What is the earliest number of days after contracting HIV that symptoms will appear?
What is the earliest number of days after contracting HIV that symptoms will appear? 
For the symptoms that occur after HIV infection, this is mainly categorized intoacute phaseof acute impairment of the immune system and symptoms of viremia, as well as entry into theAIDS periodSymptoms that occur after the body's immune system is compromised and symptoms caused by opportunistic infections.

Symptoms during the acute hiv infection phase generally occur about 2 to 6 weeks after exposure to hiv, and roughly 50 to 70 percent of infected individuals can develop viremia or symptoms caused by acute damage to the immune system. The main symptoms areFever, malaise, sore throat and general malaiseSymptoms (similar to an upper respiratory infection) can be accompanied bySwollen lymph nodes, rashetc., and some will have neurological symptoms such asGeneralized joint and muscle pain, etc.
These symptoms usually disappear within two months.
Special mention requiredThe thing is: these symptoms lack clinical specificity and are very similar to symptoms of common diseases, such as upper respiratory tract infections, dermatitis, allergies, rheumatoid arthropathy, etc. So, in determining the presence of HIV infection, it is not based on some common symptoms, but on the symptoms of the disease. Therefore, in determining the presence of HIV infection, not to some common symptoms to judge.It is primarily based on behavioral and medical tests.
relative to the symptoms of the acute phase of HIV.Some of the symptoms of entering the AIDS stage are more specific.Examples include Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, Kapos sarcoma, visceral toxoplasmosis, and cytomegalovirus infections.
There is no very clear line between the progression from HIV infection to the AIDS stage, but there is generally a transitional period known as the stage of generalized persistent lymph node enlargement and symptoms associated with hiv infection, during which generalized symptoms and generalized lymph node enlargement can occur and the number of CD4T lymphocytes in the blood begins to decline.The body's immune system is severely disrupted with a variety of viral bacterial, fungal, parasitic opportunistic infections and secondary tumors.
So, when we talk about how long after HIV infection symptoms appear, we are generally referring to acute HIV infection symptoms, and most of these symptoms appear in 2 to 6 weeks, which is often referred to as the window period.
There is no fixed medical definition for the situation in which patients who have engaged in high-risk behaviors, who have been tested repeatedly and negative for more than three months, but still have physical symptoms resembling HIV infection.I think it's related to psychological factors... Excessive tension, depression, anxiety of the psychological state, can disrupt the normal state of life, may also lead to some uncomfortable symptoms of the body, and these uncomfortable symptoms have a further increase in the psychological burden, the formation of a vicious circle between the two. So.For some patients who have had high-risk behaviors, do not use symptoms to determine their risk, subject to medical tests, subject to professional doctor's advice, do not look for symptoms yourself or think about the disease as a matter of course.If one is truly infected with HIV, has developed viremia or symptoms of acute damage to the immune system, and has been under observation for a sufficient period of time, it is possible to detect it through current medical screening techniques.
A lot of people who are afraid of HIV are prone to make the mistake of always taking some of the symptoms that appear after the high risk of rash and hiv infection early acute infectious clinical manifestations, in fact, it is not necessary.
In fact, the vast majority of people infected with HIV do not experience detectable flu-like symptoms during the acute phase of the infection, and only a very small number of immunocompromised people will experience similar mild symptoms 1 to 2 weeks after infection. These flu-like symptoms are more often found in everyday infections and colds, and those who take fever, headache, lymph swelling, sore throat, even weight loss, diarrhea and other manifestations to suspect hiv infection is completely unnecessary, it is actually a manifestation of AIDS fear obsessive-compulsive disorder.
With the gradual clarification of medical science on the pathogenesis of AIDS, the pathogenesis of the law, the test reagents of the new generation, our early diagnosis of AIDS, has long entered the era of genetic diagnosis, immunodiagnosis. Now the latest four-generation reagents have shortened the window period of HIV infection to less than two weeks, and those who take the symptoms to diagnose HIV infection have long been swept into the garbage heap of history.
