How are glucose-lowering medications safer to take?
How are glucose-lowering medications safer to take?
How to take glucose-lowering drugs more safely
So far, diabetes can not be cured, once the disease, patients will need long-term or even lifelong medication. Safe use of medication has naturally become a great concern for the majority of diabetic friends. Adverse drug reactions to this issue, patients can not be abused at will, we must weigh the pros and cons, careful selection.
Before we learn how to take glucose-lowering medications safely, let's take a look at the classification of oral hypoglycemic agents and their mechanism of action.
As the saying goes, "medicines have three poisons", there are certain adverse reactions to any drug, and hypoglycemic drugs are no exception. Oral hypoglycemic drugs commonly used in clinical practice have the following major categories:
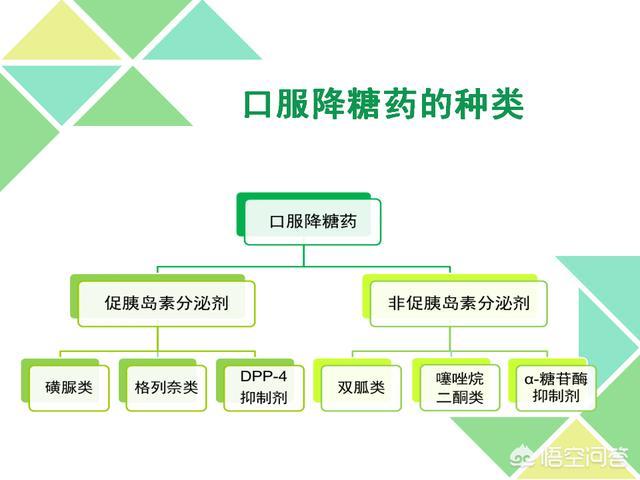
Mechanism of action of oral hypoglycemic agents:
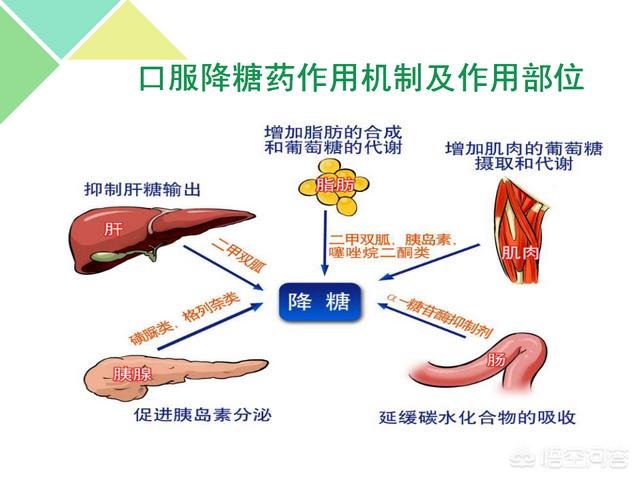
Oral hypoglycemic drugs are generally used for the treatment of the following conditions:
A. For the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with unsatisfactory glycemic control with dietary control and exercise therapy.
B. Insulin therapy is indicated when type 2 diabetes mellitus is
1. Ketoacidosis
2. Hypertonic non-ketotic acidosis
3. Combined infection, trauma or major surgery
4. Pregnancy.
In view of the classification and mechanism of action of oral hypoglycemic drugs, the following is a brief discussion of the efficacy, side effects and methods of taking various types of oral hypoglycemic drugs. By taking the appropriate hypoglycemic drugs according to your condition, you will be able to maximize the efficacy of the drugs, reduce their side effects, and achieve the goal of taking the drugs safely.
磺脲类

How to take sulfonylureas
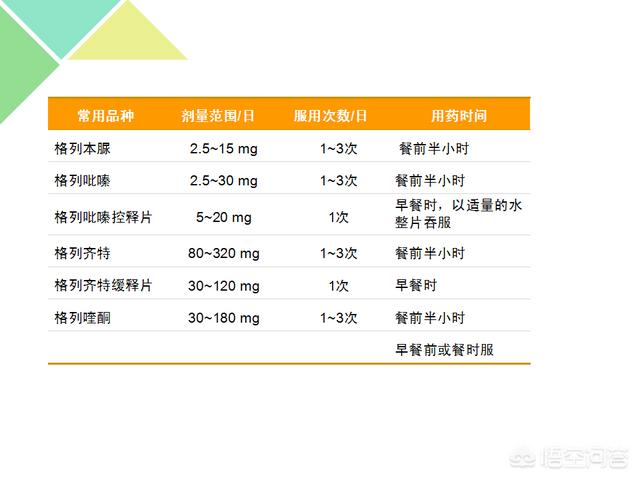
Precautions for taking sulfonylureas
1. Take the dosage as directed by your doctor, and monitor and record your blood glucose during the medication.
2. Always keep candy on hand in case of hypoglycemia
3. If hypoglycemia frequently occurs at the same time every day and lasts for more than 3 days, and the effects of diet and exercise are ruled out, medical attention should be sought promptly
Glargine analog

