Isn't gestational diabetes scary?
Isn't gestational diabetes scary? 
Moms-to-be need to know that gestational diabetes can be dangerous to your health, can cause macrosomia, preterm labor, etc., and the chances of the baby being born with hyperglycemia are also increased! It is important for mothers-to-be to be aware of gestational diabetes and to take precautions to prevent it.
Did you know these misconceptions about gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is both a type of diabetes and a "special product" of this particular period of pregnancy, and people who don't know about it often have various misconceptions about it.
Thin people don't get Haemoglobin?
Many mothers-to-be may think that most of the diabetic patients are related to obesity, as long as they are not fat, and can control their weight during pregnancy, they do not have to worry about blood sugar problems, in fact, not. Gestational diabetes is caused by progesterone-induced metabolic disorders caused by elevated blood glucose, so thin moms-to-be may also have abnormal blood glucose during pregnancy.
If you don't eat sugar, you won't get Haemoglobin?
In a way, that's true. However, it is important to realize that when you are pregnant, 50% to 60% of the total body's daily caloric needs are provided by sugar, which can be said to be the body's main source of energy. However, care should be taken to limit your intake of added sugar to no more than 50 grams per day, preferably limited to 25 grams.
Added sugars are sugars or syrups added to food or beverages, including sucrose (white, brown, granulated), dextrose, fruit, and various syrups. Excessive intake of added sugar can increase the risk of obesity, diabetes and other diseases.
Mothers-to-be who are obese, older, have a family history of diabetes, or have delivered a baby weighing more than 4 kilograms are at high risk for developing gestational diabetes.
So what can you do to prevent gestational diabetes?
1 Reasonable diet
- Eat small, frequent and regular meals, with a mix of coarse and fine;
- Moderate amounts of protein, not too much fat;
- Low GI foods are recommended. Usually GI values below 55 are called low GI foods. Foods with a GI value of 40 or less are generally safe for people with diabetes. The GI values of various types of food can be found in the table below:
2 Exercise in moderation
It is recommended that pregnant mothers adhere to half an hour of aerobic exercise every day, for example, brisk walking, pregnant women yoga, etc..
3 Reasonable weight control
Ensure that you do not gain more than 1 kg per week after the middle of pregnancy. If you gain more than 1kg with proper diet and exercise, you should consult your doctor.
4 Reducing Stress
Unresolved stress increases stress hormones, which raise blood sugar. So when a mom-to-be is emotionally unstable, try breathing deeply and relaxing, or listen to relaxing music to soothe your mood.
Gestational diabetes is on the rise in China year by year, so it is important for mothers-to-be to do a good job of maternity check during pregnancy to help mothers-to-be find problems in a timely manner, such as the discovery of abnormalities need to be treated under the guidance of the doctor as soon as possible.
All in all, if a mom-to-be wants to keep gestational diabetes away from herself, "keep your mouth shut and your legs open" is a must. Even if you become a "sugar mom" by accident, as long as you catch it in time, you can usually control your blood sugar range by changing your diet at any stage of pregnancy.
Welcome to follow @mezanewsletter and talk to us about parenting scientifically~!
Horrible to say the least. The incidence of this disease is not low. As long as the diet is well regulated and exercise is adjusted. Generally not a big problem.
There is a blood sugar screening during pregnancy. The screening is usually done during the period of 24-28 weeks. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed if the blood sugar is higher than 5.1 before a meal, or higher than 10 one hour after a meal and higher than 8.5 two hours after a meal.
Then there was no such thing before, and it didn't seem to have any effect. Why is this test being done now. The main reason is that studies have found that gestational diabetes is very bad for the body and the fetus.
May cause miscarriage, stillbirth, premature labor, etc. Neonatal effects such as low blood sugar, macrosomia, poor physical development and various other problems.

