What happened to the disc that after walking a hundred meters in therapy, I have to rest for a while and then walk again to get rid of the pain?
What happened to the disc that after walking a hundred meters in therapy, I have to rest for a while and then walk again to get rid of the pain?
Lumbar disc herniation has a symptom called intermittent claudication, although when taking an MRI, this manifestation of lumbar spinal stenosis may be found, you can not blindly diagnose it as lumbar spinal stenosis because, most of the intermittent claudication caused by lumbar spinal stenosis is bilateral and symmetrical, not unilateral pain!
You have to rest when you walk a hundred meters.
There are a lot of people, in the back and leg pain is serious, walking will be limited, may be manifested as walking pain, with the walking distance more and more far, the pain will be more and more heavy, some people have no way to walk not much farther, the quality of life has become very poor, walk walk squatting for a while, walk walk to hold something to stand for a while to become the norm, of course, the most comfortable or lying down to rest!
intermittent claudication
Some people may say that this should be considered lumbar spinal stenosis and surgery is needed. In fact, it is not. Unilateral sciatica is very common, especially in patients with L4-5 lumbar disc herniation, which is very prone to this problem, and of course, it may be accompanied by scoliosis and long and short legs (pelvic tilting) at the same time.
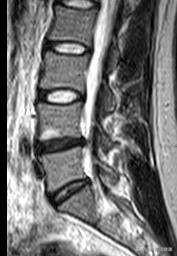
When this problem occurs, we should not rush to fix our eyes on the CT or MRI results, the herniated material may have lumbar spinal stenosis in the large report, however, it does not mean that spinal stenosis must cause symptoms, the herniated nucleus pulposus occupies the volume of the spinal canal, resulting in a reduction in the diameter of the spinal canal, which is degenerative in the sense that people with herniation may not be symptomatic.
herniated lumbar disk
Some people, due to lumbar disc herniation caused by walking 100 meters will be very painful, this is due to the activities of the lumbar intervertebral disc pressure will continue to increase, slowly for the nerve root of the irritation aggravation, induced pain, but this is part of the reason, even can be said that is not the main reason, the most important is the gluteus medius muscle syndrome.
gluteus medius syndrome (medicine)

For people with L4-5 disc herniation, there will be pain on the outside of the buttocks, long-term pain muscles will develop pain points, may press and irritate the nerves, inducing symptoms on the outside of the buttocks and legs, many people L4-5 disc herniation pain get better to a certain level and stop progressing, is because the problem of the buttocks did not pay attention to and deal with.
Gluteus medius syndrome, it is possible to lift the symptoms through self-massage, prepare a massage ball, put it between the hip pain point and the wall, to pain feel comfortable with the intensity of the pain to be carried out once a day, each time for about 5 minutes, with the massage of the pain point will gradually reduce, walking will be farther and farther.
Communicate positively
This typical performance, we must communicate with the doctor in a timely manner, to find out the core problem, do the appropriate treatment, must not miss the diagnosis and misdiagnosis, otherwise, all the efforts made will be in vain, if the long-term pain can not be improved, and do not be bedridden for a long period of time, which can easily lead to the occurrence of muscle atrophy.
Lumbar protrusion patients often encounter this situation, walking a period of intense after the pain in the waist and legs, continue to walk, the pain and numbness will be aggravated, had to stop to rest, and after a period of rest, the symptoms will be reduced again, and so on and so forth, not too injurious, but insulting is stronger, that is, it does not allow you to walk properly. This symptom is called intermittent claudication, also known as locomotor pain, let's see exactly what's going on.
