What are the complications of diabetes?
Before answering this question, let me read what the relevant experts and treating doctors have said. The ...... reads as if these people are knowledgeable, but I don't think any of them here can solve the problem, and if they can't solve the problem, it's bullshit to talk about it any more ! I am all too familiar with diabetes and its complications, having been acquainted with it for 18 years now, since 2003. Diabetes and complications, I hate him so much that I have now stopped seeing him, how did I do it ! Diabetes and complications is actually a gadget that has gradually grown because of adequate nutrition. For example: a grape seed (diabetes), because of sunlight, water and other nutrients, it has mutated, from the ground into a grape root, from the ground to grow vines and grapes, simple, is not it, that's how it is. To solve the problem, then give the grape root to it to abolish, do not give it sunlight, do not give it water ...... it is doomed to perish. Where is the root of diabetes and the nutrients that grow to make it mutate? That's the only place to start to solve the problem. Do not listen to doctors and experts blind bullshit, eat this drug, eat that drug ...... to believe in science and let the physical examination data to speak, the best doctor is their own ! You only need to do "the symptoms of diabetes, three more and one less, into three less and one more"...... grape seeds will not be in the ground to take root, in the ground to grow into a vine.
Acute complications of diabetes mellitus are acute in onset and dangerous in condition.1. Ketoacidosis. The main features are hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia and metabolic acidosis. Breath smells like rotten apples, urine is positive for ketone bodies, and in severe cases, coma.2. Hyperosmolar non-ketotic diabetic coma. The main features are significant elevation of blood glucose, increased plasma osmolality, negative or weakly positive urine ketone bodies, severe dehydration and neurological symptoms, and critical condition.3. Lactic acidosis. The condition is vicious and the mortality rate is high.4. Combined with severe infections, it aggravates the disorder of glucose metabolism and induces acute hyperglycemic events.
Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus 1. macrovascular lesions (coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, peripheral arterial disease, etc.).2. microvascular lesions (diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, etc.).3 neuropathy (peripheral and autonomic neuropathy, which are the most common chronic complications of diabetes mellitus).4. other chronic complications (diabetic foot, cataract, skin lesions, etc.).
"Happy little doctor" answers your questions.
summarize
Amputation according to the International Clinical Guidelines for the Diabetic Foot is defined as the removal of the distal end of 1 limb. Repeat amputation: a second distal amputation of a previously amputated limb that has not healed. New amputation: a distal amputation after healing of the affected area of a previous amputation. Minor Amputation: Disarticulation at and below the level of the ankle. Major amputation: Amputation above the level of the ankle.
epidemiological
1. Foreign data
(1) Diabetic patients account for 40% to 60% of all nontraumatic low amputations.
(2) Eighty-five percent of diabetes-related low distal amputations occur after foot ulceration.
(3) In diabetic patients, 4 out of 5 ulcers are induced or worsened by trauma.
(4) The prevalence of foot ulcers in diabetic patients ranges from 4% to 10%.
2. Domestic data
(1) China's multicenter data show that the percentage of lower extremity arterial lesions in diabetic people over 50 years of age is 19.47%.
(2) In the single-center study, the percentage of lower extremity arterial lesions in the diabetic population over the age of 60 was 35.36%.
(3) In a multicenter study in Beijing, the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus lower extremity vasculopathy was as high as 90.8%, of which 43.3% were severe or above. Among them, 43.3% were severe or above.
(4) In diabetic patients, bilateral lower extremity lesions develop symmetrically.
Causes of diabetic foot
The internal cause of diabetic foot persistent high blood glucose too high blood glucose is easy to cause blood hypercoagulable state, promote the formation of lower limb atherosclerosis, is an extremely important factor in the occurrence of diabetic foot. Due to unsatisfactory long-term blood glucose control, abnormal glucose metabolism causes lipid metabolism disorders, which is prone to pathological changes in the large blood vessels and microvessels of the limbs, leading to diabetic foot.
