What complications occur when you have diabetes for 3, 5 and 10 years and how can you detect them early?
My mom is a diabetic, from the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, now almost two decades have passed, the beginning of oral hypoglycemic drugs, to the current insulin injections, the good thing is that the blood glucose level control is quite OK.
The first three years did not have any obvious complications, mainly weight loss, anyone who saw her said she had lost weight, and also easily feel hungry, sometimes if not timely supplementation, may feel hypoglycemia, but the good thing is that the back has been more attention, after the blood glucose level is stabilized, and seldom occurs this kind of situation.
The most significant complication today is peripheral neuropathy, her arms often hurt and sometimes her legs feel pain as if they were pins and needles or bug bites, she was also hospitalized for a while and got a little better, but it didn't go away completely.
When she first found out about diabetes, because she always felt hungry and thirsty easily, she would often go to the toilet when she drank too much water. At first, she didn't pay attention to it, thinking that it was caused by being too busy and too tired at work. Later, she kept losing weight, and when she checked her blood sugar, it was even as high as more than fifteen points, and she was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Want to early detection, must develop a good habit of health checkups, just because the work is too busy, although he is a doctor, but has not been a good physical examination, so that the discovery of so late, if the discovery of some earlier, may be able to control a little better.
Thanks for the invitation.
Diabetes as a common chronic disease needs to be carried for life. As the title suggests, it is a battle for three, five, ten years or even a lifetime. Complications, as the "killer app" of diabetes, are a major threat to the health of the population. Along with 3 years, 5 years, 10 years and so on the prolongation of time, the probability of complications will be higher and higher, the severity of complications is also increasing, but it does not mean that to 3 years, to 5 years will necessarily occur. Therefore, here I will mainly talk about what are the complications? How should they be detected early?
complications (undesired side-effect of medical procedure)
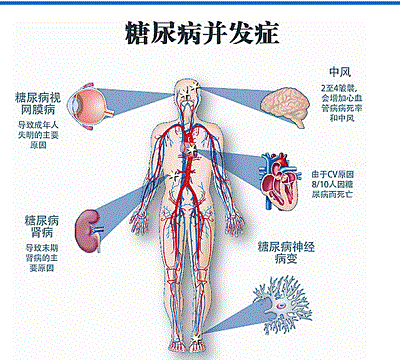
Complications of diabetes mellitus are mainly characterized by impairment of systemic microcirculation, which can occur in the cardiac vessels, cerebral vessels, retina of the eye, peripheral blood vessels of the limbs, and kidneys, and can also cause neuropathy:
- Diabetic retinopathy: commonly known as "diabetic eye";
- Diabetic nephropathy: commonly known as "diabetic kidney";
- Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: severe pain tingling, burning, numbness in the lower limbs, arms, fingers, persistent anisocoria, which can affect quality of life, sleep, mood (anxiety, depression);
- Diabetic foot: commonly known as "diabetic foot";
- Cardiovascular disease, commonly known as "diabetic heart";
How to detect early
Self-monitoring to control blood glucose and detect blood glucose abnormalities in a timely manner
Learn to have a physical exam and try to include the organs that diabetes tends to involve
Be alert to common complications and seek medical attention if anything goes wrong
If you are a diabetic, it is important to seek early medical attention and regular retesting. By following your doctor's advice and treating your condition appropriately, you can effectively prevent complications.
Follow the headline to get more health knowledge~
Diabetes itself is not scary, what is scary is the complications caused by diabetes. There are many factors involved in the development of diabetic complications, but the primary factor is the patient's blood sugar level. If the blood sugar is not well controlled, chronic complications may occur within two to three years. If the blood sugar is effectively controlled, it is possible that no complications will occur for life. As far as I can remember, Soong Mei-ling was diabetic, and because her blood sugar was always well controlled, she lived past 100 years of age!
So the question of what complications will occur in three years, five years, ten years, that's really hard to say and depends entirely on what the patient's blood sugar level is.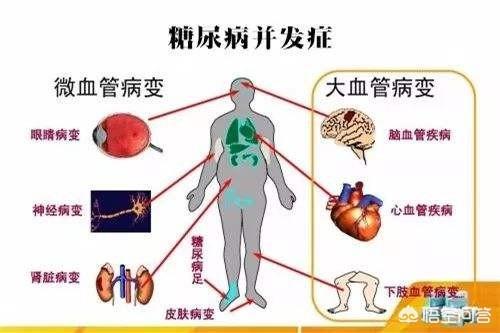
There are two types of complications of diabetes, acute and chronic.