Isn't it very serious to have so many problems, and is it going to have a big impact on the baby.
This is not necessarily the case. Because these serious harms are based on a foundation of poor blood sugar control that is consistently higher or fluctuating high and low. That's the foundation.
So we just need to keep our blood sugar under control and not let him be in a high state, so naturally no serious problems will occur. So far no one has heard that whoever it was died of diabetes.
So looking at it this way, it can be said in layman's terms that diabetes does not harm the organism, the harm comes mainly from the various complications caused by diabetes, hypoglycemic reactions, diabetic ketosis, diabetic foot and so on.
The same goes for gestational diabetes. As long as we keep the blood sugar under control, do not let it rise and do not fluctuate. Then the effect of glucose tolerance cake in pregnancy on the body is almost zero.
Gestational diabetes is more of a diagnostic significance, a constant wake-up call that we need to watch our diet, exercise. And be careful to monitor your blood sugar. Compare your diet with your baby's development. Don't let your diet stunt your baby's growth and development. So there is no need to cause emotional ups and downs, which is not good for the fetus.
Lai Ming (Director of Nutrition Department, Affiliated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southwest Medical University, 10 years working in the nutrition department of a tertiary hospital, proficient in: diet and weight loss, nutrition during pregnancy, postpartum nutrition, supplemental food for infants and young children to add, nutritional conditioning for chronic diseases, and the rest of the various types of disease nutrition. (Headline: Nutritionist Lai Ming)
Scary? Depends on how you approach gestational diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes isn't a scary thing if you're concerned about it and are actively controlling your blood sugar;
- If you are indifferent to gestational diabetes and still do what I do that would be a very scary thing.

This is because the degree of risk of gestational diabetes to the mother and child is very closely related to the condition of the diabetes and the glycemic control during pregnancy.
The terror stems from the effects of gestational diabetes on pregnant women:
- Hyperglycemia can cause abnormal embryonic development or even death, with a miscarriage rate of 15-30%;
- The likelihood of developing gestational hypertension was 2.4 times higher than in non-diabetic pregnant women;
- There is a 10% more chance of having more amniotic fluid;
- Increased incidence of macrosomia;
- Increased chance of obstructed labor, birth canal injuries, and surgical delivery;
- Prolonged labor predisposes to postpartum hemorrhage;
- Prone to ketoacidosis;
- The recurrence rate at re-pregnancy is as high as 33-69%.

The terror stems from the effects on the fetus:
- The incidence of macrosomia is as high as 25-42%;
- The incidence of fetal growth restriction was 21%;
- Miscarriages and premature births;
- Fetal malformations, etc.
The terror also stems from the effects on newborns:
- Increased incidence of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome;
- Neonatal hypoglycemia, etc.