1. Diabetic chronic vasculopathy
Due to the patient's body continues to be in high blood sugar and protein non-enzymatic glycation state, lipid metabolism disorders, high viscosity, high coagulation state of the blood as well as aging lower limb atherosclerosis, and many other factors make diabetic patient's lower limb arteries prone to vascular pathology, wall thickening, lumen stenosis, and at the same time microvascular and microcirculation have different degrees of obstacles, resulting in the lower limb vascular sclerosis of the patient's lower limb and thrombus clogging the blood vessels, and at the same time, foot Microvascular occlusion, so that the lower limb perfusion flow is reduced, the blood circulation of the extremities is impaired, local tissue hypoxia and insufficient supply of nutrients, lower limb pain, sensory abnormalities and intermittent claudication, serious blood supply shortage can lead to ulcers and gangrene of the limbs.
2. Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic complication neuropathy will lead to the endings of the limb protective sensory weakening or loss and foot biomechanical changes, etc., so that the foot lack of protection against harmful stimuli, thus very easy to cause mechanical or temperature damage; autonomic neuropathy is also related to the formation of diabetic foot, autonomic neuropathy caused by sweat secretion disorders, which can make the skin less pliable, leading to skin dryness, cracks and infections. Once the skin of the lower limb or foot is damaged, the above pathophysiological changes make the wound not easy to repair, the infection is difficult to control, and finally the foot ulcer develops or even amputation.
3. Age
Diabetic foot occurs most often in patients >40 years of age and increases with age. Some studies have reported that increasing age is an independent risk factor for the development of diabetic foot. The possible reasons for this are: ① long duration of disease, increased incidence of atherosclerosis, and altered hormone levels in elderly diabetic patients; ② decreased metabolic rate and repair capacity of tissues in the elderly, and prolonged healing time after injury; and ③ diabetic neuropathy increases with age.
4. Gender
The occurrence of diabetic foot has a certain relationship with gender. Domestic literature suggests that the incidence of diabetic foot is more common in men than in women, and the reason for this may be that estrogen has a vasoprotective effect, and thus the chances of large and small limb vasculopathy are relatively reduced in female diabetic patients.
5. Exogenous infections of the diabetic foot
Infection is an important predisposing factor for diabetic foot gangrene. The main reason is that diabetic patients have low resistance to infection, and in the case of limb ischemia and hypoxia, bacteria are very easy to invade, thus leading to serious infection of the tissues.
6. Physical damage
Styles of tissue injury, such as burns, frostbite, scratches, abrasions, abrasion injuries, pedicure injuries, bruises, manicure injuries, and post-injury infections are undoubtedly non-negligible risk factors for diabetic foot.
Complications of diabetes
1, infection: diabetic patients with high blood sugar state is conducive to the growth and reproduction of bacteria in the body, while the high blood sugar state also inhibit the ability of white blood cells to phagocytosis of bacteria, so that the patient's ability to fight infection decreased. Commonly, there are urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, skin infections and so on.
2, ketoacidosis: diabetic ketoacidosis occurs in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus untreated, treatment interruption, or the existence of stressful situations. Diabetic patients with severe insulin deficiency, accelerated lipolysis, generating a large number of fatty acids. A large number of fatty acids enter the liver for oxidation, and their intermediate metabolite ketone bodies increase significantly in blood concentration, while the utilization of ketone bodies by extrahepatic tissues is greatly reduced, resulting in hyperketonemia and urinary ketone bodies. Since ketone bodies are acidic, resulting in metabolic acidosis in the body.
3, diabetic nephropathy: also known as diabetic glomerulosclerosis, is a common and intractable microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus, one of the main causes of death in diabetes.
4, heart disease: diabetic patients the chance of coronary heart disease is non-diabetic patients 2 to 3 times, common heart enlargement, heart failure, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and so on.
