What is diabetic ketoacidosis? What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketosis (DK) and diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) are both the most common diabeticacute complication (medicine), emergency resuscitation is required.
In general, diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetic ketoacidosis are both the result of significant insulin deficiency and inappropriate elevation of gluconeogenic hormones in diabetic patients due to a variety of triggers, leading to symptoms such as hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, ketonuria, dehydration, and electrolyte disorders.

If the symptoms are only ketosis without acidosis, it is called diabetic ketosis (DK).
If it is accompanied by acidosis, it is called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), theDKA is often triggered by acute infections, inappropriate reduction of insulin or sudden interruption of therapy, improper diet, gastrointestinal disorders, stroke, myocardial infarction, trauma, surgery, pregnancy, labor and delivery, and mental stimulation.
Diabetic ketoacidosis as well as diabetic ketoacidosis often present acute attacks, before the onset of polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, etc. If the condition is further deteriorated, the patient will suffer from a drop in blood pressure, unresponsiveness, coma and other problems, and in severe cases, it may even be life-threatening.
For diabetic ketoacidosis patients, when ketone bodies appear in the urine, you need to go to the hospital in time, under the guidance of the doctor, to carry out systematic treatment and treatment, to avoid aggravation of the symptoms and cause ketoacidosis. Generally after the appearance of ketone bodies in the urine of patients, the first thing you need to do is to supplement a certain amount of extra insulin, and then drink a lot of water to replenish the body's lack of water, to accelerate the excretion of ketone bodies and other harmful substances.In those with ketosis alone, the ketones will gradually disappear with fluid replacement and insulin therapy.
If the patient is diabetic ketoacidosis, treatment is divided into the following steps.
1. Replenish fluids to restore blood volume and correct water loss, Saline is recommended as the preferred choice, and the rate of infusion needs to be adjusted according to the patient's degree of dehydration, electrolyte levels, urine output, cardiac and renal function.
2. Supplement insulin to lower blood glucose and correct electrolyte and acid-base balance imbalance.
3. Correcting acidosis.Patients will inhibit lipolysis after insulin injection, which in turn corrects acidosis. Severe metabolic acidosis may cause serious complications such as myocardial damage, cerebral vasodilatation, severe gastrointestinal complications, and coma, which should be treated with appropriate alkaline supplementation.
4. Actively seek out andremove causal factors, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and so on, to aggressively combat complications and reduce morbidity and mortality.

Blood glucose and serum ketone body values should be carefully done during treatment to facilitate treatment.
For diabetics, it is not the diabetes itself that is scary, but the various complications of diabetes. Therefore, patients must pay attention to the disease, strictly control their blood sugar, monitor it on a regular basis, have regular medical checkups, and prevent various complications.
I am Pharmacist Wang, insisting on spreading the knowledge of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases with simple and easy-to-understand words, and dedicating my own small efforts for a healthy China. If you think my answer is helpful to you, please leave a like! In addition, if you still have questions about the common complications of diabetes, welcome to leave a message, we discuss together!
Diabetic ketoacidosis is defined as a positive urine ketone check or an elevated blood ketone check, but there is no acidosis and the pH is normal when checking arterial blood gas analysis.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute complication of diabetes mellitus, with a strong positive urine ketone test, markedly elevated blood ketones, mostly above 4.8 mmol/l, and reduced carbon dioxide binding capacity, ranging from 13.5-18 mmol/l in the mild cases, to less than 9.0 mmol/l in the more severe cases, with a pH of less than 7.35.

Diabetic ketoacidosis is mostly seen in type I diabetes or type 2 diabetes that occurs only after certain triggers, commonly infections, interruption of insulin therapy or improper diet, trauma, surgery, pregnancy and childbirth.
Diabetic acidosis occurs mainly due to the disorder of glucose metabolism, insulin secretion is seriously insufficient, not able to break down and use of blood glucose, resulting in accelerated fat mobilization and decomposition, a large number of fatty acids in the body oxidation to generate a large number of acetoacetic acid, hydroxybutyric acid and acetone.

