What are the symptoms of people who are living with HIV? Can they be detected in life?
What are the symptoms of people who are living with HIV? Can they be detected in life? 
Not all AIDS patients have symptoms, even if we are lucky enough to meet an AIDS patient, as a health care worker I would like you to look kindly on them, sometimes they are a not so small, sometimes they are also victims!
I remember when I came to the hospital, at that time another classmate of mine went to the Laboratory Department, and he told me that in fact, every now and then, there would be one or two patients who tested positive for HIV, but their reasons varied, some of them were infected accidentally because of occupational exposures, working as related staff, some of them were transmitted by their boyfriends, and some of them were indeed complicated sexual relationships, and thatIn general, however, the ratio of men to women is 3.7:1, and the most important point to note is that, for young men, homosexual contact is the main mode of transmission.
However, not all AIDS patients can show typical symptoms, because AIDS has a test has a "window period", you may test negative for AIDS today, but after a few weeks, it becomes positive, which is very possible!Therefore, different periods of AIDS can only be detected in different ways!
- Asymptomatic stage: This is really only diagnosed by asking about private life or any occupational exposure, and most of all by going to the hospital for an HIV antibody test, if positive!In normal life, you basically can't find out! Nowadays, there are many ways to test for AIDS in hospitals.Such as HIV antibody and P24 antigen, HIV viral load (to quantify HIV-1 nucleic acid), CD4 lymphocyte count (to assess immunodeficiency), etc., which has a quick method that is done in ten minutes!

- Symptomatic Period:The patient may have recurrent diarrhea for more than a month and not less than 3 times a day, as well as recurrent Candida albicans infections in the mouth, and deep tissue fungal infections; typically, this may also lead to unexplained and irregular recurrent fevers for a month; and in some cases, recurrent herpes simplex infections. Attention to go to the hospital for HIV exclusion, especially if there is some risk of HIV transmission or possible transmission!Clinically, it is found that 80% of HIV-infected patients infected with HIV can detect antibodies in the initial screening test in about 6 weeks, and almost 100% of infected patients can detect antibodies after 12 weeks of infection, and only a very small number of patients can be detected within 3 months or 6 months after infection. This is actually the so-called AIDS "window period"!

- Onset period.Mainly persistent fever, diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, various encephalopathies, mobility disorders and a series of other manifestations, relatively complex and serious.At this time in fact, we also just look at the symptoms you can not say that he is suffering from AIDS, many clinical diseases, in addition to clinical symptoms, is necessary to combine with the results of clinical laboratory diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis, because there are a lot of diseases are very likely to appear similar symptoms!
Whether or not there are symptoms of AIDS has to do with the stage of progression of the disease and, of course, with one's own physical condition. I once saw two news stories about AIDS.
- The first one talks about a female college student who, after having sex with a man who informed her that she had AIDS, had sex, i.e., in retaliation, the female college student hugged her head and cried in remorse.
- The second is about a child whose parents were AIDS patients, who was diagnosed with AIDS when he was 1 year old, as a result of a blood transfusion from his father. He learned the news when he was 12 years old and was at peace with himself. Fortunately, he was not infected himself. By this time he realized why his mother never let him touch her intimate things. Now after 18 years of living with his parents, it's like a normal family except for the fact that they don't share dishes. And, other than the family's closest relatives, no one else knew anything about it.
The purpose of these two cases is to prove that not all AIDS patients have symptoms, and that if the patient deliberately hides them, he or she can certainly conceal them. Even the people closest to them may not be able to detect the symptoms. What is more, what about people who are just colleagues and casual acquaintances?
What are the symptoms of people who are living with HIV? Can they be detected in life?
HIV infection has a latent period, during which the patient has no obvious symptoms, just like normal people. The incubation period is not the real meaning of AIDS people, can only be regarded as HIV carriers, and even some people can not be detected for several years. Research has found that the incubation period of HIV is 9 years on average, some may be only a few months, while some are as long as 10 years. Therefore, it is not reliable to rely solely on symptoms to determine whether a person has AIDS.