Some people in the occurrence of high-risk behavior will worry about their own AIDS, but due to the existence of the window period of AIDS, patients can only be three to six weeks before the antibody test, therefore, people in this period will be due to worry about the more tormented, but in the early stages of infection of AIDS will appear some symptoms to help us determine, then the fastest days of these symptoms appeared?
Generally the earliest 2 to 4 weeks some acute symptoms will be initially manifested, 1 to 2 weeks these symptoms will slowly disappear, in the AIDS long more than 8 years after the incubation period, some clinical symptoms will be manifested. Let's take a look at the early acute symptoms of AIDS:
In the first 2 to 4 weeks after HIV infection, the patient will usually experience significant weight loss and loss of appetite; large, non-itchy or painful spots on the skin or in the mouth; palpable swollen, hard, immovable lymph nodes in the neck; frequent unexplained night sweats and fever, and often fatigue, with a lack of interest in doing things; diarrhea more than 10 times a day for no apparent reason; vomiting; men with itchy and scaly patches on the pubic area and women with gynecological problems such as vaginal itching and leucorrhea; shortness of breath and dry cough for no apparent reason, Vomiting; itchy and scaly patches on the pubic area in men and vaginal itching and leucorrhea in women; shortness of breath and dry cough without cause, accompanied by loss of vision and headache.
The specific appearance of these symptoms is not always absolute, but also depends on the person, some people have poor immunity in, may be a week after the symptoms, while some people have strong immunity, may be three or four weeks after the symptoms, but if these symptoms do not worry too much, these symptoms may also be due to a cold or inflammation, etc., the key is to be patient and wait for the window period passed, the hospital or the CDC antibody test results. The key is to wait patiently for the results of the antibody test at the hospital or CDC after the window period has passed.
Instructor: Zhou Lijun, Deputy Chief Physician, Department of Infection, General Hospital of Tong Coal Group Company.
He specializes in the treatment of chronic liver disease, bacillary dysentery, typhoid fever, brucellosis, and infectious diseases such as chickenpox, hand-foot-mouth disease, mumps, scarlet fever and measles in children.
If you find this article useful, please feel free to like or recommend it to your friends and follow [Medlink Media].
Hello, I am a medical worker Zhang, a practicing physician, can popularize health knowledge for everyone, if you know more, pay attention to me!
AIDS is an extremely dangerous infectious disease caused by infection with HIV, a virus that attacks the human immune system. HIV is a virus that attacks the human immune system, taking CD4T lymphocytes, the most important cells in the human immune system, as its main target, destroying a large number of these cells and causing the human body to lose its immune function. As a result, the human body is easily infected with various diseases and can develop malignant tumors with a high mortality rate.The incubation period of HIV in the human body is 8-9 years on average, and it is possible to live and work for many years without any symptoms during the incubation period of HIV.

How long does it take for symptoms to appear after hiv infection
How long does it take for symptoms to appear after HIV infection? There are three stages of HIV infection. The first stage is the acute phase, also known as the "window period", in which the symptoms disappear naturally within two to three weeks. The second phase is called the "asymptomatic phase", which is the longest and accounts for about 80% of the disease. Patients in this phase are called "HIV carriers". On the surface, they appear to be healthy, no different from normal people, but their immune system is struggling with HIV.
In normal people, there are 800-1000 immune cells per cubic millimeter of blood, while in infected people, the number of immune cells per cubic millimeter of blood decreases at a rate of 50-70 per year, and the rate of decline accelerates when the number of immune cells decreases to only about 200 per cubic millimeter of blood.HIV destroys a large number of immune cells every day, and the bone marrow compensates for the loss of immune cells by accelerating the production of new immune cells, but the rate of compensation of new immune cells can never catch up with the rate of loss of immune cells, which is the law of AIDS development. HIV destroys a large number of immune cells every day, and the bone marrow compensates by accelerating the production of new immune cells, but the rate of compensation by new immune cells always fails to catch up with the rate of immune cell loss, which is the law of the AIDS development process.
When the immune cells in the infected person's body are no longer able to fight against HIV, they enter the final stage of infection, called the "symptomatic stage", at which time the patient is called an "AIDS patient", and is very prone to a variety of infectious diseases, which can no longer be controlled in this stage. At this stage, it is impossible to control the progress of the disease, and most people die within six months to one and a half years. Its specific situation, and the patient's physical fitness and weakness has a direct relationship; the physical fitness of the disease progress slowly, survival time is long, and vice versa is short.