5, neuropathy: in the state of high blood sugar, nerve cells, nerve fibers are prone to lesions. Clinical manifestations are spontaneous pain, numbness and sensory loss in the limbs. Individual patients appear local muscle weakness, muscle atrophy. Plant nerve dysfunction is manifested as diarrhea, constipation, urinary retention, impotence and so on.
6, eye lesions: diabetes disease duration of more than 10 years, most patients with different degrees of retinopathy. Common lesions include iritis, glaucoma and cataract.
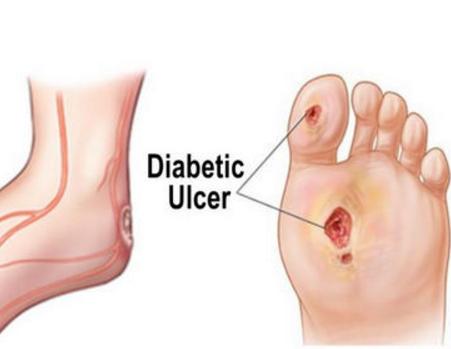
7, diabetic foot: diabetic patients due to peripheral neuropathy, lower limb blood supply is insufficient and bacterial infection caused by foot pain, ulcers, gangrene and other lesions, collectively known as diabetic foot.
Ways to prevent diabetes complications.
1、Self-massage method
2. Dietary therapy
Dietary treatment is not complicated, just use the "4321" pyramid program on the line. The bottom of the pyramid for grain, legumes 400 grams per day, preferably rich in dietary fiber coarse grains; the middle of 300 grams of vegetables; milk and dairy products 200 grams; the tip of the pyramid refers to a small amount of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, 100 grams per day. The intake of cooking oil, salt (less than 6 grams per day) and sugar is strictly controlled, reflecting diversity and balance.
3. Daily exercise
Daily exercise is not an adjunctive treatment, but is the primary treatment for obese diabetes. Exercise must be done half an hour after a meal, and the therapeutic effect of exercise wears off after 24 hours, so it must be done consistently for half an hour every day. Replace the elevator with climbing stairs. If you work on the 10th floor, you can take the elevator to the 9th floor and climb back up. Walking is especially beneficial. "Set yourself a goal of walking 10,000 steps a day.
4. Resolutely quit smoking
For diabetic patients who smoke, smoking cessation must be an integral part of diabetes complication prevention and treatment. Smoking significantly aggravates insulin resistance, raises blood glucose, dysfunctions the vascular endothelium and accelerates the development of coronary heart disease and diabetic nephropathy.
5. Weight control
Since obesity increases the risk of death from any cause, it is the most important of the modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes. A weight loss of 5-10 kilograms in one year produces a significant benefit, i.e., a 25% reduction in mortality.
6. Adjusting blood sugar levels
It is necessary to go at different moments of the day to see what is the state of our blood sugar, so that we will know if the efforts we have made before are bearing fruit, if we need to change some measures, etc.".
7. Detecting blood pressure
Monitoring blood pressure and controlling it must become an indispensable daily task for people with diabetes. Intervention in diabetics should begin with a blood pressure greater than or equal to 130/80 mm Hg.
8. Dealing with insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a reduction in the ability of physiologic doses of insulin to lower glucose, and if significant insulin resistance exists it will cause vascular damage and contribute to deterioration of islet function
9、Lower cholesterol
Patients with diabetes should have their blood lipids checked once a year, and their low-density cholesterol (LDL-C) should be less than or equal to 2.6 mmol/liter.
Focus on health, focus on the "happy little doctor."