How to take Glargine-based medications
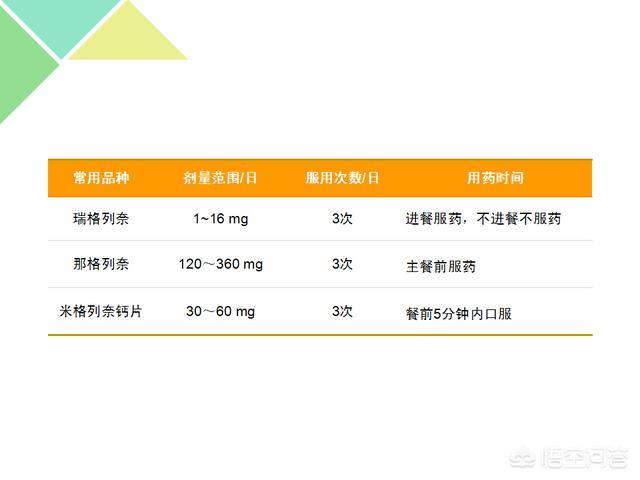
Glargine-based medication dosing precautions
1. Please take the dosage according to the doctor's instruction, and do blood glucose monitoring and record during the medication.
2. Always keep candy on hand in case of hypoglycemia
3. If hypoglycemia frequently occurs at the same time every day, and the effects of diet and exercise are excluded, and lasts for more than 3 days, consult a doctor promptly
DPP-4 inhibitor

DPP-4 inhibitor dosing regimen
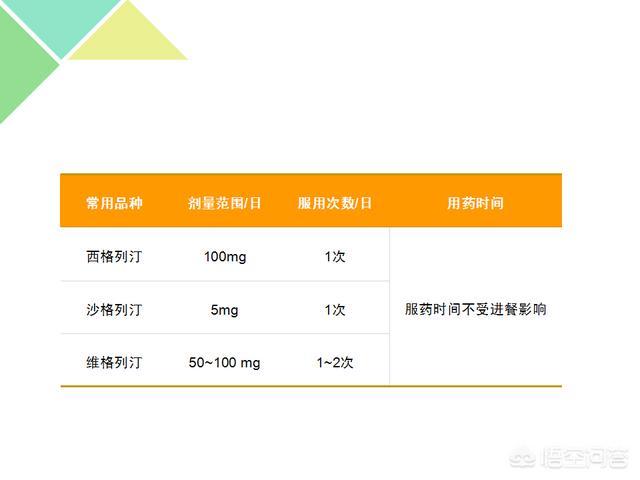
DPP-4 Inhibitor Medication Precautions
1. Take your medication as regularly as possible
2. Blood glucose should be monitored and recorded properly during the medication
Biguanides (star drugs)

Metformin dosing regimen
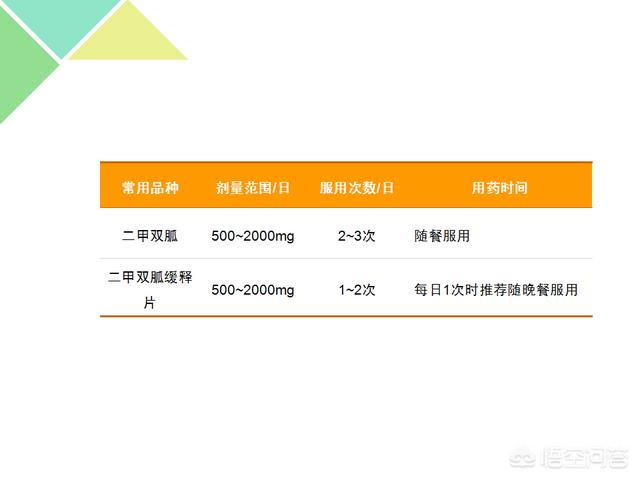
Precautions for taking biguanide
1. Please take the dosage according to the doctor's instruction, do blood glucose monitoring and record during the medication, and limit alcohol consumption
2. Gastrointestinal reactions may be reduced by starting with small doses; enteric-coated tablets reduce gastrointestinal reactions
3. Take medication at regular times and intervals throughout the day as much as possible
Thiazolidinediones