In addition, the psychological state of the patient is one of the most important factors in survival.... When an individual is infected with HIV, he or she may be lost, fearful, depressed, anxious, uneasy, angry, in denial, and other mentalities, all of which are harmful and unhelpful. Patients should maintain optimism, enterprising spirit, actively engaged in public welfare or collective activities, so that their own value to give full play to the highest point; infected people should take a healthy lifestyle, to avoid re-infection of HIV, avoid contact with other triggers that may promote the development of the disease, such as smoking, alcohol, etc.; regulate the diet, strengthen the nutrients, do not take illegal drugs, pay attention to avoid infection of other diseases, such as found that If you feel unwell, consult a doctor in time to strengthen your body and slow down the development of the disease.
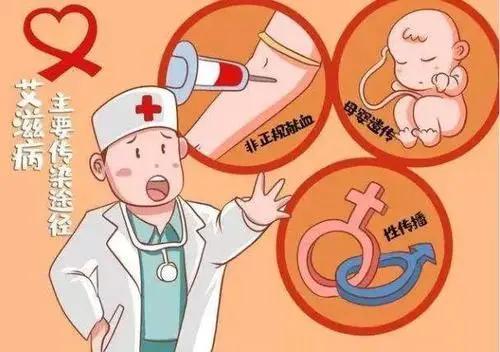
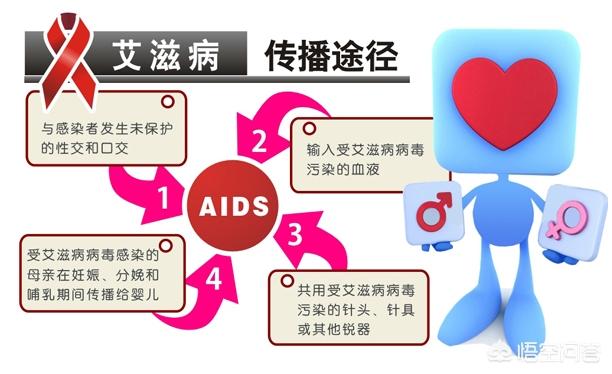
The length of time an AIDS patient survives is in turn closely related to the route of infection
1. If a person is infected with HIV through blood transfusion, the probability of infection is 100%, and the patient usually develops the disease in 4-5 years and dies in 6-18 months.
2, mother-to-child transmission of AIDS disease with the mother (including HIV carriers) through the placenta, the birth canal, breastfeeding, etc. to the fetus, the baby's chance of transmission, generally 50%, these infected with AIDS, most of the sick children, the onset of the disease at the age of 5 years old, survived to the age of 10 years old is extremely rare.
3. There are various ways of sexual transmission. It has been reported in the literature that one of the parties is an AIDS patient or HIV carrier, spreading in sexual intercourse, according to the calculation of one-time life, the man passes to the man (homosexuality), and its chance of infection is 1/10~1/1500; the woman passes to the man /700-1/3000; the man passes to the woman 1/200~1/XX; the woman passes to the woman is 1/10,000 or so. The number of HIV infections that enter the body varies depending on the chance of transmission, and even if an infection occurs, the survival period is usually about 10 years.
In the West, it has been reported that the survival period of patients with sexually transmitted AIDS is 11 to 13 years. China has reported that the mortality rate of AIDS patients is 50% in the first year, 70% in the second year, 85% in the third year and 100% in the fifth year.
HIV testing
With the development of HIV testing techniques, it is now considered accurate to rule out over 99.98% of infections after 6 weeks of testing. The incubation period for HIV begins at the time of infection, and before the advent of newer combination therapies, the incubation period averaged five to ten years, depending on the level of self-care of the individual, but may be longer.