The main complications of diabetes are diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and diabetic foot, which are described in turn by the following pharmacist at Escape:
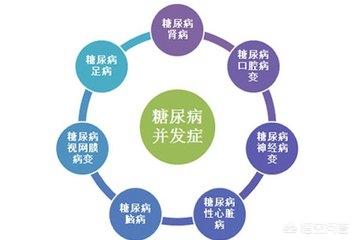 1. Diabetic retinopathy:Diabetic retinopathy is a major chronic complication of diabetes mellitus and an important cause of blindness. Early symptoms are blurred or decreased vision, flashing sensation, and fundus hemorrhage. Regular fundus examination for diabetic patients is very important, and the funduscopic findings of diabetic retinopathy include microvascular tumors, retinal hemorrhagic spots, and flocculent white spots, and in the advanced stage, there can be preretinal hemorrhage, vitreous hemorrhage, proliferative retinopathy, and maculopathy, and regular fundus examination can lead to early detection, prevention, and treatment.
1. Diabetic retinopathy:Diabetic retinopathy is a major chronic complication of diabetes mellitus and an important cause of blindness. Early symptoms are blurred or decreased vision, flashing sensation, and fundus hemorrhage. Regular fundus examination for diabetic patients is very important, and the funduscopic findings of diabetic retinopathy include microvascular tumors, retinal hemorrhagic spots, and flocculent white spots, and in the advanced stage, there can be preretinal hemorrhage, vitreous hemorrhage, proliferative retinopathy, and maculopathy, and regular fundus examination can lead to early detection, prevention, and treatment.
2. Diabetic nephropathy:Due to the elevation of blood glucose, the filtration pressure of glomerulus increases, protein leakage gradually increases, and further nephrotic syndrome and renal failure can be developed. The early symptom of diabetic nephropathy is edema, which often occurs in the face, ankle, abdomen and so on. Patients with diabetic nephropathy should actively control blood glucose, blood pressure, blood lipids, diabetic patients from the emergence of microalbuminuria, with or without hypertension should take angiotensin inhibitors (such as Benadryl) or angiotensin receptor antagonists (such as Irbesartan), because such drugs not only reduce hypertension, but also reduce urinary albumin and delay the progression of renal damage.
3. Diabetic neuropathy:Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes mellitus, with lesions involving both central and peripheral nerves, the latter being particularly common. Among them, distal sensory neuropathy is the most common lesion, accounting for more than 50% of all diabetic neuropathy. Clinical manifestations are: sensory impairment or abnormality, symmetrical pain; numbness, ants, worms, heat, electric shock-like sensation. Common therapeutic drugs include, methylcobalamin (e.g., Microphenoxal), alpha - lipoic acid, cilostazol, prostaglandin, beclomethasone sodium, epalrestat, and stilbestrol granules.
 4. Diabetic foot:Diabetic foot refers to the infection, ulcer formation and/or deep tissue destruction of the lower extremities in diabetic patients due to the combination of neuropathy and various degrees of peripheral vasculopathy. Diabetic foot is the result of diabetic patients due to long-term poor control of blood glucose and other reasons, resulting in blood vessel stenosis, occlusion, blood flow obstruction, which in turn leads to ischemia of nerve cells in the foot, and then lead to sensory nerve, motor nerve damage, the clinical manifestations of the foot cold, numbness, pain, ulcers, gangrene, intermittent claudication and/or infection, etc., and in severe cases, need to amputate the limb. Clinical treatment measures include glycemic control, anticoagulation, thrombolysis, vasodilatation, and anti-infection.
4. Diabetic foot:Diabetic foot refers to the infection, ulcer formation and/or deep tissue destruction of the lower extremities in diabetic patients due to the combination of neuropathy and various degrees of peripheral vasculopathy. Diabetic foot is the result of diabetic patients due to long-term poor control of blood glucose and other reasons, resulting in blood vessel stenosis, occlusion, blood flow obstruction, which in turn leads to ischemia of nerve cells in the foot, and then lead to sensory nerve, motor nerve damage, the clinical manifestations of the foot cold, numbness, pain, ulcers, gangrene, intermittent claudication and/or infection, etc., and in severe cases, need to amputate the limb. Clinical treatment measures include glycemic control, anticoagulation, thrombolysis, vasodilatation, and anti-infection.