1. Acute infection period:HIV infection starts from the acute infection stage, which usually occurs 2-4 weeks after infection. The main symptom of this stage is prolonged fever with inexplicable lethargy, malaise, weakness, night sweats, headache, muscle aches, diarrhea, etc. It can be easily mistaken for influenza, and in some cases persistent bleeding from the mouth, oral ulcers, skin rashes, and enlarged lymph nodes.

2. Asymptomatic period:The acute stage of infection is followed by a long asymptomatic period, during which the patient may be asymptomatic or have only mildly enlarged lymph nodes, as the immune system fights the virus.
3. Complete AIDS period:After the asymptomatic period, it is considered to have entered the full AIDS stage, that is, the true meaning of AIDS patients, at this time the patient began to appear serious systemic discomfort, including persistent fever, cough, chest tightness and shortness of breath, dyspnea, chest tightness, wasting, general weakness hood, in addition to systemic infections, such as folliculitis, infectious warts, genital herpes, thrush, rashes and so on, serious there will be a systemic organ Infection, endangering the heart, liver, kidney and other organs, until the patient's life is jeopardized, resulting in death.
Therefore, for people infected with AIDS, the initial stage of infection is like a cold, and there are no symptoms in the middle stage of infection, and it is only in the final stage that the disease can be detected by outsiders, and the period may be several decades. Still, it is not reliable to rely solely on symptoms to determine whether a person has AIDS or not, not to mention that when one has this disease, the patients will conceal it, and it is unlikely to be easily detected by others.
I am Pharmacist Wang, insisting on spreading the knowledge of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases with simple and easy-to-understand words, and dedicating my own small efforts for a healthy China. If you think my answer is helpful to you, please leave a like it! In addition, if you still have related questions, welcome to leave a message, we discuss together!
AIDS carriers often have no specific symptoms, and there is no way to distinguish between them through some very common symptoms, so you can't simply use symptoms to judge in life. The judgment of this disease should be based on medical tests.
Common Symptoms of AIDS:
● Typical symptoms: Typical symptoms include persistent fever, weakness, night sweats, and persistent widespread generalized lymph node enlargement. It is especially pronounced in swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits and groin.
● Weight loss: up to 10% or more within 3 months, up to 40%, with wasting being particularly pronounced.
● Symptoms of various opportunistic infections such as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, tuberculosis, nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, toxoplasmosis encephalopathy, and fungal infections.
● Opportunistic tumors, common AIDS-related lymphoma with Kaposi's sarcoma, etc.
● Other symptoms
The long-term development of HIV can lead to respiratory symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing;
Gastrointestinal symptoms: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, etc;
● Neurological symptoms: dizziness, headache, unresponsiveness, mental retardation, etc.; skin and mucous membrane damage, etc.
Note: Quoted from Encyclopedia of Famous Doctors
Not to mention for ordinary people, even for professional medical personnel, it is difficult to judge from some common symptoms, this disease is judged by medical tests. Many patients are examined and found in the course of physical examination or medical treatment or hospitalization.
In addition to the acute stage and the AIDS stage, there is also an asymptomatic period in the middle of the AIDS patient, this process usually ranges from a few years to more than ten years, and there are large differences in each person, and each person's physical condition, diet, living habits, psychological state and many other factors related to.
In the asymptomatic phase, patients can have no symptoms or some mild symptoms that lack specificity such as malaise and enlarged lymph nodes.
Currently, there are autonomous and passive testing for the detection of AIDS patients. For sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis and AIDS, patients who are hospitalized are basically screened, and many invasive treatments or surgeries such as plastic surgery and tooth extraction are also screened.
In the clinic also met some patients, have had high-risk or similar high-risk behavior after the fear of HIV infection, through the network to search for relevant information, and then according to some of the symptoms of the right, in the psychological pressure, and even a lot of patients through the medical examination and more than three months negative, but stubbornly obsessed with some of the symptoms, such as fever, enlarged lymph nodes, fatigue, diarrhea and so on, so that there is no way to get rid of the fear of AIDS, affecting the normal work or study, causing great distress to themselves or their families. So much so that there is no way to get rid of the fear of AIDS, affecting normal work or study, and causing great distress to themselves or their families.