When the virus enters the human body, it produces antibodies, and the current test is based on the detection of antibodies. However, at this time, the concentration of antibodies is not sufficient to produce the correct result, and the test must wait for a certain period of time, which is called the window period. For most people, the window period is three months long. In other words, if you had risky sex on December 1, the window period would begin to run, and the effective date of the test would be March 1, in other words. Another requirement is that you must not have any other risky sex during the three months, or the test must be recalculated. However, there are still some rare people, the window period may be more than three months, half a year or more; in addition, there are also some friends may be in a long-term window state (such as persistent multiple partners, intravenous drug addiction, or even housewives), if so, we recommend that you rely on the number of sexual partners, the frequency of sexual behavior as the basis for regular testing. If you have a large number of partners, it is recommended that you take the test every six months; otherwise, it is sufficient to take the test once a year.

Conclusion: For the human body, HIV violates the TH lymphocytes of the cellular immune system, resulting in immunocompetence defects, and the majority of patients end up with advanced infections with clinical symptoms; for the antigens and antibodies specific to the virus itself, the growth and decline of the two can indicate the state of the disease, and at the same time, guide the diagnosis of the clinical staging.
AIDS is a disease that almost everyone knows about, but doesn't understand; AIDS is a phonetic name, its full name in Chinese is "Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome", the English abbreviation is "AIDS" (AIDS), it is a chronic disease caused by infection with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). It is a chronic disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus, which does not directly cause the body to get sick, it is a direct attack on the body's immune system, resulting in a decrease or even absence of immunity, and eventually the person dies due to other infections, or the development of tumors.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus, which does not directly cause the body to get sick, it is a direct attack on the body's immune system, resulting in a decrease or even absence of immunity, and eventually the person dies due to other infections, or the development of tumors.
Because the HIV virus attacks immunity, and human immunity is exceptionally strong and cannot be knocked out instantly, the HIV virus is always a game in the human body, and this game is divided into several stages:
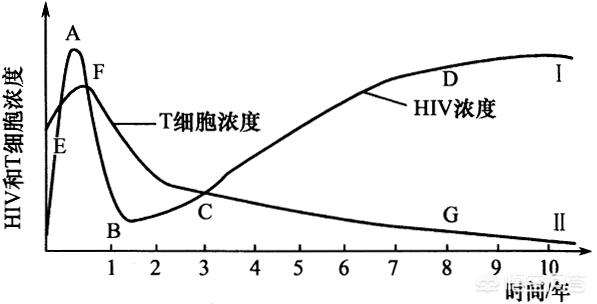
1. Acute phase
Period during which the infection first shows symptoms -Acute phase (but not in everyone)
The time it appears is related to a number of factors, including the amount of virus at the time of infection, the genotype of the virus, the route of infection, and the infected person's own immunity.
It usually appears 2 to 4 weeks after infection!
At this time, the virus proliferates and spreads throughout the body, and can manifest itself in the following ways: symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections, muscle and joint pains, enlarged lymph nodes, etc. These symptoms last for 1 to 3 weeks and then disappear.

2. Asymptomatic period
After the acute phase clears up it goes into the asymptomatic phase, but there are people who don't have an acute phase and go straight to the asymptomatic phase.
This period usually lasts 6 to 8 years.
3. AIDS period
It starts to show various symptoms, among which the more typical ones are Pneumocystis infection, Kaposi's sarcoma, and so on.
Since the onset of AIDS is related to a number of factors, it is impossible to say for sure how many days it will take for an infection to set in, as asked in the question!
Finally, although there is no cure for AIDS so far, there are many HIV antiviral drugs in the clinic that enable patients to live a normal life like those with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
Did the above help you?
If you have any questions, please leave a message.

What is the earliest number of days after contracting HIV that symptoms will appear?
The acute phase of HIV infection usually occurs after the host (human)One week to 10 daysThe initial clinical symptoms are usually mild and short-lived, and can be easily overlooked and often dismissed as cold symptoms. Serum HIV antibodies become positive about 3-5 weeks after the onset of symptoms. Thereafter, a relatively healthy incubation period of varying length occurs.