Other complications of diabetes are urinary tract infections, oral diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, gastroparesis, itchy skin, fatty liver, and osteoarthropathy.
There are multiple complications of diabetes, the most serious of which are ketoacidosis, as well as blindness, foot rot, and heart disease. To prevent these complications, the first thing to do is to do a good job of the five carriage conditioning program, which aims to repair the normal function of the five organs and six organs. In particular, the pancreas function should be repaired properly, the pancreas function is normal, in order to normal secretion of insulin, in order to do all of the above, must achieve balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, moderate exercise, a good state of mind.
Nowadays diabetes is becoming more and more common, in our country every 10 people have one with diabetes, every 5 elderly people in one is an old sugar lover. It is said that diabetes is not scary, the scary thing is the complications, then how scary are the complications of diabetes?

1. Diabetic cardiovascular disease:It is the first killer of diabetes, and the probability of stroke in diabetic patients is 2-4 times higher than that of non-diabetic patients, and in serious cases, it can lead to myocardial infarction, heart failure, cerebral vascular blockage, hemiplegia and so on.
2. Diabetic nephropathy:It is one of the leading causes of death in diabetic patients, with data suggesting that the incidence of nephropathy can be as high as 10-20% in diabetic patients with a disease duration of more than 10 years. If left unintervened, it can lead to uremia, requiring hemodialysis or kidney transplantation to sustain life.
3. Diabetic retinopathy:It is the most common microvascular complication of diabetes and the leading cause of blindness in adults. Data show that 20-40% of adults with type 2 diabetes will develop retinopathy and 8% vision loss.
4. Diabetic neuropathy:It is closely related to disease duration and poor glycemic control. The prevalence can reach 30-40%, 60-70% and 90% in patients with a disease duration of 5, 10 and 20 years, respectively. When neuropathy occurs, patients often experience numbness of the extremities, pain, abnormal sensation, nausea and vomiting, and difficulty in urination.
5. Diabetic foot:It has a prevalence of up to 15% and patients often suffer from loss of protective sensation in the foot and prolonged wounds that can lead to gangrene of the foot and amputation of the lower limb. Once diabetic foot occurs, it can cause a huge financial burden and has a low survival rate after amputation.
The above five are the most common complications of diabetes, but of course there are other complications of diabetes, such as periodontitis, tuberculosis, infections and so on. There are also some acute complications, such as ketoacidosis, hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Once the blood sugar control is poor, these complications may come to your door.
Key measures to prevent complications: control blood glucose, control weight, control blood pressure and blood lipids, exercise consistently, limit salt, eat a balanced diet, use medication, and have regular checkups.
More complications related knowledge, you can send us a private message to send the keyword [blood sugar] to get, there is a complete list of food glycemic index, diabetic practical life manual, expert complications to explain the video and so on. These learning materials are free of charge to all sugar friends, I hope this answer can help you, remember to click a like oh!
I am an endocrinologist, outpatient wards every day to face a lot of diabetes patients, among them, some of them because of high blood glucose to consult the doctor, however, more most of them are not because of high blood glucose but because of diabetes caused by complications caused by the pain, affecting the quality of life, and even a great deal of damage to the body to come to the doctor! Today, we will talk to you about the chronic complications of diabetes. At the end of the article there are knocking on the blackboard to highlight the dry knowledge haha!
Many people have a misunderstanding, found that blood glucose elevated a little, think nothing ah, I have nothing to feel don't care, in fact, there are many studies have shown that, for example, China's research for 20 years of the Daqing study found that early detection of pre-diabetic patients, intervention, than not intervene, the chances of progression to diabetes and the chances of heart attack are significantly lower. High blood sugar in diabetes is not scary, what is scary is that diabetes is a gentle and silent killer, and the complications it brings can not only affect the quality of life, but is even an important cause of death and disability today.