As long as you don't panic once you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes during pregnancy, most gestational diabetes can be brought under satisfactory glycemic control with a series of medical nutritional treatments and exercise.
【Author Introduction】Ding Huai Lian/Trainee of Mr. Wang Xing Guo's first special training class/Chief Lecturer of Heng Cuisine College/Kindergarten Health Doctor/AiYi Nutrition Director
Currently, more than 199 million women worldwide have diabetes, and 2.1 million women die from diabetes each year. One in seven deliveries is affected by gestational diabetes, and half of all gestational hyperglycemia occurs in women under 30 years old. A few days ago, this reporter traveled to the Hospital of Integrative Medicine of Southern Medical University and interviewed Han Yajuan, deputy chief physician of the Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, to understand the real face of gestational diabetes.
Glucose tolerance test for pregnant women
According to Han Yajuan, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is diabetes mellitus that occurs or is detected for the first time during pregnancy. She pointed out that hyperglycemia may cause increased incidence of miscarriage, preterm delivery, infection, excessive amniotic fluid, obstructed labor, and birth canal injury in mothers; and serious harm to fetuses such as malformations, perinatal deaths, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, respiratory distress, hyperbilirubinemia, and so on.
"The prevalence of gestational diabetes is 16 to 17 percent, which is more common on a daily basis, so we recommend that all moms-to-be have an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) at 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy." Han Yajuan said the test is performed in three separate sessions by drawing blood, and gestational diabetes is diagnosed if fasting blood glucose is ≥5.1 mmol/L, OGTT 1-hour blood glucose is ≥10.0 mmol/L, and OGTT 2-hour is ≥8.5 mmol/L.
Most return to normal blood sugar after delivery
Han Yajuan revealed that the occurrence of the disease is mainly related to the glucagon hormone secreted by the placenta during the middle and late stages of pregnancy, which leads to high blood sugar. "Most pregnant women can return to normal blood sugar again after giving birth, because the delivery of the placenta, the hormone's influence on the body declines or even disappears."
Han reminds that all pregnant women with gestational diabetes need to be retested with an oral glucose tolerance test six to 12 weeks postpartum to assess whether they have developed type 2 diabetes. "Even if you don't develop type 2 diabetes, you need to be retested every three years for the rest of your life."
85% can normalize blood sugar with diet and exercise
"85 percent of gestational diabetes can be controlled simply through diet and exercise to bring blood sugar to normal levels." Moms-to-be don't need to worry too much, Han Yajuan said.
{!-- PGC_VIDEO:{'thumb_height': 360, 'thumb_url': '5c460005220cefd2c7c6', 'vname': '', 'vid': '98df818fb76644d09fe414a697adb23d', 'thumb_width': 640, 'src_thumb_uri': '5c460005220cefd2c7c6', 'sp': 'toutiao', 'update_thumb_type': 1, 'vposter': 'http://p1.toutiaoimg.com/origin/5c460005220cefd2c7c6', 'video_size': {'high': {'duration': 164.8, 'h': 480, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 854, 'file_size': 4959582}, 'ultra': {'duration': 164.8, 'h': 720, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 1280, 'file_size': 9663437}, 'normal': {'duration': 164.8, 'h': 360, 'subjective_score': 0, 'w': 640, 'file_size': 3751221}}, 'duration': 164.8, 'file_sign': '8c90387dd3c72bd01cf73ef8973c13fb', 'md5': '8c90387dd3c72bd01cf73ef8973c13fb', 'vu': '98df818fb76644d09fe414a697adb23d'} --}
[Column introduction]
"The topics you care about are answered by the authoritative experts of the three-A hospitals" - "Health Intelligence Bureau" is a brand column of big health science and technology exclusively produced by Guangming.com, which was founded in June 2016, and won the "Healthy China" Innovative Communication Column Award from the National Health and Family Planning Commission, and was invited to become a member of the "China Medical Self-Media Alliance" of the National Health and Family Planning Commission. Founded in June 2016, it has won the award of "Healthy China" Innovative Communication Column Award from the National Health and Family Planning Commission, and has been invited to become a member of "China Medical Self-media Alliance" of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, and a branded column of Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Stereoscopic Communication Alliance.
[Guest] Ma Liangkun, Chief Physician of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, and mother of a second child at an advanced age.
【Topic of this issue】How to prevent gestational diabetes
Not horrible! I was in our province's best women's and children's hospital, was also gestational diabetes, the professor just said don't eat fruit, even hypoglycemic drugs are not prescribed, there is no blood glucose monitoring, after giving birth to the child doctor gave an insulin infusion, asked what need to pay attention to, the answer: do not need to be just a great rate of diabetes in the future, my baby is now 9 years old, and after giving birth to the child also did not monitor the blood glucose last October! Physical examination found high blood sugar, estimated to be high for 2 years too much trouble there are 8 years without a physical examination, and now have not gone to the endocrinology department to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes, not so scary, just a chronic disease, there are 20 years old diabetic patients in the area, as long as the control of blood glucose, there will not be complications, the long-term survival of the general as high blood pressure; with the old sugar friends to take the advice: do not eat fried food, foods containing sucrose; less starch-heavy The old sugar friend advice: do not eat fried food, food containing sucrose; eat less starch-heavy vegetables, fruits with high sugar content, processed foods, animal accounts, 4 mouth vegetables and a mouthful of meat, control your mouth and open your legs. My blood glucose indicators back then is not estimated to be a lot higher, you can find a good obstetrics and gynecology hospital professors to take another look; the level of doctors in small hospitals is not very high to make a fuss about the doctors in large hospitals to see a lot of really not a big deal; so I have high blood glucose did not rush to make an appointment with a good hospital doctor to see the time to wait; the hospital in our province is considered a good hospital in the country. Diabetes is not scary, scary is diabetes complications, as long as the control of blood sugar, complications will not find the door.