With regard to situations like this one
1. If you have had high-risk behavior, it is recommended that you go to your local hospital for testing after three weeks.
2. Don't use symptoms to diagnose yourself, medical tests should prevail.
3. Believe in science, observe for enough time and pass a negative medical test, that means there is no infection, no need to dwell on some symptoms.

(web photo)
Thanks for the invitation!
An HIV-infected person is one who is infected with HIV but does not show clinical signs and symptoms, while an AIDS patient is one who is infected with HIV and shows clinical signs and symptoms. From the initial infection of HIV to the eventual development of AIDS patients, the process is medically categorized into four stages:
acute infection period
In the early stages of infection, some infected people may experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, diarrhea, etc., but they are often mild and easily overlooked, and some infected people do not experience any symptoms. In the early stage of infection, HIV replicates heavily in the body, but HIV antibodies cannot be detected in the blood. The period from the time of HIV infection to the time when HIV antibodies can be detected in the blood is called the "window period". The window period is usually 2 weeks to 3 months.
A person infected during the window period has a large amount of the virus in his body, which is extremely contagious and can be passed on to other people, so it is important to avoid unnecessary blood transfusions to prevent the introduction of window-phase blood. If you suspect that some of your behaviors may be infected with HIV, you should take an antibody test 3-6 months after engaging in risky behaviors to determine if you are infected with HIV.
incubation period (of disease)
The period from the infection of the virus to the emergence of clinical symptoms is called the incubation period, also called the asymptomatic period, which is 7-10 years on average. During this period, the infected person may not have any symptoms, can work, study and live normally, and looks exactly the same as a healthy person, but this period is not a static period, let alone a safe period, the virus is still reproducing in the body, and it is contagious, and the virus is continuously destroying the immunity of the human body.
Pre-AIDS
When the body's immunity is damaged by HIV to a certain extent and the body cannot resist the attack of external pathogens, some early signs and symptoms related to AIDS will appear, such as unexplained fever, weight loss, fatigue, diarrhea, genital herpes and so on.
AIDS period
When the body's immunity is further compromised until it breaks down completely, the patient develops serious opportunistic infections (e.g., tuberculosis, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, cryptococcal meningitis, cytomegalovirus encephalopathy, etc.) and malignant tumors (e.g., Kaposi's sarcoma), and the patient ultimately dies from any one or more of the above diseases.
Among them, tuberculosis is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDS patients, and one-third of the AIDS patients who have died worldwide have died of tuberculosis. Whether or not a person is infected with HIV cannot be diagnosed by outward appearance or clinical symptoms, but only by a confirmed positive HIV antibody diagnosis.
[What are the symptoms of HIV infection?
{!-- PGC_VIDEO:{'thumb_height': 360, 'file_sign': 'b6494da2a62c5111eaeacfee06934a98', 'vname': '', 'vid': 'v02019bd0000bd3ene2iv570554d25ng', 'thumb_width': 640, 'vu': 'v02019bd0000bd3ene2iv570554d25ng', 'src_thumb_uri': '9829000e80a60034f47f', 'sp': 'toutiao', 'update_thumb_type': 1, 'vposter': 'http://p1.toutiaoimg.com/origin/9829000e80a60034f47f', 'video_size': {'high': {'duration': 139.12, 'h': 480, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 854, 'file_size': 4211573}, 'ultra': {'duration': 139.12, 'h': 720, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 1280, 'file_size': 8058843}, 'normal': {'duration': 139.12, 'h': 360, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 640, 'file_size': 3110570}}, 'duration': 139.12, 'thumb_url': '9829000e80a60034f47f', 'md5': 'b6494da2a62c5111eaeacfee06934a98'} --}
[How to prevent AIDS?]