Acute complications are rapid and can be life-threatening in a short period of time. The most common complication is hypoglycemia, which occurs very easily during the treatment of diabetes, even though diabetic patients have high blood glucose. Hypoglycemia occurs when there is panic, sweating, hand tremors, dizziness and other symptoms, and in severe cases, coma. So diabetics should always have a small dessert in case of emergency. There are also ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic crisis with polydipsia, weakness, nausea and shock.
Focus on the chronic complications of diabetes. Hyperglycemia mainly damages blood vessels and nerves, causing various organ dysfunctions. When it affects the large blood vessels, it mainly manifests as vascular blockage lesions, such as coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, etc., which manifests as chest tightness, panic, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, hemiplegia and other symptoms. When it affects the blood vessels of the lower limbs, there are abnormal sensation of the feet, terminal skin ulcers, until the whole foot is infected and necrotic. When it affects the small blood vessels, it mainly damages the eyes and kidneys. Diabetic retinopathy, early only blurred vision, serious blindness. Diabetic nephropathy is asymptomatic in the early stage, with only proteinuria in the urine routine. In the late stage, it is uremia. Diabetic neuropathy is mainly peripheral nerve sensory abnormalities.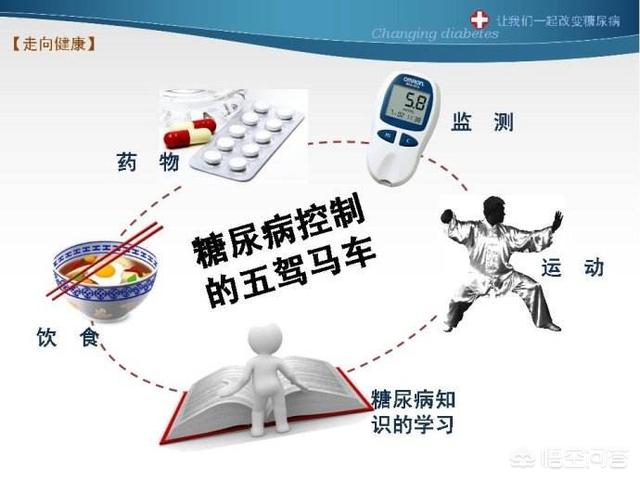
Early symptoms of chronic complications of diabetes are often not obvious, and once they do appear, irreversible damage to organ function has already occurred. Therefore, the emphasis is on prevention as well as early detection. Prevention is actually to pay attention to strict control of blood sugar, diabetes treatment includes diet therapy, exercise therapy, drug therapy, blood glucose testing and diabetes education five measures, as long as the implementation of the in place, the majority of diabetic patients are difficult to effectively reduce the control of blood glucose, but also can effectively avoid complications. At the same time pay attention to regular physical examination, can find hidden stage of diabetes complications, early intervention, can save organ function.
I'm FooDaddy, a clinical dietitian, so if you think I'm making sense, give me a like 😜 Follow my headline for more nutrition and health information.
With diabetes, we always emphasize the need to control blood glucose, but the ultimate goal of controlling blood glucose is not clear to many friends - the ultimate goal of controlling blood glucose in diabetes is to control blood glucose, reduce the incidence of diabetes-related complications, obtain a better prognosis for health, and reduce the health hazards and health risks associated with diabetes. In fact, many diabetics can live a long and healthy life as normal if they can control their blood sugar levels properly!
Correcting a misunderstanding, the chance of diabetes complications, and the duration of diabetes does have a certain relationship, but there is not an exact point in time, such as 3 years will occur which complications, 5 years will occur which complications, or even said that with diabetes, how many years you can still live this kind of statement, will occur which complications, how much life expectancy is still, a lot of times depend on the intervention of diabetes early and late, long-term blood glucose control standard and so on a number of factors The life expectancy depends a lot on how early the diabetes intervention takes place, how well the blood glucose is controlled over the long term, and other factors.
To give you a brief overview of the complications of diabetes
The most common complications of diabetes can be categorized into two main groups, macrovascular complications and microvascular complications.
