient unless he declared it first! He got the disease from injecting drugs with shared needles and syringes. The doctor said that the main symptoms of AIDS were shingles, tuberculosis, enteritis, pneumonia, and diarrhea several times a day. Also before this, once crossing the street, was deliberately turned a bit, then stopped, the guy pulled up the corner of his pants, there are hard scabs after herpes. ___ encountered "touch magnetism", meaning to call for compensation. You want to swindle people? I don't even have a door! Then yelled at the guy "dog day, you a drug addict, you are afraid of 110." The guy hurriedly rolled!
With the rapid advancement of information, AIDS has become well known to many people, however, people with HIV usually don't show symptoms right away, so they may not realize they have them. Today, let's take a look at what symptoms a person with HIV can actually have.

Early HIV symptoms
After being infected, people usually look and feel healthy for a long time. HIV can take 10 years or more to show any symptoms, and you may feel feverish, achy, and sick for the first 2-4 weeks after being infected with HIV. These flu-like symptoms are your body's first response to HIV infection. During this time, there are many viruses in your system, so it is easy to spread HIV to other people. Symptoms only last for a few weeks and then are usually symptom-free for many years.
HIV destroys cells in the immune system called CD4 cells or T cells. Without CD4 cells, it's hard for your body to fight the disease. This makes it easier to get real infections that usually don't hurt you. Over time, the damage HIV does to the immune system can lead to AIDS.
AIDS is possible when a patient develops a rare infection (called an opportunistic infection) or type of cancer, or if the body has lost a certain number of CD4 cells. Without effective treatment, it usually occurs 10 years after contracting HIV. With treatment, it may take longer to develop AIDS.
Signs of AIDS include:
Thrush (thick white coating on the tongue or mouth), sore throat, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease , bad infections galore, feeling really tired, dizziness, headaches, weight loss, prolonged diarrhea, fever or night sweats, swollen or hard glands in the throat, armpits, or groin, feeling breathless, bleeding from the mouth, nose, anus, or vagina, rashes, feeling numbness in the arms and legs, loss of control over muscles and reflexes , inability to move, decreased muscle strength.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.