{!-- PGC_VIDEO:{'thumb_height': 360, 'file_sign': '591a0b08f132870aa6b43a7d5da549d7', 'vname': '', 'vid': 'v02019190000bd3enrj2ap9c7ptknb10', 'thumb_width': 640, 'vu': 'v02019190000bd3enrj2ap9c7ptknb10', 'src_thumb_uri': '983e000399c4ac9729ff', 'sp': 'toutiao', 'update_thumb_type': 1, 'vposter': 'http://p1.toutiaoimg.com/origin/983e000399c4ac9729ff', 'video_size': {'high': {'duration': 226.76, 'h': 480, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 854, 'file_size': 6481472}, 'ultra': {'duration': 226.76, 'h': 720, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 1280, 'file_size': 12316274}, 'normal': {'duration': 226.76, 'h': 360, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 640, 'file_size': 4810717}}, 'duration': 226.76, 'thumb_url': '983e000399c4ac9729ff', 'md5': '591a0b08f132870aa6b43a7d5da549d7'} --}
主讲人:吴昊——首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院感染科主任 主任医师 教授 博士生导师;北京市性病艾滋病诊疗中心主任;北京市艾滋病重点实验室主任; 享受国务院政府特殊津贴专家;卫生部艾滋病专家咨询委员会专家;卫生部传染病标准 He is a member of the AIDS Expert Advisory Committee of the Ministry of Health; an expert of the AIDS Antiretroviral Treatment Demonstration Area of the Ministry of Health; a national member of the Infection Branch of the Chinese Preventive Medical Association; a standing member of the Infection and Immunity Branch of the Chinese Medical Association; a vice-chairman of the Beijing Municipal Society of Virology; and a vice-chairman of the Beijing You'an Home for Love.
If the answer is helpful to you, give the expert a point of praise, there are other questions can be in the comments section to reply Oh, we will try to answer, good health.
Early on, there may be fever, headache, sore throat, night sweats, malaise, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, arthralgia, swollen lymph nodes and neurological symptoms. However, none of these symptoms are specific, so if you have high-risk sex, don't be right, or get an early lab test.
In the incubation period and the early stage of infection, patients with HIV do not have any obvious characteristic symptoms, and they will not be detected in their normal life as normal people, but they can definitely be detected when they undergo blood tests. This is what makes this incurable disease more and more prevalent in the population and leaves people defenseless. In order to screen and detect potentially infected people, medical structures qualified for laboratory tests have made laboratory tests for hepatitis B virus surface antigen, hepatitis C virus antibody, AIDS antibody, hepatitis A antibody, and hepatitis E antibody mandatory after hospitalization, before invasive tests, and before the importation of blood or blood products.

When the HIV virus continues to replicate in the human immune system, causing the immune system to malfunction or collapse under attack, it will cause some abnormal cells in the body to grow rapidly, multiply and develop into various types of cancerous tumors, and various serious infections will occur and many related symptoms will appear. The development of a typical AIDS patient is divided into the following four stages:
1.Acute Infection Period:A small number of infected individuals will experience fever, sweating, fatigue, myalgia, arthralgia, anorexia, rash, and swollen lymph nodes for 2 to 6 weeks, which usually lasts for 3 to 14 days and then enters an asymptomatic period.
2.Asymptomatic period:The vast majority of HIV-infected people start with no symptoms, as if they were healthy, and therefore do not know when they are infected. The scary thing is that these asymptomatic HIV carriers are the main source of infection.
3.Early onset:In the early stage of AIDS, patients have enlarged lymph nodes all over the body, often in the neck, armpits and groin. The enlarged lymph nodes are mostly symmetrical, characterized by hardness and non-adhesion, without tenderness and fluctuating sensation. A few patients may present with mild anemia. But there are no obvious other symptoms.
4Onset period:Presence of prolonged fever (up to one month or more), progressive weight loss (more than one-tenth of body weight loss in 2 months), persistent diarrhea, malaise, anorexia, mental retardation, and unresponsiveness. Common opportunistic infections such as tuberculosis, hepatitis B, oral and pharyngeal mycobacterial infections, and herpes zoster occur as a result of complete loss of immune function in AIDS patients. Malignant tumors such as Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and renal carcinoma can also be complicated.