In recent years, with the continuous improvement of people's living standard, the population of gestational diabetes is increasing. Gestational diabetes is currently the most worrying disease for pregnant women, not only affecting the health of pregnant women, but also affecting the health of the fetus, the incidence of which is about two to three percent. Therefore, pregnant women must do a good job of preventing gestational diabetes.
1What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes mellitus is diagnosed when various degrees of impaired glucose tolerance or overt diabetes mellitus are first detected after a pregnancy has been established, regardless of whether insulin or dietary treatment alone is required, and regardless of whether this condition persists after delivery.
Studies have shown that a family history of diabetes is a risk factor for gestational diabetes, with the incidence of gestational diabetes in those with a family history of diabetes being 1.55 times higher than in those without a family history of diabetes, and rising to 2.89 times higher in those with a family history of diabetes in a first-degree relative. The risk of gestational diabetes in pregnant women aged 40 years and above is 8.2 times higher than that in pregnant women aged 20 to 30 years. In addition, the obesity factor is an important contributor to gestational diabetes.
2Common Complications of Gestational Diabetes
Pregnant women:
1, gestational diabetes mellitus may occur early miscarriage, preterm labor, or fetal death in late pregnancy. The incidence of preterm labor is about 10% to 25%.2 Pregnant women are prone to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.3 Due to the decline in resistance of diabetic patients, pregnant women are prone to co-infections, especially urinary tract infections are the most common, and sepsis may occur in acute pyelonephritis, which affects the health of the fetus.4 The incidence of excess amniotic fluid is 10 times higher than that of normal pregnant women.5 Severe diabetes mellitus may result in ketoacidosis and even Coma. 6. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes give birth to huge babies causing difficult labor, obstetrical injury, and increased chances of surgical delivery, prolonged labor, and mothers are prone to postpartum hemorrhage. 7. Most mothers with gestational diabetes will return to normal after delivery, but some women will develop type II diabetes in the next 20 years.
Fetus:
1. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes give birthgiant babyThe likelihood is as high as 25% to 40%. 2. Gestational diabetes can also lead to intrauterine growth restriction of the fetus if severe vasculopathy occurs.fetal abnormalityThe rate is 6% to 8%. 3. Neonatal occurrencerespiratory distress syndromeof increased risk.
3Individual genetic differences are one of the main factors contributing to gestational diabetes mellitus
After long-term scientific research by gene decoding experts, it is found that gestational diabetes is mainly controlled by genes, and a number of genes, such as ADIPOQ and IL6, are closely related to the occurrence of postpartum obesity. ADIPOQ (lipocalin), an adipose-specific protein with the ability to improve insulin resistance and anti-atherosclerosis, is involved in biological processes in lipid and energy metabolism and the regulation of insulin sensitivity. When ADIPOQ is risky, the ameliorative effect on insulin resistance is reduced, thus increasing the risk of developing gestational diabetes.
4Canonical genetic testing to prevent gestational diabetes
Non-invasive genetic testing for gestational diabetes provides you with the optimal solution to reduce the incidence of gestational diabetes. Gamma Genetics can quickly and effectively detect pregnant women at high risk of gestational diabetes, and based on the test results, provide personalized, scientific and high-quality preventive solutions, reasonably guide pregnant women to healthy diets and lifestyles, reduce the risk of the onset of gestational diabetes, and help expectant mothers to give birth to a healthy new life.
For pregnant mothers who are already gestational diabetics, Jiaxue Genetics has fully researched the process of blood glucose regulation, and through the guidance of gestational diabetes medication, we can develop the most effective medication program for you to avoid ineffective medication.
5Key Testing Population
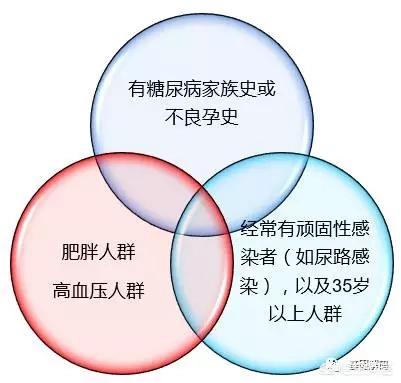
Learn something about gestational diabetes first so you won't be afraid.
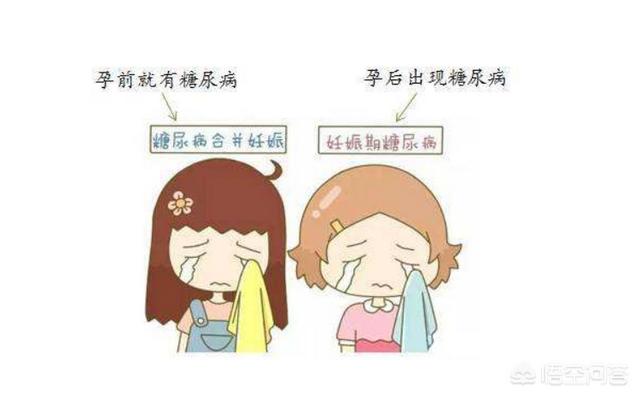
Gestational diabetes mellitus consists of two conditions: i. Gestational diabetes mellitus which means that diabetes mellitus occurs or is detected for the first time during pregnancy. Second, diabetes in combination with pregnancy, which means that diabetes was already present before pregnancy.
Why pregnancy predisposes to diabetes:
Because of pregnancy, the body's secretion of some anti-insulin hormones increases, making insulin requirements significantly higher. For patients with insufficient pancreatic reserve function are prone to diabetes during pregnancy.