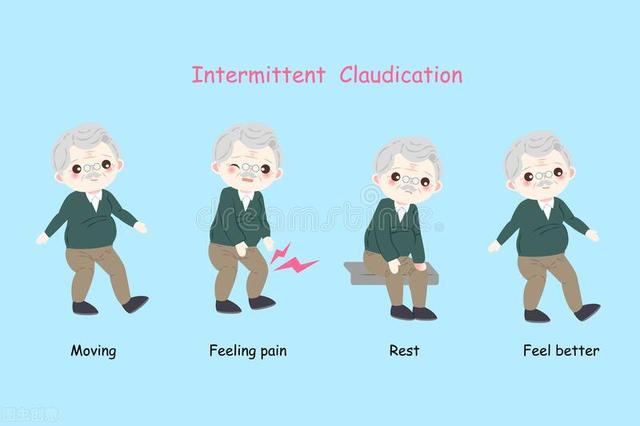
Intermittent claudication is a major symptom of lumbar disc herniation
The most typical symptom of lumbar disc herniation is low back and leg pain, which is also the most familiar symptom. Lumbar and leg pain is further divided into lumbago and leg pain, while leg pain is sciatica.
- 腰痛-Mostly stabbing pain, accompanied by numbness, soreness and swelling. Those with mild symptoms can continue to work, while those with severe symptoms have severe pain and often have to rest in bed. The pain is mainly in the lower back and lumbosacral region, mostly persistent pain, aggravated after exercise and relieved after rest, and aggravated after sneezing, coughing and straining to defecate.
- sciatica--Lumbar disc herniation leads to sciatic nerve root involvement, with pain radiating from the lumbosacral region, posterior gluteal region, posterior-lateral thighs, lateral calves to the heel or dorsum of the foot. Generally occurs in one side of the lower limbs, a small number of patients with central herniation can be radiating pain from both lower limbs, generally light on one side and heavy on the other.

The third major symptom is intermittent claudication as described in this article.The main reason why patients with lumbar protrusion develop intermittent claudication is secondary to spinal stenosis for the following reasons:
- When the herniated intervertebral disc compresses the nerve root and the volume of the spinal canal decreases, inflammatory reactions such as nerve root congestion and edema occur. When walking, due to increased venous return flow to the lower extremities, the obstructed vertebral venous plexus in the spinal canal gradually expands, aggravating the compression on the nerve root, causing hypoxia and thus the symptom of intermittent claudication.
- Neurogenic intermittent claudication can also be caused if the patient has a congenital bony tuberosity and a lumbar disc herniation, thickening of the ligamentum flavum, and connective tissue hyperplasia, resulting in compression injury to the cauda equina and spinal nerves.

In fact, intermittent claudication is the main feature of lumbar spinal stenosis, except that lumbar protrusion is prone to secondary spinal stenosis, especially in severe patients with bony encumbrances at the lateral posterior margin of the conus and the articular eminence, which makes it more likely to secondary lumbar spinal stenosis, resulting in intermittent claudication symptoms. Therefore, patients with lumbar protrusion should also consider whether there is a possibility of combined spinal stenosis after the emergence of intermittent claudication.
Patients with lumbar protrusion avoid intermittent claudication by actively treating the protrusion itself
In addition to the low back pain, sciatica and intermittent claudication mentioned above, the symptoms of lumbar protrusion also include numbness and abnormal sensation of the lower limbs, weakened or paralyzed muscles and cauda equina symptoms, etc. When the patient develops the suspected symptoms, he/she should seek medical treatment in time for early detection of the condition and active treatment.
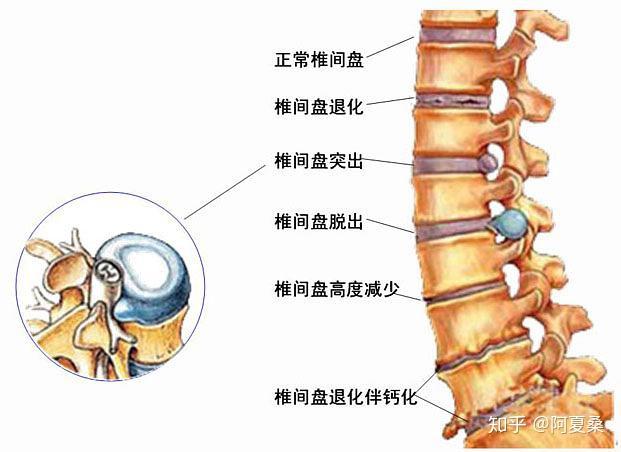
Patients with lumbar herniation will aggravate the symptoms of low back and leg pain due to the increase in walking distance. In the face of intermittent claudication, patients have to avoid walking long distances and rest autonomously every time they walk for a certain distance, so as to minimize the impact of intermittent claudication on pain. Of course, to completely reduce intermittent claudication, patients still need to actively treat lumbar disc herniation.