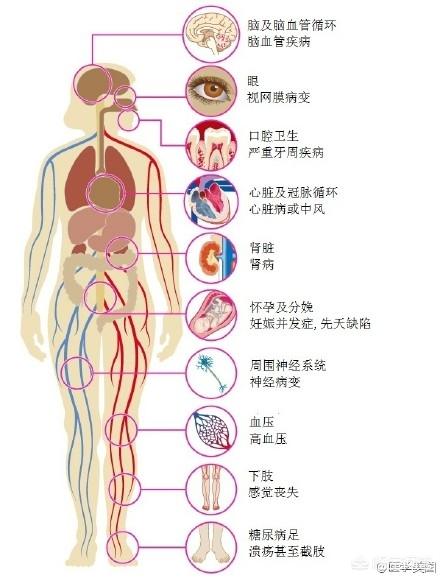
We can clearly see what chronic complications of diabetes there are in the medical image above, but it is important to talk to you in more detail here, including the categorization, and the chronic complications of diabetes that are not mentioned in the image above.
Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus include two categories, the first category is called macrovascular complications, the second category is called microvascular complications, don't worry, the next step is to say what is called macrovascular, what is called microvascular art of war this.
As the name implies, large vessel complicationsIt refers to the long-term high blood sugar of diabetes has produced damage to the body's large blood vessels, which is often referred to as atherosclerosis, what are the larger blood vessels?There are large blood vessels that supply blood vessels to the brain, and lesions can occur that can lead to cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, andIt can also lead to an increased incidence of Alzheimer's disease in older people. Then there are the large blood vessels that supply the heart, which we all know are called the coronary arteries, coronary atherosclerosis leads to angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, heart failure.Difficulty in breathing and other physical decline. There are also large blood vessels that supply the extremities, and because the foot is the furthest from the heart and has the most terminal blood supply, problems are usually the earliest to occur, first with atherosclerosis of the foot vessels, and then, when the vessels are blocked, there is a rupture, and what we call diabetic rotting feet! This carries a risk of amputation. Whether the amputation rate is high or not depends on the severity of the condition, so you can't generalize whether it's high or not. Diabetic foot is called diabetic foot, which is caused by long-term hyperglycemia leading to common lesions of blood vessels and nerves.
Moving on to microangiopathy.As the name suggests, it is the tiny blood vessels that supply blood and nutrition to some of our organs, such as the kidneys, whose microvessels are chronically affected by hyperglycemic toxicity and develop proteinuria, which we calldiabetic nephropathy.Heavy times will occurInsufficiency of the kidneys, also known as kidney failure, and if it still doesn't care, it's dialysis. Then there are the ones that supply the eye, like the retinal vessels, which we call theDiabetic retinopathy, with blurred vision and, in severe cases, retinal detachment.It's like a movie theater where the projection screen falls off and you can't watch the movie anymore, as opposed to a person who justlose one's eyesightLike that. And then there's theNeuropathy.More common is sensory neuropathy of the limbs, mainly manifested as numbness and pain in the tips of the fingers and toes, and decreased or even loss of perception of heat and cold.
Tap the blackboard for emphasis:In addition to the chronic complications of diabetes mellitus, many clinical epidemiologic findings of many diseases for long-term failure to control blood glucose type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with the following diseases is also significantly higher than the incidence of blood glucose in the normal population, such as dementia mentioned above, such as erectile dysfunction in males (ED, or impotence, which is also the most common type of diabetes mellitus chronic morbidity), such as depression, gout, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, sleep apnea, periodontal disease, vulvar itching in women, skin lesions, malignant tumors, polycystic ovary syndrome in women that affects fertility, and so on.
Dr. Haixia Liu, Department of Endocrinology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, and any other questions are welcome.
There will always be some people with diabetes who will think that high blood sugar does not did not affect their normal life and thus will not take diabetes seriously.