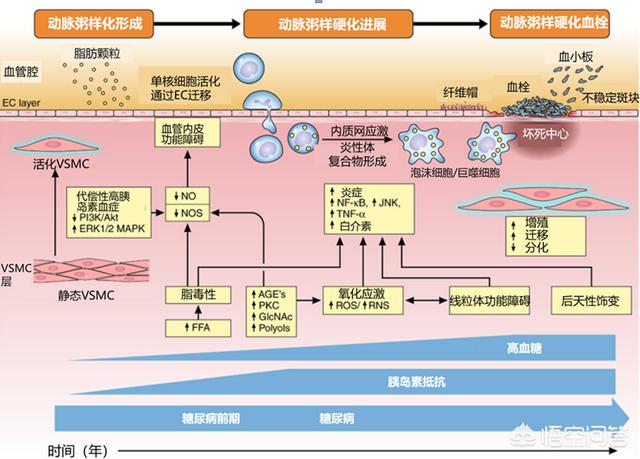
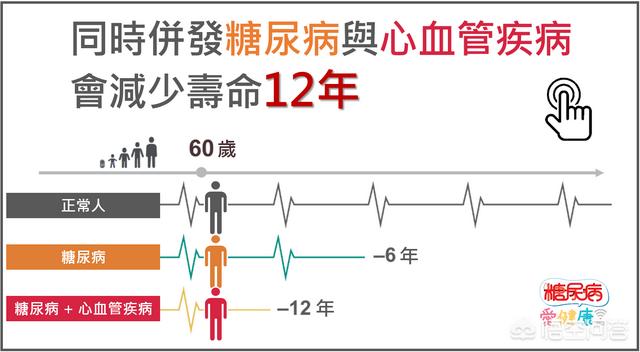
Macrovascular complications are primarily the increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease associated with diabetes. Cardiovascular disease is one of the most common complications of diabetes, with approximately 32% of diabetics suffering from cardiovascular disease, the most common of which are atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease and heart failure. Macrovascular complications of diabetes are complications that seriously affect the prognosis of diabetics, and about 50% of diabetics die from cardiovascular disease.
Diabetic patients with high blood sugar, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia and other problems, will increase the free fatty acids in the blood, and ultimately cause the inflammatory reaction of the inner wall of the blood vessels as well as dysfunction, affecting the health of the inner wall of the blood vessels, at the same time diabetes will also affect the lipid metabolic process of the body, leading to abnormal lipid metabolism, so that lipids are more likely to form an accumulation in the lower endothelium of the blood vessels, these factors, all of which are important risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, therefore, diabetes is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular health. These factors, all of which are important risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, make diabetes an independent risk factor for cardiovascular health, and it is especially important to control blood glucose if you want to control the risk of cardiovascular disease.
After talking about the macrovascular complications of diabetes, let's talk about the microvascular complications of diabetes. There are many more microvascular complications of diabetes, including diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic neuropathy, all of which fall into the category of microvascular complications.
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the major microvascular complications of diabetes. And statistical studies have found that diabetic patients in Asia have a higher chance of developing renal complications, and about 20-40% of diabetic patients in China have diabetic nephropathy in combination, which has become a major cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Abnormalities in glucose metabolism, diabetes-induced changes in renal hemodynamics, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system are all influencing factors that lead to damage to kidney health.
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic microangiopathy, and is also the first factor affecting irreversible blindness in people of working age. Almost the vast majority of proliferative retinopathy is due to the long-term effects of hyperglycemia, which causes a variety of metabolic processes, all of which can cause damage to the microvasculature, resulting in increased capillary permeability, vascular occlusion, and weakening of vascular support, among other problems. These are the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic neuropathy is a chronic complication of diabetes that may affect central and peripheral nerves, usually the peripheral nerves. In fact, the common diabetic foot is one of the external manifestations of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vascular disease. One of the mechanisms is that high blood glucose makes glucose build up outside the nerve cells, which is broken down into sorbitol and fructose by the relevant enzymes in the body, while the nerve cells do not contain enzymes to break down fructose, which results in the deposition of these two substances in the peripheral nerves, leading to an increase in osmotic pressure in the nerve cells, nerve cell edema and fiber degeneration and necrosis. Therefore, diabetes-induced peripheral neuropathy is also closely related to long-term poor control of hyperglycemia.
The key to reducing the complications of diabetes is "early"!
With the deepening of diabetes research, modern medicine increasingly emphasizes the importance of early detection, early intervention and early treatment of diabetes.
In fact, for glucose metabolism, it would be a better best practice to start strengthening glucose control from the pre-diabetic stage when impaired fasting glucose or abnormal glucose tolerance is detected, to reduce the chances of new onset of diabetes and to minimize complications after subsequent development of diabetes.