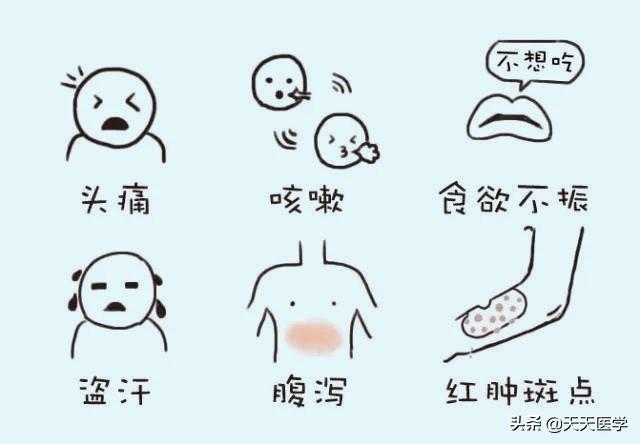
Since there is no effective prevention or treatment for AIDS, prevention can only be achieved by effectively cutting off the source of infection. If you suspect that you are infected with AIDS, you should first review whether you have engaged in "risky behaviors" (mainly referring to unsafe sex; sharing unclean needles for intravenous drug use; accepting potentially contaminated blood or blood products; and using needles that have not been sterilized strictly or other instruments that may cause bleeding, such as razor blades, piercing needles, and tattooing equipment; Delivery by HIV-infected pregnant women, etc.).
When HIV enters the body there is no quick onset of abnormal sensations. For the first few years, there may be no symptoms and you may look completely normal on the outside. It is possible to work and live without any symptoms for several years. But it can develop symptoms related to swollen lymph nodes, skin rashes, night sweats, headaches, coughs, etc. sometime within 7 to 10 years. If people with high-risk behaviors develop symptoms such as prolonged low-grade fever, chronic diarrhea, weight loss, coughing, night sweats, etc., they should be highly suspected of being infected with HIV, and should go to hospitals and health epidemiological departments with the necessary conditions as soon as possible to take an HIV antibody test. In order to determine whether it is infected with HIV. Every person who is newly infected with HIV can usually test positive within two weeks to six months after risky behavior. However, to rule out infection, the test must be repeated after six months with a negative result to confirm that the person is not infected with HIV.

Follow Daily Medicine for more health knowledge. Inadequate, please correct and add.
Thanks for reading!
As long as we don't have sex together, why do we have to be so concerned and panicky about whether or not the people around us have AIDS, not to mention the fact that people with HIV rarely have symptoms until they develop the disease. Maybe we have been in contact with people with HIV in our lives, but we just don't know it. HIV cannot be transmitted in daily life, such as shaking hands, hugging, eating together, sharing towels and mattresses, getting a haircut, and so on. For one thing, the amount of virus in the bodily fluids of such transmissions is too low, and for another, HIV leaves the host body and dies quickly.
It must be said that it is very difficult to detect and that many people living with HIV may not realize they have the disease until they have an attack.
It is understandable that society wants the general public to have a peaceful attitude towards the sick and to accept them, because we already know the main forms of transmission of AIDS when the State organizes publicity campaigns, and it is perfectly possible to live normally with the sick. However, what is often worrying is that people living with AIDS do not understand their own situation and become an invisible bomb to those around them.
So, my personal advice is to go for yearly health checkups, not so much for some mass private life, but to prevent forced infections in unusual ways. A doctor I know was treating wounds of patients who didn't know they were carrying AIDS, oops, rather unfortunate. Do the health check, not just for yourself, but for others as well.
Generally the incubation period of AIDS is very long, on average there are 9 years, short months will show symptoms, long 15 years will show, in such a long incubation period, the virus is in the body constantly replicating, the immune system is also deteriorating.
Whereas patients with the disease can live perfectly well as normal people, only when the lymphocytes drop very much do they show symptoms.

- Low-grade fever lasting a month;
- Frequent night sweats, diarrhea, unexplained weight loss of 10% or more;
- Appearance of malignant lymphoma.
There are also many people who don't show any unusual changes other than being immunocompromised, so many people can't tell the difference by clear symptoms.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.