Treatment varies at different times of lumbar protrusion:
- Treatment of the acute phase of lumbar protrusion--The acute stage is mainly manifested as nerve root irritation edema, and the treatment in this stage is also based on the principles of dehydration and anti-inflammation, stabilization of joints and correction of mechanical imbalance. Treatment includes bed rest, dehydration treatment, anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication, closed treatment, lumbar girdle protection, traction treatment, local physiotherapy, acupuncture treatment and so on.
- Treatment of the chronic phase of lumbar protrusion--Patients in the chronic stage have their symptoms relieved and enter the period of repairing nerve and soft tissue injuries. The focus of treatment in this stage lies in the adjustment of imbalanced joints and the restoration of joint function training. Treatment includes manipulation, self-weighted traction, orthopedic shoe therapy, physical therapy, nutritional nerve therapy, and rehabilitation exercises.
- Treatment of lumbar protrusion during rehabilitation--When the patient recovers further, lives a fully self-care life and stabilizes his/her basic condition, he/she enters the rehabilitation period of his/her condition. During this period, patients basically do not need medical interventions, and mainly recover step by step through daily exercise management and posture management, with the specific exercise process carried out in a safe and orderly manner according to the patient's tolerance.

It is important for patients with lumbar protrusion to develop good living habits to achieve a good recovery, which mainly include:
- Avoid bad posture--Patients should pay attention to maintaining a healthy posture when standing and sitting at work. When standing, the hip and knee joints are slightly flexed, the abdomen is naturally contracted, and the bilateral buttock muscles are contracted inward so that the pelvis is tilted forward and the lumbar spine is straightened. Adjust the height of the seat when sitting, so that both knees can freely flex and extend, the upper lumbar spine and backrest chair close to keep the spine straight. In short, to avoid prolonged bending, stooping and weight-bearing and other bad posture.
- Rational Exercise Labor-Engaged in physical labor, we should try to do a good job of labor protection, improve working conditions, do not stay in a fixed position for a long time, especially long hours of stooping work or weight-bearing work, labor time is not too long. Engaged in physical exercise, to avoid too strenuous exercise, try to engage in low intensity, sustainable aerobic exercise, so as not to cause acute trauma or chronic strain. Daily attention should also be paid to the waist to keep warm, to avoid the stimulation of cold and damp.
- Change bad habits-Life if there is smoking, drinking alcohol, drinking a lot of strong tea and coffee drinks and other behaviors, is also not conducive to the health of the lumbar spine, to pay attention to change these bad habits, especially smoking, on the one hand, can make the blood vessel contraction, blood vessel wall ischemia and hypoxia, accelerating the degeneration of the intervertebral discs, on the other hand, can cause coughing, causing the pressure within the discs to rise, promoting Intervertebral disc degeneration. Therefore, patients with lumbar disc herniation should quit smoking.

Intermittent claudication is not unique to lumbar synostosis, so be on the lookout for both of the following conditions
Intermittent claudication is not a symptom specific to lumbar disc herniation. When intermittent claudication occurs, in addition to being wary of lumbar disc herniation, beware of other conditions, especially the following two.