Thiazolidinediones dosing regimen
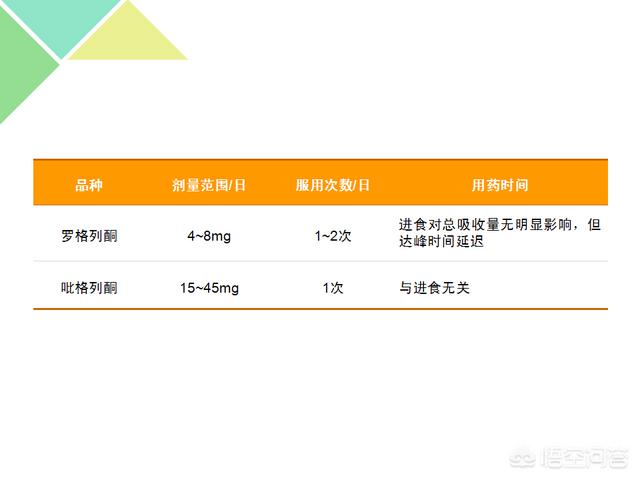
Thiazolidinediones Dosing Precautions
1. Please take the dosage strictly according to the doctor's instruction, and do blood glucose monitoring and record during the medication.
2. Take your medication as regularly as possible
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors

Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor dosing regimen
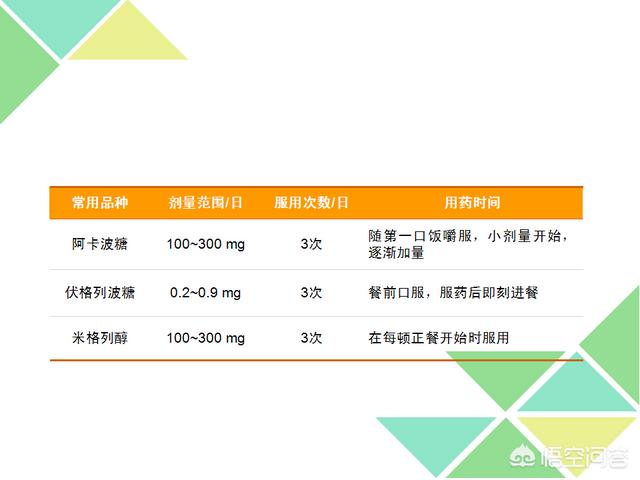
Precautions for taking alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
1. Please take the dosage according to the doctor's instructions, and do a good job of blood glucose monitoring and recording during the medication.
2. Start with a small dose and gradually increase the dose to help reduce gastrointestinal reactions
3. Take medication at a relatively regular time each day
In general, take the following precautions with oral hypoglycemic drugs:
1. Before starting drug therapy, liver and kidney functions, blood lipids, electrocardiogram, etc. should be checked to understand the functional status of the patient's organs and to guide the scientific use of drugs.
2. While taking the medication, you still need to adhere to diet and exercise therapy.
3, follow the doctor's instructions according to the dose of medication, correctly grasp the time of different drugs, blood glucose monitoring and record during the medication, in order to understand and evaluate the role of the drug for the individual, so as to facilitate the doctor according to the fluctuation of blood glucose on the adjustment of the drug.
4, each oral medication has different mechanism of action, applicability and side effects, there is no "best" medication or treatment program, diabetic patients may need to take more than one drug, or take medication and insulin injection at the same time, can not arbitrarily stop taking medication, change the medication and dosage, so as not to cause fluctuations in blood glucose.
5, familiar with the indications and contraindications of various types of hypoglycemic drugs, rational choice of drugs. Such as chronic hypoxia, hepatic and renal insufficiency, severe infections, severe anemia, as well as the imaging test patients avoid the use of biguanide; cardiac failure, edema, active liver disease and severe osteoporosis patients avoid insulin sensitizer; chronic enteritis, diarrhea, abdominal surgery recovery and hernia patients avoid the use of α-glucosidase inhibitors; pregnant women in addition to biguanide, all other types of drugs should be prohibited in principle.
6. If you go out to eat, please bring your hypoglycemic medication with you and try not to "take a refill" after the meal.
7, must be under the guidance of the doctor strictly according to the doctor's instructions, do not self-selected drugs or in order to pursue rapid results and blindly increase the dose of drugs. In the process of medication, regular monitoring of blood glucose and liver and kidney function and other indicators.
Please follow the doctor's instructions, in addition to close monitoring of blood glucose, regular diet, control blood glucose standard and stable.
I am also a diabetic. More than ten years of experience tells me that the medicine must be taken in accordance with the doctor's advice. Because diabetes medicine has a characteristic, more than the lowering of sugar over, less than the purpose can not be achieved. Another depends on how to serve (because most of them are taken before meals, not according to the requirements can not achieve good results). Diabetes is not terrible, I over ten years over, but must respect the doctor's advice, regular, quantitative medication. You should also control your diet!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.