What if I know my blood sugar is not normal? If you wait for the typical diabetes symptoms such as drinking, eating, urinating and weight loss before checking your blood glucose, it is still a little late, or we recommend that friends with the conditions, should be conducted annually for blood glucose checkups, especially with a family history of diabetes, or overweight obesity and other high-risk friends, it is more important to strengthen the blood glucose measurement on a regular basis, blood glucose is often not all of a sudden rise in blood sugar, and timely detection of the trend of blood glucose elevation When you find an elevated trend of blood glucose in time, you can intervene and control your blood glucose through dietary control and exercise, which not only reduces the incidence of new-onset diabetes and slows down the process of diabetes, but also has an important significance on the prognosis for many years to come, even if it turns out to be a diabetic problem after a certain period of time.
This word is not out of thin air, China involves 110,000 people screened, through decades of tracking diabetes prevention study - Daqing study, from the data to prove this point, the specific data will not be shared, this large-scale prospective study of diabetes ultimately concluded that: diabetes high-risk groups, as early as possible, to carry out life control The final conclusion of this large prospective study is that early life control interventions in people at high risk for diabetes can significantly reduce the incidence of diabetes, and that people who intervene early in their glucose metabolism continue to experience long-term health benefits after developing diabetes, and have significantly lower rates of macrovascular and microvascular complications than those in the control group who do not actively engage in life control interventions.
Therefore, if you want to control diabetes, reduce the incidence of diabetic complications, improve the quality of life of diabetic patients and life expectancy, as early as possible to the problem of elevated blood glucose early control, early intervention is a very important thing, regular monitoring of blood glucose, blood glucose in the discovery of the trend of elevated blood glucose, as early as possible to strengthen the dietary control and exercise interventions, the blood glucose control as far as possible, even if it develops into a diabetic problem, it also Even if the problem develops into diabetes, it is still important to pay attention to it positively, and control the blood glucose index well with reasonable medication at the same time of life conditioning, in order to reduce the complications and health hazards brought by diabetes to the body better.
What factors are associated with complications of diabetes?
Complications do not necessarily occur with diabetes. If the fasting blood sugar is less than 6 and the postprandial blood sugar is less than 8, there are generally almost no complications. If fasting blood sugar is less than 7 and HbA1c is less than 6.5 it is also possible to be complication free for about twenty years.
The main cause of diabetes complications is high blood sugar, such as fasting blood sugar 8 to 10 or a little higher, may be about five years will cause other diseases. Diabetic patients can adjust the diet to lose weight, appropriate exercise, take hypoglycemic drugs to control blood sugar stabilization, if you still hope to live another twenty years or more should fasting blood sugar less than 7.
Common complications of diabetes are nerve end-stage lesions, macrovascular lesions, and microangiopathy.
1. Retinopathy: the most likely nerve ending lesion with the highest probability of developing. Vision loss at the beginning can lead to blindness in severe cases. Initial diabetes mellitus should carry out fundus examination to facilitate later control to find the progress of the disease changes.
2、Renal lesions: belong to microvascular lesions. Kidney function decreases, even kidney failure. Laboratory urine routine can help early detection.
3、Neurologic lesions: such as numbness of fingers and toes, skin tingling, etc.
4, diabetic foot: macrovascular lesions, such as swelling of the lower extremities, feet appear long-lasting ulcers.
5. Hypertension, cardiovascular lesions.
6. A variety of cancers caused by high blood sugar.
However, the above six complications are only caused by high blood sugar. And the most common diabetes complications: respiratory sleep hypoventilation syndrome, the cause is unknown, the prevalence of this syndrome up to about 70%, that is, diabetic patients sleep with low ventilation, the blood red blood cells carry insufficient amount of oxygen that Osahs, in the blood glucose control is very good will also occur, only the symptoms of light and heavy. The mildest hypoxia is only noticeable once or twice a year. Typical symptoms occur ten or more times a night with hypoxia, triggering multiple awakenings in the middle of sleep. In severe cases, breathing is often interrupted, making it impossible to complete a ninety-minute sleep cycle and requiring: a ventilator or pure oxygen, an oxygen machine, or a temporary blood transfusion to raise hemoglobin levels. Thus, sleep hypoxia is the number one life-threatening complication in diabetics, and there is no cure.

A familiar phrase: "diabetes is not scary, the scary thing is the complications", 3 years, 5 years and up to 10 years or more, if the blood glucose control is not good, let it develop, diabetes complications will become more and more obvious, and the damage to the body will become more and more significant. Long-term blood sugar increases, macrovascular and microvascular damage and endanger the heart, brain, kidney, peripheral nerves, eyes, feet, etc. According to the World Health Organization, diabetes complications up to more than 100 kinds of diabetic complications, is known to have the most complications of a disease.