Case: Mr. Zhang is a type 2 diabetic, since he found out about diabetes, he did not pay attention to the disease, he always said, diabetes does not affect my food and drink, I do not have to pay attention to it, I have never taken hypoglycemic drugs, and in the diet is what you want to eat, did not control the diet as others. However, in recent times, Mr. Zhang found that foam appeared in his urine, he did not know what was going on, and went to the hospital for examination, but it was diabetic nephropathy caused by diabetes. Mr. Zhang finally realized the terrible consequences of not actively controlling his blood sugar, and hastened to ask his doctor what complications diabetes would lead to besides kidney disease.
Complications caused by diabetes mellitus mainly include acute complications and chronic complications. Acute complications mainly include hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic patients need to strengthen the blood glucose monitoring in daily life, in order to be able to timely detection of acute complications of diabetes, to avoid the danger of occurrence.
Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus is mainly due to high blood sugar on the large blood vessels and microvascular damage caused by the human body are distributed throughout the body of large and small blood vessels, so it can be said that diabetes mellitus complications can be spread throughout the body, the more common chronic complications of diabetes mellitus, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, vascular disease in the lower limbs, diabetic foot disease and so on. Diabetic neuropathy can involve both central and peripheral nerves, and peripheral neuropathy is the most common clinical condition. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy includes distal symmetric polyneuropathy, proximal motor neuropathy, polyneuropathy, autonomic neuropathy and so on.
 Before answering this question, let's look at the question: Where in the body are there no blood vessels? I believe that if you count every part of your body, you will not find a place without blood vessels. Therefore, once the blood vessels have problems, the disease can occur anywhere in the body.
Before answering this question, let's look at the question: Where in the body are there no blood vessels? I believe that if you count every part of your body, you will not find a place without blood vessels. Therefore, once the blood vessels have problems, the disease can occur anywhere in the body.
Diabetes mellitus is one such disease, known as the source of all diseases, in fact, among the various complications it causes are due to damage to blood vessels. Prolonged hyperglycemia or blood sugar fluctuations cause damage to the endothelium of blood vessels, and then various lipids in the blood are deposited on the walls of blood vessels, causing atherosclerosis.
After atherosclerosis occurs, blood vessels will become thicker causing a decrease in elasticity, an increase in brittleness, and localized arterial plaques may also form. It causes obstruction to the blood flow and reduces the oxygen and nutrients supplied to the surrounding tissues and organs, resulting in dysfunction. If plaque rupture occurs, it will cause platelet aggregation and the formation of blood clots to block the blood vessels, causing necrosis of the surrounding tissue cells. These lesions occur in the major organs, which causes a variety of common complications.
peripheral neuropathyDue to the relatively slow blood flow at the end of the limbs away from the heart, the blood vessels here are most likely to be damaged and cause a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the peripheral nerve cells, causing nerve cell dysfunction and symptoms such as numbness, tingling, itching, pain, and so on, which is known as peripheral neuropathy, which is the earliest complication of diabetes, mostly appearing in diabetic patients with the disease for 10-15 years.
diabetic retinopathyThe distribution of blood vessels in the fundus is very rich and subtle, and it is also the blood vessels that are most susceptible to injury. These blood vessels will rupture and bleed after injury, which will continuously stimulate the growth of new blood vessels, and at the same time, the bleeding blood vessels will fibrosis and pull the retina, which may cause retinal detachment, resulting in vision loss or even blindness, and if a large amount of hemorrhage covers the macular region in the visual center, it will lead to immediate blindness.
diabetic nephropathyAnatomically, the vasculature of the fundus and the renal vasculature are very close to each other in terms of publication and nature, so that the two complications often occur almost simultaneously, most often about 15 years after the onset of diabetes mellitus. Since the blood vessels in the fundus can be seen through fundus imaging and other tests, regular checkups are very important for detecting and determining diabetic fundopathy and nephropathy.