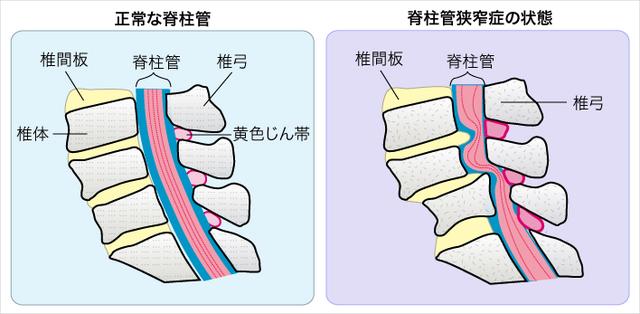
01 / Vertebral stenosis
As already mentioned, intermittent claudication is a common symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis, and for this reason it is important to be alert to spinal stenosis. Lumbar spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spinal canal, nerve root canal, and intervertebral foramina are narrowed for a variety of reasons and the spinal cord, cauda equina, or spinal nerve roots are compressed in the corresponding areas. In the clinical manifestations there are also symptoms such as lower back pain, compression of the cauda equina or lumbar nerve roots, and neurogenic intermittent claudication. Lumbar spinal stenosis is also likely to occur secondary to lumbar disc herniation in moderate or severe periods.
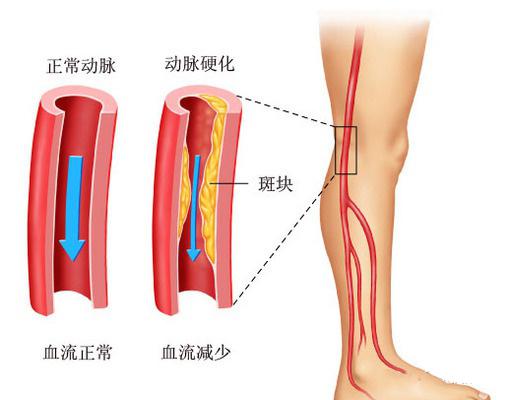
02 / Lower extremity arterial occlusion
There is another cause of intermittent claudication, that is, lower limb arterial occlusive disease, the full name is lower limb atherosclerosis occlusive disease, because the plaque attached to the lower limb arterial wall, caused by lower limb arterial stenosis occlusion, arteries gradually become narrower, slow down the speed of blood flow, blood flow reduction, chronic ischemia of the limbs and cause a series of symptoms. Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus and smokers are prone to this lesion, which leads to lower extremity cold, walking fatigue, intermittent claudication, rest pain and even ulcer gangrene and other symptoms.
To summarize, intermittent claudication is one of the main symptoms of lumbar disc herniation, but lumbar protrusion patients with symptoms, but also to check whether there are other diseases, especially whether the combination of lumbar spinal stenosis. And once intermittent claudication, patients should be alert to whether the condition has developed to moderate or severe, and at the same time to self-check whether to adhere to standardized treatment and good life care, do not do a good job of aspects to be corrected in a timely manner.
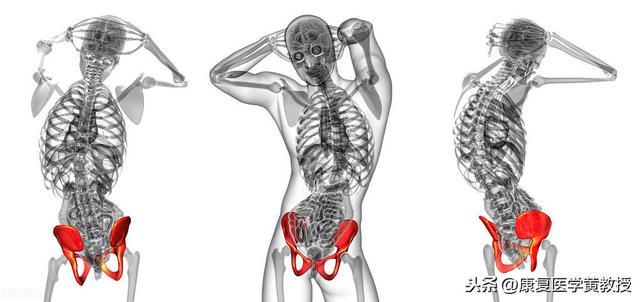
Clinically we call it Intermittent claudication, which is one of the symptoms of bulging discs compressing the nerves, so to understand this symptom or what to do in this situation, we must first talk about the structure and function of the disc.
Intervertebral discs.