To address the common complications of diabetes, Dr. Nan summarized the following, which are very common in clinical practice and require high alertness:
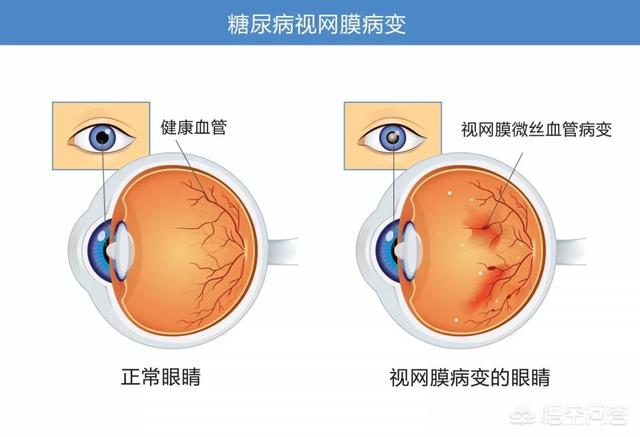
diabetic retinopathy
Patients may feel that their vision is getting blurred and they can't see well, and they may think that it is due to cataracts, but in fact it is the most important manifestation of diabetic microangiopathy, which is a kind of fundus lesion with specific changes, and it is one of the serious complications of diabetes mellitus. It can beEvaluation by fundus examination, it is worthwhile to be alerted that this is an irreversible lesion.
Early detection methods: Regular funduscopic examinations are particularly important from the point of view of preventive treatment.Diabetic patients without retinopathy are recommended to be examined once every 1 to 2 years; patients with mild lesions are examined once a year; patients with severe lesions are examined every 3 to 6 months; and pregnant women need to be examined more frequently. Eye examination items include visual acuity, intraocular pressure, atrial angle, fundus (observation: microangioma, intraretinal hemorrhage, hard exudation, cotton-chip spots, intraretinal microvascular abnormalities, venous beading, neovascularization, vitreous hemorrhage, preretinal hemorrhage, fibrous hyperplasia, etc.) and so on, among which venous beading refers to localized dilatation of retinal veins like beads strung on a string, which is a typical manifestation of diabetes mellitus.
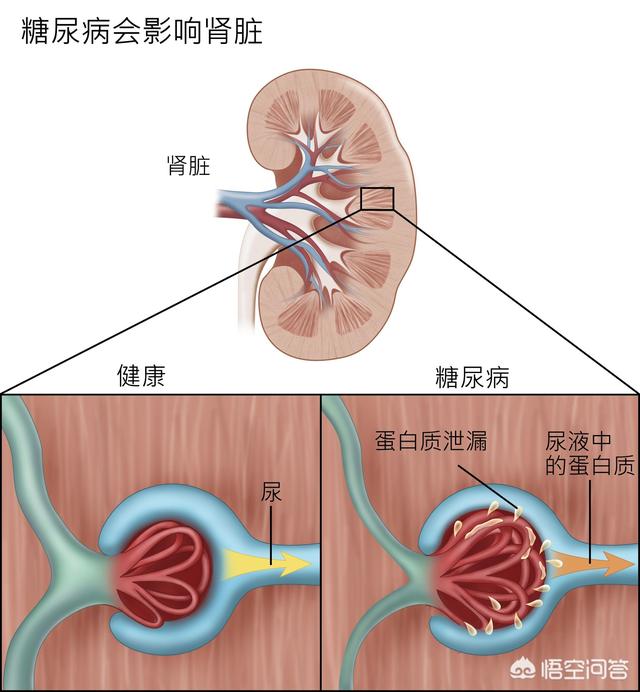
diabetic nephropathy
The incidence of diabetic nephropathy is on the rise, and is now the second cause of end-stage renal disease and a population of potential uremic patients requiring hemodialysis treatment. Due to the complex metabolic disorders present in diabetic patients, once end-stage renal disease has progressed, it is often more difficult to treat than other renal diseases. However, active and appropriate interventions, such as quantitative urine testing for microalbumin and nephroprotective therapy, can significantly reduce and delay the onset of diabetic nephropathy, especially early in the course of the disease.
Early detection methods: Detection of microalbumin level in urine is the most commonly used method for early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathyThe methods of urine retention are (1) retention of urine at any point in time for determination of the albumin-to-creatinine ratio, (2) retention of urine for 24 hours for determination of the amount of albumin, and (3) retention of urine over a period of time (4 hours or overnight) for measurement of the urinary albumin excretion rate. If the results are abnormal, the test should be repeated within 3 months to clarify the diagnosis.