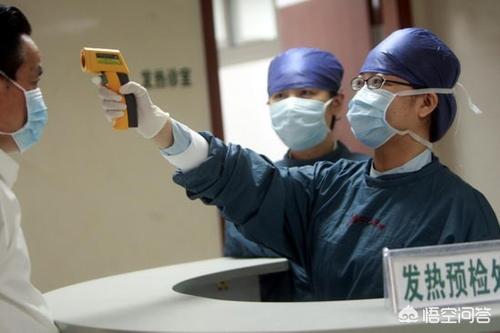
During the acute infection period, HIV virus replicates profusely while the number of CD4+ T-lymphocytes drops dramatically, resulting in some infected individuals developing HIV viremia and clinical symptoms arising from acute damage to the immune system.
The main manifestations are systemic as well as cutaneous, neurologic and intestinal symptoms. Systemic symptoms include fever, sore throat, night sweats, arthralgia, enlarged lymph nodes and hepatosplenomegaly. Skin lesions are mainly characterized by a rash, mostly non-itchy red in color
Maculopapular rash, with occasional diffuse urticaria or blisters, most often on the face, trunk, and in severe cases, all over the body. Acute HV meningitis occurs in about 9% of patients with neurologic injury and is characterized by fever, headache, vomiting, and meningeal irritation. Cerebrospinal fluid is characterized by an increase in mononuclear cells. Egg autoconjugation is increased. Gastrointestinal symptoms commonly include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, oral and esophageal candidiasis.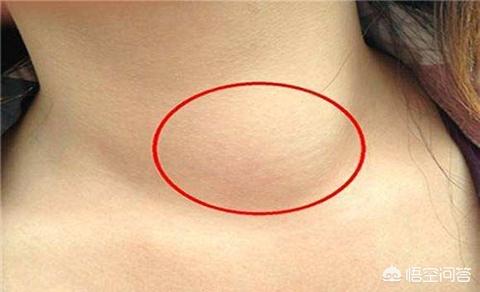
Thus, having had high-risk sexual behavior or having been exposed toGet tested if you experience any of these symptoms。
About infectious diseases can be concerned about Dr. Li Ping, health road with me!
Hello, after being infected with HIV, there will be a window period between the time you are infected and the time you are currently screened positive for HIV, and the length of time varies from person to person.
If you are infected with HIV through high-risk behavior, after the HIV virus enters your body, over a period of time, your body will produce antigenic antibodies to HIV, which can be detected through laboratory testing, a time often referred to as the window period.
Usually this window period is 4-6 weeks, which means that HIV antibodies can be detected in the blood in about 4-6 weeks using a common enzyme-linked test or gold standard test. The detection rate is usually more than 98% at around four weeks.
Nowadays, some hospitals or testing centers are using the new chemiluminescent method of testing, which measures not only antigen and antibody, but also antigen of AIDS, so the test can be done much earlier, usually in about three weeks. If you test positive, it does not necessarily mean that you have an infection, and you should go for further tests to confirm the diagnosis.
HIV infection can be ruled out if the HIV antibody test is still negative six months after high-risk sex.
I hope my answer will help you.

Responding to this question at the invitation of my friend I'm a cup of Monk1.
After infection with the AIDS virus (HIV), symptoms of acute-phase infection usually appear in 2 to 4 weeks (as soon as 5 days).
After HIV enters the body, it reaches the local lymph nodes in 24-48 hours, and viral components can be detected in the peripheral blood in about 5 days, which then produces viremia and leads to acute infection.
The acute phase often occurs 2 to 4 weeks after the initial HIV infection. Symptoms are mild and non-specific, not easy to distinguish from colds, manifested by fever, which may be accompanied by sore throat, night sweats, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, joint pain, swollen lymph nodes and neurological symptoms. If you have unclean sexual intercourse, sharing needles and drug use and other high-risk industries, you can carry out a test for HIV antibodies, and nowadays the test room can usually detect antibodies 3 weeks after infection.
Some patients may go directly to the asymptomatic phase without an acute phase.
The above was replied by Dr. Wang Cheng based on ''AIDS Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines Third Edition (2015 Edition)'' from AIDS Group, Infectious Diseases Branch, Chinese Medical Association.

When someone has AIDS, the physical symptoms I don't know about, the psychological symptoms are absolutely immediate.

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.