Diabetic cardiovascular diseaseThis is the most serious complication of diabetes mellitus and the main cause of the ultimate death of diabetic patients, such as coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, etc., which is either fatal or crippling once it occurs, and the consequences are the most serious.
The ultimate goal of diabetes mellitus treatment is to control and delay the occurrence of various complications, improve the quality of life and prolong the life span as much as possible. To achieve this goal, not only should blood glucose be controlled within the target range, but also the control of blood lipids and blood pressure should be given high priority, especially with the prolongation of the course of the disease, the control of blood pressure and blood lipids is even more important than the control of blood glucose.
Glucose control targets: The ideal goal is a fasting blood glucose of less than 6.1 mmol/L and a 2-hour postprandial blood glucose of less than 7.8 mmol/L; the general goal is a fasting blood glucose of less than 7.0 mmol/L and a 2-hour postprandial blood glucose of less than 10.0 mmol/L; the ideal goal for glycosylated hemoglobin is less than 6.5% and the general goal is less than 7.5%.
Lipid control goals:: Ideal goal is LDL less than 1.8 mmol/L; general goal is LDL less than 2.6 mmol/L.
Blood pressure control goals: The ideal goal is less than 120/90 mmHg; the general goal is less than 140/90 mmHg.
Diabetes is also known as the "mother of all diseases", which can cause dozens of complications, including blindness, kidney failure (uremia), myocardial infarction, stroke, numbness of the limbs, gastrointestinal disorders and urinary difficulties and other symptoms. So, what are the complications of diabetes? Is there any good prevention method?
1. Diabetic nephropathy
The prevalence of diabetic nephropathy has been on the rise in recent years and is a major complication of diabetes. Moreover, diabetes is 17 times more likely to develop uremia, which is one of the most important causes of death in diabetics.
Therefore, it is important for diabetic patients to pay more attention to their kidneys and develop relevant preventive measures to slow down the progression of the disease.
2. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy is also a common complication in diabetic patients, diabetic patients should strengthen eye health care, avoid overuse of the eyes, more rest for the eyes, reduce bright light stimulation, sleep with the head slightly elevated 15-30 degrees.
In addition, to reduce the pressure on the blood vessels behind the eyes, it is important to avoid strenuous exercise, prevent constipation, and prevent forceful sneezing and coughing. If blood sugar control is unstable, it can accelerate the development of diabetic retinopathy, which may lead to blindness.
3. Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is also a complication of diabetes mellitus, the lower limbs are more serious than the upper limbs, clinically there is a sock or glove-like distribution of the limb end of the strange sensation, at the same time, the sensation will have burning sensation, pins and needles, numbness, limb pain. At night or in the cold winter, the symptoms will be aggravated, long-term accumulation, affecting the motor nerves, muscle weakness to muscle atrophy and paralysis. Therefore, it should be actively treated to prevent secondary infection.
4. Diabetic foot
This is a serious complication of diabetes, which is the main cause of amputation and even death. Diabetic patients should know the basics of foot protection, wear soft shoes and socks that fit well, avoid foot pressure and friction to avoid breakage, protect the skin of the feet to be clean and dry, change shoes and socks diligently, and develop a good habit of washing the feet every day.

To stay away from diabetes complications, you need to control theBlood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugarThe effects of the "three highs" are inextricably linked.
Some of the ways to prevent diabetes are: performing blood glucose monitoring, eating a healthy diet, exercising moderately, not smoking, reducing stress, getting enough sleep, checking feet daily, maintaining oral hygiene, maintaining oral hygiene, some other regular checkups: performing a glycosylated hemoglobin test performing dental cleanings and checkups; dilated pupil checkups, regular physical exams, cholesterol testing, microalbumin and creatinine tests to check for kidney damage.
In fact, people with diabetes can reduce the risk of diabetic complications and live a long life with the disease by adhering to a healthy lifestyle with medication or insulin therapy.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.