The main clinical manifestations are polyuria, thirst and fatigue a few days before the onset of the disease, followed by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, often accompanied by headache, lethargy, irritability, deep and rapid breathing, and the odor of rotten apples in the exhaled breath. With the development of the disease, there can be severe water loss, decreased urine output, poor skin elasticity, sunken eyes, decreased blood pressure, and in the late stage, there can be lethargy or even coma, and a few patients show abdominal pain.
 For patients with coma, acidosis, water loss, and shock, all should consider the possibility of diabetic ketoacidosis, especially for those with unexplained consciousness disorder, ketone odor of expiration, and low blood pressure with high urine output, early relevant laboratory tests should be performed for early diagnosis and treatment.
For patients with coma, acidosis, water loss, and shock, all should consider the possibility of diabetic ketoacidosis, especially for those with unexplained consciousness disorder, ketone odor of expiration, and low blood pressure with high urine output, early relevant laboratory tests should be performed for early diagnosis and treatment.
This problem I think so, type one diabetes and type two diabetes they will be ketoacidosis, got diabetic too much or too little will produce ketoacidosis, so what kind of situation diabetic will produce ketoacidosis? Tigers will also sleep, diabetics forget to take their morning medication and injections, go out in the morning and forget to eat breakfast or eat less, this time due to the digestive system into the endocrine breakdown of insulin cells produce resistance, because diabetic insulin cells are relying on medication and insulin needles to break down, however, glucose decomposition can not be entered into the bloodstream renal function is extremely destructive, the human body began to dizziness, the face whitens, the person will pass out! Life is threatened or even death, this is the typical diabetic hypoglycemic ketoacidosis. So; diabetic patients once the medicine and injection to life-long medication and injection, to pay attention to produce hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis, go out with an apple or sugar water, in case of hunger caused by dizziness to drink sugar water. This is the minimum medical knowledge for diabetics.
In diabetics, the body lacks insulin (type II) or has no insulin (type I), and the body cannot utilize the glucose in the blood properly, even though the blood sugar is high. This is when the body mechanism secretes glucagon, which causes muscle and fat to break down with the aim of making glucose; when breaking down fat, ketone bodies are also produced, which consist of three components - acetoacetic acid, beta-hydroxybutyric acid, and acetone. Normally, the body produces a small amount of ketone bodies, which are transported with the bloodstream to the tissues such as the heart, kidneys, and skeletal muscles , which are utilized as a source of energy. The concentration of ketone bodies in the blood is very low, usually no more than 1.0 mg/dl, and ketone bodies are not measured in the urine. However, diabetics are unable to utilize glucose in the blood, coupled with glucagon continues to break down muscle fat, the body is therefore high on blood glucose, ketone bodies are extremely increased, which acetoacetic acid, β-hydroxybutyric acid will cause the body to become acidotic, an abnormal increase in this ketone body is called ketosis, excessive ketone bodies can lead to ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis is a life-threatening acute complication of diabetes mellitus, the main symptoms are fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat, dehydration in severe cases, or even coma, life-threatening, so there are uncomfortable symptoms must be timely to the hospital.
It is very important for diabetics to control their blood sugar to avoid ketosis and ketoacidosis.
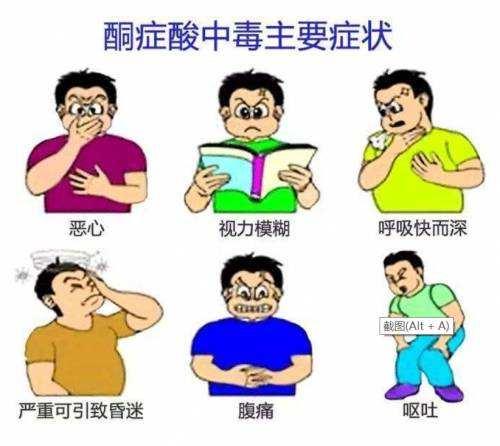
Diabetic ketosis is the most common acute complication in patients with diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a syndrome of severe disorders of sugar, fat, and protein metabolism caused by insufficient insulin and inappropriately elevated glucagon, clinically characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis.
Manifestations of diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is clinically categorized as mild, moderate and severe. If there is only ketosis without acidosis, it is called diabetic ketoacidosis, mild to moderate ketosis, and mild to moderate acidosis; severe is defined as impaired consciousness or acidosis with acid in the serum but no consciousness. Less than 10 mmol / L.
It is characterized by polyuria, polydipsia, polydipsia and increased fatigue. Compensatory disorders, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, frequent headaches, restlessness, drowsiness and other symptoms, shortness of breath, the expiratory process of the apple flavor deterioration of the stage; the further development of the disease, severe water loss, decreased urine output, dry skin and mucous membranes, orbital settling, rapid and feeble pulse, decreased blood pressure, cold extremities, late, various reflexes become blunted or even disappeared, and ultimately become sleepy

Causes of diabetic ketoacidosis
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is prone to diabetic ketoacidosis; type 2 diabetes mellitus may also occur; common causes are acute infections, inappropriate insulin reductions or sudden treatment interruptions, poor diet, gastrointestinal disorders, strokes, myocardial infarctions, traumas, surgeries, pregnancies, deliveries, and mental stimulation.
How Sugar Lovers Recognize Ketoacidosis
The best way to deal with diabetic ketoacidosis is to detect and act on it without taking the level of acidosis in the presence of ketosis, while diabetics should monitor blood ketones or ketones. But due to conditions, many diabetics are unable to do this. Therefore, diabetics and their family and friends need to be aware of the different clinical signs of diabetic ketoacidosis for timely detection and early treatment. Efforts to avoid diabetic ketoacidosis in patients have been around for a long time and have even tragically been saved after surgery.
How to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis
Various common causes of stress diabetic ketoacidosis, including acute infections, inappropriate insulin reduction or sudden treatment interruptions, poor diet, gastrointestinal disorders, stroke, myocardial infarction, trauma, surgery, pregnancy, and labor and delivery Thus, when the above problems occur in diabetic patients, for example, psychological stimuli, special attention needs to be paid to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Long-term blood glucose control is the most effective means of preventing diabetic ketoacidosis. As long as a person with diabetes can control their blood glucose and check their blood glucose frequently, the person with the condition will be tested for bleeding ketones or urinary ketones immediately if their blood glucose exceeds 16.7 mmol / L. Unconditional contact with a doctor or immediate medical attention can effectively prevent diabetic ketoacidosis.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.