Diabetes Cardiovascular Disease
Diabetes mellitus is a cardiovascular disease equivalent, meaning that patients with diabetes have a significantly increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including diabetic cardiomyopathy and coronary artery disease, which are two common cardiovascular diseases in which not only does the myocardial tissue undergo alterations and degeneration, but also the blood vessels of the heart become narrowed or even obstructed, which can have a serious impact on the treatment of the patient's life and can also be life-threatening.
Early detection methods:For the evaluation of cardiovascular diseases, ECG, cardiac ultrasound and exercise plate examination can be used as safe and reliable means to screen for the above diseases respectively. Electrocardiography is a widely used clinical test for heart disease. ECG can help diagnose cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction and its location, enlargement and hypertrophy of the heart, and determine the effects of medications or electrolytes on the heart, etc. Type 2 diabetic patients need to undergo an ECG once at the time of diagnosis, and then annually thereafter, which can help in the early detection of cardiac pathology.
diabetic foot
Diabetic foot disease is one of the most serious and costly chronic complications of diabetes mellitus, and can lead to amputation in severe cases. Lower extremity vascular disease is one of the most important factors leading to diabetic foot, and peripheral arterial disease is one of the most important factors contributing to podiatry. Patients with severe peripheral arterial disease may present with the typical symptom of intermittent walking pain, but the majority of patients with severe peripheral arterial disease may have foot ulcers without such a symptom or may experience foot lesions aggravated by ischemic lesions following injury to the foot, which lacks sensation.
Early detection methods:Peripheral arterial disease can be detected in time by palpation of the dorsalis pedis artery, which is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery. Using the index fingers of both hands to apply the same pressure, the strength of the dorsalis pedis arterial pulsations on both sides can be sensed, and if the pulsations are significantly weakened or disappear, then it is abnormal.
Patients with diabetes need 1 dorsal foot artery palpation when they are first diagnosed and then every 3 months thereafter.
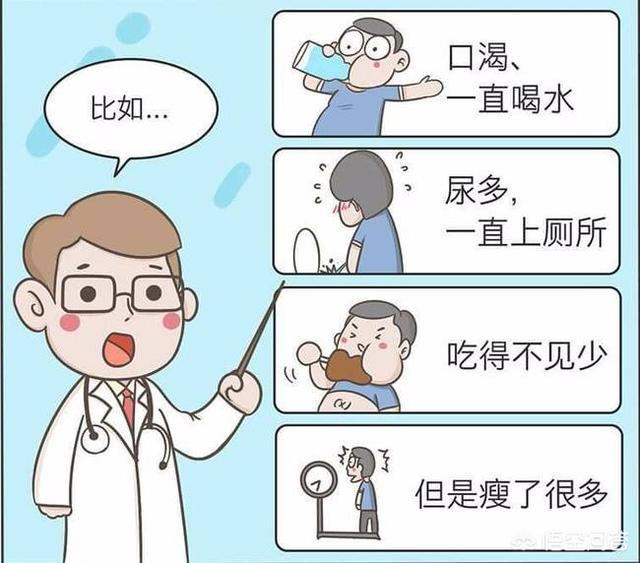
Different types and stages of diabetes have different appearances, ranging from mild and senseless to life-altering; they can be typical symptoms or non-specific and seemingly difficult to associate with diabetes. Typical symptoms are excessive urination, drinking, eating and weight loss.
Polyuria.This is because the efficiency of converting food into sugar in the organism decreases, resulting in increased sugar levels in the blood. The body has to excrete the excess sugar through urine in order to protect itself, resulting in a significant increase in urine output.
Thirst.Increased urination can lead to dry mouth, so don't quench your thirst with sugary drinks, which can increase the sugar content in your blood and aggravate your condition.
Slight weight loss.Being overweight is a risk factor for diabetes, and a slight weight loss may not sound like a sign of diabetes. In fact, there are two main reasons why diabetes causes a slight weight loss: first, some water is excreted in the urine; second, frequent urination also takes away some calories.
Weakness and hunger.Hyperglycemia means that the body is having problems regulating blood sugar. If you eat high-carbohydrate foods (such as refined rice and white flour), insulin will rise, causing a rapid drop in blood sugar. This can cause a person to feel weak and in turn crave more carbohydrates, leading to a vicious cycle.
A feeling of constant fatigue.Constant fatigue is an important sign, which can mean that the food eaten is not being broken down or utilized by the cells. Since the body is not getting the energy it needs, it is tired. people with type 2 diabetes tend to experience these symptoms more slowly as their blood glucose levels rise over a period of time.