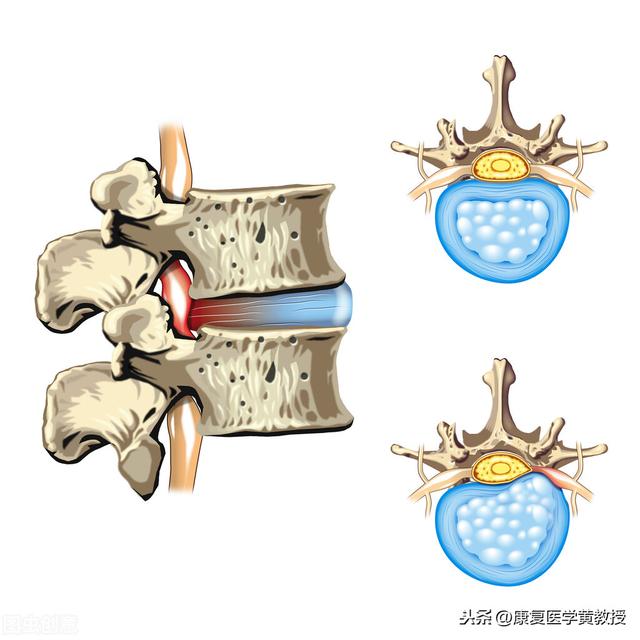
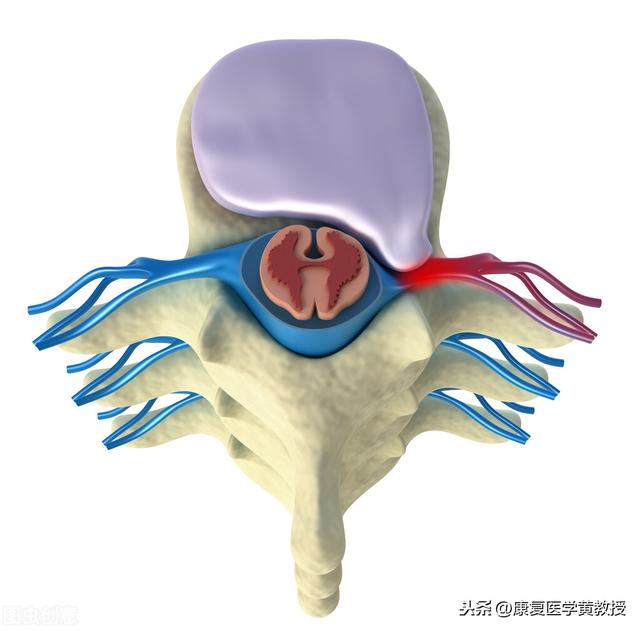
Humans are the only mammals on earth that walk on two feet, so in order to counteract the force of gravity and the reaction force of the ground, the human body has developed a very delicate shock absorption system, and the intervertebral discs are one of them. The human spine, excluding the sacrum, has 24 vertebrae, which are separated from each other by intervertebral discs, except for Cervical 1 and Cervical 2, which have no intervertebral discs, there are 23 intervertebral discs in total. The intervertebral discs may seem to be independent in structure, but they are connected to each other, and thus to Prof. Hwang, the spine is a single entity that cannot be separated.
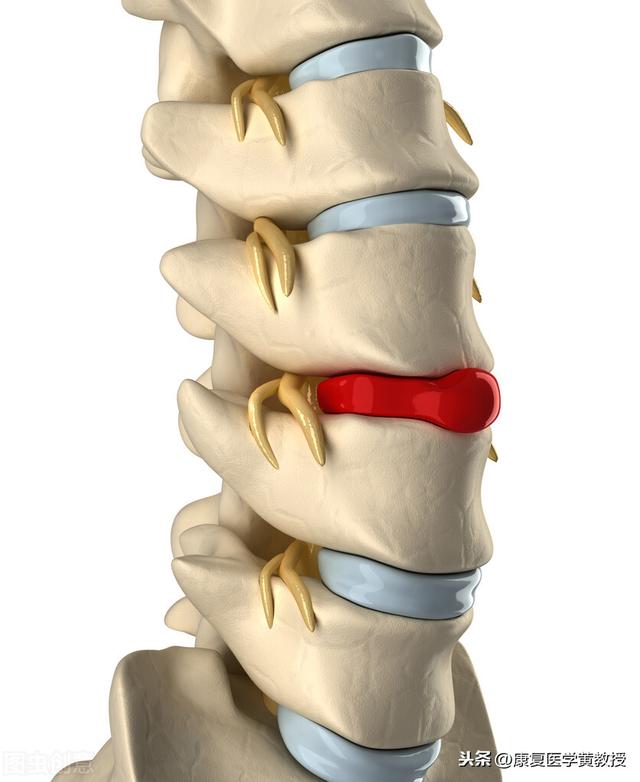
The intervertebral disc is a disc-like structure with the three most important components being the nucleus pulposus in the center, the surrounding annulus fibrosus, and the surrounding fluid (90% water), and an end plate at the top and bottom of the disc to separate the vertebral bodies. The intervertebral disc does not have nerve innervation and blood circulation, therefore, the disc itself does not have the ability to move and does not feel pain after being damaged, but its most important role is to cushion and reduce pressure and pre-deformation ability, which can effectively protect the central nervous system of the brain, and to be more rigorous, in fact, the structure of the human body has evolved in order to be able to survive, and therefore it is very important to protect the brain's life center. Therefore, it is very important to protect the life center of the brain.