Symptoms and dangers of gestational diabetes:
Most people with gestational diabetes do not have the typical "three more and one less" symptoms of diabetes, i.e., excessive drinking, excessive urination, excessive eating and weight loss. Many of them are found only after the relevant examinations during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes should not be taken too lightly, and blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, urine ketone bodies, etc. need to be monitored. Gestational diabetes patients are prone to gestational hypertension, but also pay attention to monitoring blood pressure, urine protein, liver and kidney function. Gestational diabetes can lead to an increased incidence of fetal malformations, and may also affect the development of the fetus in the womb, the risk of producing a huge child, etc., so the growth of the fetus in the womb during pregnancy should also be monitored.

Treatment of gestational diabetes:
Don't worry too much after being diagnosed with gestational diabetes. Doctors can give medical nutrition and exercise therapy according to the individual's specific situation to ensure reasonable nutritional intake of the pregnant woman and fetus, and to reduce the occurrence of complications in the mother and fetus. Through lifestyle changes, reasonable dietary arrangements and appropriate nutritional education, the treatment of most patients can be met, and medication can be added if blood glucose still does not meet the standard. The drug of choice is insulin; other drugs lack adequate research.
(All the above pictures are from the Internet)
Gestational diabetes, code-named GDM, is simply an awkward encounter between diabetes and pregnancy.
There are two broad categories of patients: those who are diabetics who are pregnant, which in academic language is called "Gestational diabetes". This group needs to follow the doctor's instructions to the letter to ensure the safety of mother and baby.
There's another one.Gestational diabetesThis group of people did not have diabetes before pregnancy, but it was only due to pregnancy that their glucose metabolism became abnormal.

Here's what you need to know about gestational diabetes.
Pregnancy leads to abnormal hormone levels, obesity, and mobility issues, and they are what keep the pregnant mother's blood sugar high.
So is high blood sugar in pregnancy scary or not? And how scary is it?

Let's start by looking at how high blood sugar can hurt your mom's health!
High blood sugar thickens the inner walls of mom's otherwise smooth blood vessels and narrows them.This is likely to cause an increase in blood pressure in the mother-to-be, which we call "hyperemesis gravidarum".
Hyperemesis gravidarum is no joke, and in severe cases, it can directly jeopardize the lives of both mother and child.
High blood sugar also tends to cause excessive amniotic fluid in the mom.
Due to excess amniotic fluid, the fetus is more mobile in the uterine cavity and is prone tomalpositioning of the fetus;
Overstretching of the uterus and high pressure can easily causepremature labor。
And babies in a prolonged high blood sugar environment can grow up with too much absorbed sugargiant baby。
The two roadblocks, huge baby and fetal malposition, both greatly increase the mother's difficulty in labor .

Plus, sugar is a favorite of bacteria.High blood sugar can also make it easy for pregnant moms to be in the midst of a regiment of bacteria.
Candida, for example, can cause vaginitis, and untreated vaginitis can lead to intrauterine infections, which may be fatal to the baby.


Read more about how high blood sugar treats babies!
In early pregnancy, the baby's tissues and organs are at the stage of differentiation and formation.
High blood sugar can affect the normal differentiation of the baby's tissue cells, resulting in malformed babies and, in severe cases, even miscarriage.
And as the weeks of pregnancy increase, by the time the baby's lungs are developing, high blood sugar can in turn prevent the production of alveolar surface-active substances, which can interfere with lung maturation.


The baby plays around in the placenta, and the blood keeps sending sugar to the baby through the umbilical cord. When the baby eats well, nutrition is not a problem, so as long as there is enough blood sugar, the baby grows like a charm, fatter and fatter, bigger and bigger. Bam!giant baby。
Huge babies are usually stuck in the pelvis during labor due to their excessive weight and broad shoulders, and are prone to bone damage through the process of reluctant pulling, and sometimes suffocation or even death due to the prolonged duration.