Blurred vision.In the early stages of diabetes, the eyes are unable to focus because glucose builds up in the eyes and temporarily changes their shape. About six to eight weeks after the blood sugar stabilizes, the blurred vision disappears and the eye adjusts itself. It is important to note that this symptom in the early stages of diabetes is most often not diabetic retinopathy.
Slow wound healing.Diabetics have elevated blood sugar levels and reduced immune function, leading to a weakening of the body's ability to heal itself.
Tingling feet.Mild nerve damage may occur with elevated blood glucose levels, causing numbness in the feet.
Summarize: Whether it is early detection of diabetes, or to assess the complications of diabetes, the key is through regular physical examination, this is a very important measure, because nowadays the symptoms of diabetes are more and more atypical, only early health checks can find the first signs of the disease, through timely control of blood glucose, you can greatly reduce the occurrence of diabetic complications.
[Focus on health, focus on Dr. Nan]

For diabetes mellitus, although controlling blood glucose is very important, it is not the ultimate therapeutic goal, and the ultimate goal is to stop or delay the development of various complications as much as possible. However, diabetic patients, due to the body sugar, lipid metabolism function abnormalities and disorders always exist, after the disease will inevitably have complications.
Studies show that: after 3 years of diabetes, the complication rate is about 46%; after 5 years of the disease, the complication rate is about 61%; and after 10 years of the disease, 98% of the patients have more or less, more or less serious complications. Therefore, it is important for diabetic patients to have early detection, early intervention and early treatment of complications.
So how can early detection be achieved? Regular checkups are the most important and effective measure, and diabetics should have a more comprehensive checkup at least once a year. Since the root cause of all diabetic complications is damage to the blood vessels, the damage to the blood vessels can be divided into three major areas:
Peripheral neuropathy examination
This is the earliest and most likely to occur in diabetic patients complications, super originating from the damage to the distal small blood vessels of the limbs, often from the numbness of the limbs, pins and needles, burning sensation or ants crawling on the skin and other sensations as a manifestation of the nylon filament and other checks can be carried out annually, or through electromyography, lower extremity ultrasound to determine whether there is damage to the distal nerves, blood vessels, which is the main checkup items to detect and prevent diabetic foot.
Examination of microangiopathy
The blood vessels in the fundus are rich and subtle, representing the microvessels of the organism, and they are also the only blood vessels in the human body that are visible to the naked eye. Therefore, diabetic patients should undergo a fundus examination once a year, such as fundus photography, fundus imaging, etc., which is the most direct and effective method for early detection of microvascular lesions. At the same time, because the structure of human kidney blood vessels is similar to that of fundus blood vessels, if the fundus blood vessels have problems after examination, it suggests that the kidneys also have the same vascular lesions.
Because of this, diabetic patients should be 1-2 times a year urine microalbumin examination, if abnormally elevated, at the same time, fundus examination of blood vessels there are hardening, rupture, hemorrhage, or neovascularization, it suggests that there is an early diabetic eye disease and nephropathy occurs. Early diabetic eye disease or nephropathy can be reversed by intervention, but the term development such as diabetic nephropathy into the 4 uremic stage will be irreversible, patients must rely on dialysis to maintain life.
Examination of large-vessel lesions
This is the most important fatal complication of diabetes and is a key complication to guard against, which generally requires regular checkups depending on the checkup program, for example:
Fasting blood glucose should be checked frequently, the ideal level should be less than 6.1mmol/L, at least should be controlled at 7.0mmol/L or less 2 hours after meal blood glucose should be checked frequently, the ideal level should be less than 7.8mmol/L, at least should be controlled at 10.0mmol/L or less Glycosylated hemoglobin should be checked once in every 3 months, less than 6.5% indicates that the blood glucose control is more satisfactory, if it is more than 7% it means that If it exceeds 7%, it means that the treatment program needs to be adjusted urgently, otherwise the risk of macrovascular damage is very high.
LDL in blood lipids should be tested every 3-6 months, the ideal level should be less than 1.8mmol/L, at least less than 2.6mmol/L Blood pressure should be tested frequently, the ideal blood pressure is less than 120/80mmHg, at least should be less than 130/80mmHg Men's waist circumference should be controlled to less than 85cm, and women's waist circumference should be less than 80cm should be carried out once a year. Carotid ultrasound to check for the presence of atherosclerosis and plaque, and carotid ultrasound to predict and assess the risk and extent of cardiovascular and cerebral and other macrovascular pathologies. In conclusion, diabetes mellitus is a lifelong disease, with the prolongation of the course of the disease, the occurrence of complications is inevitable, but active intervention will be able to greatly slow down the process of the development of complications, so as to achieve the same life expectancy as normal people. To achieve such a result, early detection of complications is necessary for early intervention.