Decompression.
Why does indirect claudication occur after a bulging disc? Because we are walking upright, most of the body pressure will occur in the lumbar 4-5 and lumbar 5 sacral 1 disc, and in addition to the nucleus pulposus, most of the intervertebral discs are water, with the walking posture is different, the center of gravity changes, the pain caused by bulging discs, resulting in uneven tension, or because of the long-term pelvic position is not correct (anterior and posterior tilt lateral tilt or rotate), the disc in the water pressure will constantly change the location of the nucleus pulposus, if the nucleus pulposus rushes to the posterior oblique, it is very likely that claudication occurs indirectly after a bulging disc. If the nucleus pulposus is directed to the posterior oblique direction, it is very likely to press on the nerves and cause soreness and weakness. However, it is very likely that after stopping for a rest and moving the legs to change the posture, the symptoms will be relieved and you can continue to walk.
The most important thing to do at this point is to decompress the intervertebral discs, and the ways of decompression can be distinguished as followsPassive vs. active stress reduction

Passive Decompression.
1: bed rest: we lie down in the position of the lowest disc pressure, conducive to the nucleus pulposus back to the middle of the position, remember to put a pillow under the knee joint, conducive to maintaining the physiological curvature of the lumbar spine
2. Mechanical traction: Calculating a reasonable weight based on body weight, the space between the vertebrae will be pulled apart, which is favorable for decompression of the discs.
3: myofascial manipulation relaxation: most of the causes of disc bulging, is from long-term myofascial asymmetry and imbalance, so passive manipulation before, there must be an accurate assessment of the work, definitely not the massage of the muscles of the lumbar region, many of the causes of bulging discs are not in the lumbar.
4: Lumbar Wear: When you need to walk upright, you can wear moderate pressure lumbar protection, which can not only share the pressure of the intervertebral discs, but also relax the muscles because of spasm.

Active decompression.
1: Re-establish correct breathing patterns. Almost 80% of patients with low back pain have incorrect breathing patterns, and professional instruction on how to initiate abdominal breathing is the first step in active decompression.

2: Weight control: Starting to reduce the burden on the body is a job that can be done from daily life operations, and controlling the diet is the first step.
3:Learning simple stretching exercises: Most of the discs are imbalance of muscle tone, through the guidance of professionals, stretching exercises can be taken as a homework from daily life.

4:Posture correction (personalized instruction)
5:Neuromuscular activation (personalized instruction)
6: Re-establishment of correct intra-abdominal pressure (personalized instruction)
7, Functional training (personalized instruction)
A bulging disk is not a disease.
Most clinicians are unable to answer how long it takes to recover from a bulging disc, because for generalized illnesses, there should be a reference course of treatment through medication or injections, such as the flu. However, bulging discs vary from person to person, and each person has different symptoms and causes, so how can one set a timetable for treatment. According to Prof. Wong, a bulging disc is a spinal dysfunction, and the dysfunction can have multiple causes, such as anterior pelvic tilt, changes in the physiological curvature, and the muscles producing the inferior cruciate syndrome, all of which need to be re-established, so doctors are not sure how long it will take to get well.