High blood sugar can be stressful for babies, too! In order to convert the large amount of blood sugar into cells, the baby's pancreas then begins to secrete insulin at a faster rate.
This prolonged overuse of the pancreas can predispose the baby topancreatic injuryThis is the root cause of diabetes when the baby grows up!
According to statistics, the chances of such children being detected with diabetes at the age of 20 are 24%, and at the age of 24 the chances of being detected with diabetes are up to about 40%.

If you have gestational diabetes, you will be nervous and you will not care, but if you take it seriously and control your diet strictly, gestational diabetes will not be a problem at all, so listen to your doctor's advice and control your blood glucose level well.


Gestational diabetes is well controlled and many people will automatically revert to it after giving birth, but poorly controlled diabetes can have a huge impact on both the child and the pregnant woman.

gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition of pregnancy in which those who do not have diabetes before pregnancy, after pregnancy in the development of hyperglycemic disease. (If you had diabetes before you got pregnant, it's called a diabetic co-pregnancy, which is different from gestational diabetes.)
Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
The most typical symptoms are three more and one less, i.e. more drinking, more eating, more urination, but weight loss. Vulvar itching, and vulvar candida infection can also occur during pregnancy, and ketoacidosis with coma occurs when symptoms are severe.
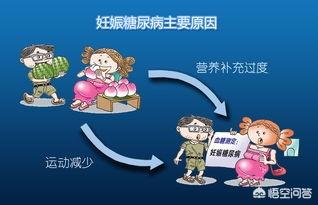
There is also a portion of patients who do not have the three more and one less symptoms, showing symptoms of severe vomiting of pregnancy in early pregnancy, abnormal fasting blood glucose test findings or positive urine glucose, usually these patients have a family history of diabetes mellitus or a history of poor fertility.
Self-testing for gestational diabetes
Regarding gestational diabetes, pregnant women are screened. The screening process is: between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, drink 50 grams of sugar water, one hour after the blood glucose test, if the glycemic index exceeds the limit, it is more dangerous, it is best to do another 100 grams of sugar tolerance test.

Gestational diabetes and macrosomia
Pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus, due to abnormal glucose metabolism in the body, a lot of glucose directly into the bloodstream, and the fetus is through the placenta from the mother to obtain nutrients, the mother's blood sugar increases, then the fetus will be out of the high sugar state for a long time, resulting in insulin hyperplasia, secretion increase, promote protein and fat synthesis, which directly lead to the fetus subcutaneous fat abundance, rapid growth in body weight, and the formation of a huge child.

Macrosomic babies can cause great harm to labor and delivery. Common ones include causing obstructed labor, cranial hematoma in the newborn, and clavicle fracture. There is also a situation where the mother's diabetes is so severe that the vascular lesions can restrict the growth of the fetus to become preterm or smaller than gestational age.
At the same time, it is easy to be complicated with hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, excessive amniotic fluid, premature rupture of membranes, infection and preterm labor. Therefore, poorly controlled gestational diabetes is still very scary, which requires pregnant women to pay attention to every aspect of their daily lives.
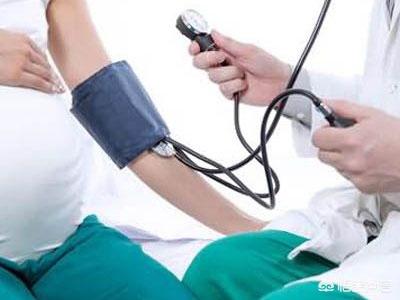
Precautions for patients with gestational diabetes
Diagnosed with gestational diabetes mothers do not have to worry too much, the vast majority of gestational diabetes can be cured by controlling the diet, coupled with the amount of exercise, simply put, is to control the mouth, open legs, basically not a big problem.
Expectant mothers who find out about gestational diabetes do not need to worry too much because most gestational diabetes can be cured through proper dietary control and exercise, and gestational diabetes is not a lifelong disease.

This part of the pregnant mother should first learn to control the diet, using the method of small meals, to control the blood sugar in a reasonable range, through the time, consume more food rich in vitamins and fiber, to maintain a balance of calories, fat, protein, etc., to protect the healthy growth of the fetus.

Coupled with the food amount of exercise. It is generally recommended that you can do half an hour of aerobic exercise (do not do strenuous exercise), through exercise to eliminate toxins in the body and accelerate the body's metabolism.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.