--This answer is organized by Xi'an Dingang Digital Currency Intelligent Quantitative Automatic Coin Speculation Robot (Historical Gains, Data Reconciliation, Live Streaming).
Diabetes, if not properly treated and controlled, can lead to many complications. These include acute complications, and chronic complications. The so-called acute complications are those that can occur in the short term. Chronic complications, on the other hand, usually take several years or even 10 years of illness before they occur.
Let's talk about the acute complications, the common acute complications of diabetes are ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma, these are caused by a sharp rise in blood glucose, for example, many news reports of a diabetic patient, drank a lot of sugar water or cola, short-term glucose pugilistic high, up to 50 μmol / L, which is quite high blood glucose, so high blood glucose, the body can not be utilized, then this will lead to an acute attack of complications, such as the above mentioned ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma Complications such as ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma mentioned above. If resuscitation is not timely, death can occur at any time. These are very serious and rapidly developing complications.
Then there are the chronic complications.
Chronic complications of diabetes, which usually occur after 5 years, can occur in all organs of the body, commonly in the heart, brain, kidneys, nerves, blood vessels, eyes, and so on.
For example, the eyes, diabetic patients, the disease more than 5 years, may occur microvascular lesions, the eyes of the retina inside a lot of small blood vessels, the disease more than 10 years, these small blood vessels lesions, may bleed diabetic retinopathy, at first not serious, the latter can lead to blindness, it must be early control of blood sugar. So if you see a diabetic patient has serious retinopathy, that means his diabetes should be more than 10 years, and these 10 years have not been good control of blood sugar.
There is also kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, and diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. Usually also more than 10 years of diabetes before the development of nephropathy. At first it is only a mild kidney lesion with abnormal urine routine, and then it can gradually develop into kidney failure and uremia. The prevention method is also to control the blood sugar.
Diabetic foot, which is a great concern for everyone, many diabetic feet require amputation, very poor. Minor diabetic foot injuries may be just foot deformities, dry skin and coldness, while serious ones may develop gangrene and ulcers, which are inseparable from the nerves and blood vessels of the foot.
Diabetics can cause many complications. There is only one way to prevent these complications and that is to control your blood sugar properly.
1、Adhere to glucose-lowering drug treatment, or adhere to insulin treatment, to control blood glucose in the appropriate range
2、Frequent retest of blood glucose, there are blood glucose meters at home, often measuring fasting, pre-meal and postprandial, pre-bedtime blood glucose, according to the situation to adjust the treatment program
3, the diet should be controlled, high sugar content of the food should not eat more, or even do not eat. Eat more fresh vegetables
4, maintain due exercise exercise, walking, jogging, swimming are available
5. Protect your feet from injuries, and socks and shoes that fit your feet.
A large body of evidence suggests that people with diabetes have to control their blood glucose stabilization by modifying their diet, exercising appropriately, and taking hypoglycemic drugs.
If blood sugar control is not satisfactory, it is prone to a number of complications over time. However, it must be reminded that these complications do not appear sequentially according to a fixed rhythm of 3, 5 or 10 years, but manifest themselves in different ways according to individual circumstances, commonly:
1. Retinopathy: It starts with vision loss and can lead to blindness in severe cases. Examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist can help with early detection.
2、Renal lesions: decline in renal function, or even renal failure. Laboratory urine routine can help early detection.
3、Neuropathy: feeling numbness in fingers and toes, skin tingling, etc.
4, diabetic foot: feet appear long lasting ulcers.
While knowing the above information can help in the early detection of diabetic complications, no early detection measures for complications can catch up with receiving standardized treatment to prevent them at the root.
I'll post an inspirational one. My neighbor's grandmother is 72 years old and she was diagnosed with diabetes at age 32. She is a pediatrician. Has had a son and daughter both in perfect health. She said that 40 years ago the medical level is very low, often no insulin, no home blood glucose meter, and do not know anything about sugar control knowledge, just at home haphazard control, but she is now in good health. Two years ago, she had problems with her eyes and recovered after surgery. Maybe it is because she is a doctor herself, and she is relatively rational about life, death and old age. She has a very good mindset, unlike people nowadays, who once diagnosed with diabetes, feel that the world is coming to an end and have no courage to live. The key is the mindset.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.