Disc problems, or we should say spine protection and maintenance, should start from our daily life, just like high blood pressure and diabetes, regular blood pressure and insulin every day, we need to move the spine every day, give mobility training and muscle training, so that we can heal the bulging disc and have a healthy spine. Professor Huang specializes in treating bulging discs, welcome to follow @ProfessorHuangRehabilitationMedicine.

Traction therapy for lumbar disc herniation is a method to achieve therapeutic purpose through special traction device by applying the relationship between action force and reaction force in mechanics. Fixation and braking of the lumbar region: When traction is applied, the lumbar region is in a relatively fixed state under the equilibrium of action force and reaction force, and the range and amplitude of lumbar movement are further restricted compared with bed rest and wearing a waist cuff, so as to reduce or eliminate local inflammatory reactions such as congestion, oozing, edema, and so on. Relaxation of lumbar back muscles: lumbar disc herniation, due to spinal nerve compression or stimulation, is often accompanied by spasm of the lumbar back muscles, which not only leads to lumbar pain symptoms, but also constitutes the lumbar vertebrae of the incorrect line. Traction therapy can gradually relax the lumbar back muscles and release the muscle spasm. Restoring the normal alignment of the lumbar spine: If the patient's lumbar spine is placed in a physiologic curve during traction, the malalignment can be gradually restored to normal with the extension of the traction period. Improve the relationship between the herniated material and the nerves: for patients with mild or early lumbar disc herniation, traction therapy can gradually open up the intervertebral space, which is conducive to the reduction of the herniated material. For patients with relatively long course of the disease, traction can be combined with the adhesive tissue and contracture of the ligament and joint capsule to widen the intervertebral space accordingly, and the narrow intervertebral foramen on both sides can be opened at the same time, which can alleviate or eliminate the oppression and irritation to the nerve root, and have a better effect on the reduction of numbness and pain in the lower limbs.
This situation is called intermittent claudication, because the lumbar disc herniation in the development of a certain degree will be extruded to the spinal canal, extrusion to the spinal canal typical symptom is to walk a two hundred rest for a while in order to relieve!
The question itself is a bit problematic. A disc in the middle of treatment? Meaning it wasn't like this before and it came up during treatment? Or was this the case before and is now being treated as a herniated disc.
Walking 100 meters requires a break and can be done again, symptomatically it is interstitial claudication , usually preferring to squat or sit down to rest. The most common is spinal stenosis, either bony spinal stenosis or spinal stenosis secondary to a herniated disc. If walking is only 100 meters and the diagnosis is supported on imaging, surgery should be considered.
Do you want to get well soon? Then take lots of rest and breaks, lie down as much as you can to give your back the process of repairing itself, and walk away from your illness to recuperate. [Bares teeth]
Walking for a long time lumbar pain, after rest will not hurt, may be because of lumbar muscle strain, lumbar trauma disease caused by the activity of the lumbar pain, rest pain symptoms to reduce the symptoms.
It may also be caused by lumbar spinal stenosis, the central spinal stenosis squeezes the spinal cord will affect the blood supply to the spinal cord, when walking the spinal cord to increase the demand for blood can cause ischemia of the spinal cord, the occurrence of lumbar pain, lumbar spinal flexion can make the volume of the spinal canal increase, at the same time, the spinal cord blood demand decreases the pain can be disappeared.
It may also be caused by lumbar disc herniation, when walking lumbar disc pressure is relatively large, the nucleus pulposus protrudes, the annulus fibrosus breaks, causing pain in the lumbar region, resting so that the pressure on the lumbar discs to reduce, the pain symptoms will also disappear.
After more than 40 years of being an old Chinese medicine practitioner, I've seen this symptom too many times, medically this is calledintermittent claudication, a common symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis, occurs after walking a few hundred metersWeakness, numbness, accompanied by pain in the lower extremitiesThe pain is so severe that one can continue to walk after taking a break, and then the pain comes back, and then one can take a break and walk again, and the cycle repeats itself. So people are not tired, the heart is tired, and even negative psychology, think there is no salvation, can not even walk. In fact, there is not much hopelessness, many patients can be relieved through the treatment.
I. Conservative treatment
1. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) techniques:The use of manipulation on the epidermis of the body, along the muscle texture, dredge the meridians and collaterals, the tendon rectification, improve blood circulation, improve metabolism, expand the inner volume of the spinal canal, relief of pain, and actively cooperate with the doctor's treatment program, and can even achieve healing.
2、Hot compresses of traditional Chinese medicine: Hot compresses make the capillaries in the waist open, and the traditional Chinese medicine penetrates from the epidermis of the body to achieve the therapeutic effect. We use traditional Chinese medicine mainly some herbs that activate blood circulation and eliminate blood stasis to promote blood circulation and activate the function of nerve cells, which is the safest treatment, easy to relieve the pain, and can even be cured in a long period of time and not easy to recur.
3. Acupuncture treatment: Pain is alleviated by stimulating specific points. After the therapeutic effect of the acupuncture process, it is also effective in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Still, acupuncture should be done in regular hospitals and outpatient clinics.
ii. medication.Nowadays, the main medications used to treat lumbar spinal stenosis are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve pain.
III. Surgical treatment:Surgery is usually chosen as a last resort when conservative treatments do not work. Surgery is generally not recommended because of the higher risks and slower recovery.
Fourth, proper physical exercise:Do more low back muscle exercises to strengthen your muscles and protect your low back. For example, Xiaofei Yan.

swallowlet
There is a clinical concept of "intermittent claudication", this kind of patients in walking a distance (from dozens to hundreds of meters), will be in the lower back or the affected side of the lower limbs of the pain, numbness, the need to stop walking to rest, generally take a squatting position or sitting position to rest for a while can be relieved, but if you continue to walk after the pain and discomfort will occur again. However, if you continue to walk, the pain and discomfort will reappear.
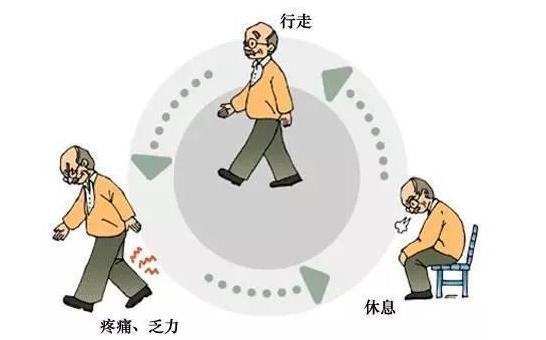
Why is this happening?
The main reason for the patient's intermittent claudication should be the presence of lumbar spinal stenosis.
During walking, the obstructed venous plexus in the spinal canal will gradually expand, which is proportional to the walking time and distance, when it expands to a certain extent, it will make the nerve overpressure, which will cause the nerve root to be ischemic and hypoxic, so the patient will have more obvious discomfort, and need to rest to relieve.
If not treated effectively, the consequences are more serious!
Intermittent claudication has a great impact on the lower limbs, if not controlled at an early stage, it will make the lower limbs ischemia more and more serious, occurring at a later stage, even if the rest does not move, but also let the foot to appear "resting pain", and if a foot gangrene, it may also need to be amputated.

Intermittent claudication should not be treated blindly!
Intermittent claudication can be caused by a variety of reasons, such as lumbar disc herniation, inflammation of the femoral head, spinal nerve injury, etc. The treatment options for intermittent claudication caused by these reasons are fundamentally different and cannot be generalized.
The exercise rehabilitation promoted by some people is only suitable for some patients, and only in the early stage. For some cases where the diagnosis is unknown, blindly performing certain intensity of exercise not only can't help the recovery of the condition, but may aggravate the symptoms, so caution is needed.

I hope my science helps!
If there's anything you don't understand, comment and private message me!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.
