How is diabetes tested? What are the symptoms?
As an endocrinologist I am happy to answer your questions. Diabetes mellitus is characterized by a diagnosis of blood glucose in the plasma that exceeds the criteria that we define. That's why the blood glucose check is very important, but in many diabetic patients, his fasting blood glucose is normal, so there are a lot of people who may have diabetes but just checking the fasting blood glucose could potentially miss the diagnosis. So I think if you want to screen for diabetes, it's best to check fasting, 2 hours postprandial and glycosylated hemoglobin so that basically you don't miss the diagnosis, and if you're still not sure you can only do a glucose tolerance test.
Typical symptoms of diabetes include excessive drinking, excessive urination, excessive eating, weight loss, and blurred vision, but type 2 diabetes can be asymptomatic, so diagnosing diabetes cannot be based on symptoms. However, type 1 diabetes often has more typical symptoms, and some people may also have digestive manifestations such as malaise and vomiting, which debuts with ketoacidosis. Check your blood sugar if you feel you are at risk for diabetes.
I kind of had this idea in the back of my mind that we could promote theShared blood glucose meters, making it very convenient for everyone to check their blood sugar. I don't know what you think of this idea, is it worth pushing? Welcome to leave a comment at the bottom. Because we have 30-50% of pre-diabetics in this country who don't realize it themselves, and this is the group that has the most hope for reversal.
Welcome to my headline, I try to answer your questions in simple and efficient language!

First, what is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, is caused by defective insulin secretion or its impaired biological action, or both. The prolonged hyperglycemia present in diabetes leads to chronic damage and dysfunction of various tissues, especially the eyes, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, and nerves.

Second, what are the signs of diabetes?
1. Excessive drinking, urination, eating and weight loss
The typical "three more and one less" symptoms of severe hyperglycemia are most common in type 1 diabetes. When ketosis or ketoacidosis occurs, the "three more and one less" symptoms are more obvious.
2. Fatigue and obesity
It is mostly seen in type 2 diabetes mellitus. type 2 diabetes mellitus is often preceded by obesity, and if it is not diagnosed in time, there will be a gradual weight loss.
Third, how is diabetes tested?
Top 9 tests and reference values for diabetes, bookmark it to stop being confused by labs!
1. Urine sugar
Normally, urine contains only trace amounts of glucose and a urine glucose test is negative.
When blood glucose increases to a certain level (≥8.96 to 10.08 mmol/L), the renal tubules of the kidneys are unable to absorb all of the glucose in the urine, theIt's a positive for urine sugar.The labs are written with“+”The number indicates.
In general, urine glucose reflects blood glucose, but urine glucose is also influenced by many other factors (which ones can be entered in the platform dialog box: n1), which sometimes do not coincide exactly with blood glucose.
2.hypoglycemia
Fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/Land/orBlood glucose ≥11.1 mmol/L 2 hours after mealcan be diagnosed asdiabetes;
A fasting blood glucose of 6.1 to 7.0 mmol/L is considered impaired fasting glucose (IFG), and a 2-hour postprandial blood glucose of 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L is considered impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and are collectively referred to aspre-diabetes。
3.Glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
Normal values: fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1 mmol/L, blood glucose peaks at 0.5-1 hour of oral glucose, peak <8.89 mmol/L, blood glucose <7.8 mmol/L after 2 hours, blood glucose returns to normal after 3 hours.
The glucose tolerance test is of great diagnostic value in diabetes.
For those suspected of having diabetes mellitus with normal or suspiciously elevated fasting blood glucose and suspiciously elevated 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, a glucose tolerance test must be relied upon to make the final diagnosis.
4.Glycated hemoglobin and glycated serum protein
Glycated hemoglobin reflects the average blood glucose level in the 2 to 3 months prior to blood collection, and its normal value is 4% to 6%.
It is not affected by an occasional rise or fall in blood glucose, so measurement of glycated hemoglobin provides a more comprehensive picture of the level of blood glucose control over time. Currently, China has set the standard for glycosylated hemoglobin for diabetic patients at 6.5% or less.
5.Pancreatic Islet Function Measurement Test
It is primarily used to understand the functional status of pancreatic islet B cells, to assist in determining the type of diabetes and to determine treatment options.
Usually included:
● Insulin release test: 75 grams of glucose or two buns were taken orally, and plasma insulin levels were measured before and after meals.
The normal fasting insulin value is 5 to 25 microunits/mL, rising to 5 to 10 times the fasting level 1 hour after sugar intake and returning to the fasting level after 3 hours.
● C-peptide release test: Fasting plasma C-peptide values in healthy individuals are 0.8 to 4.0 micrograms/liter, increasing 4 to 5-fold 1 to 2 hours after a meal, and basically returning to fasting levels after 3 hours.
6. Urine microalbumin (UAER)
Urine microalbumin measurement is a sensitive indicator of early kidney damage, and urine microalbumin over 30 mg/24 hours, or 20 micrograms/minute, is indicative of early kidney damage.
At this time, if you can strictly control blood glucose and blood pressure and cooperate with other treatments, most of the kidney function can be restored to normal.

7.Blood, urine and body
Due to severe insulin deficiency and impaired glucose utilization, severe glucose patients suffer from lipolysis, which results in the production of large amounts of ketone bodies and their accumulation in the blood, causing diabetic ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening if it is not detected and treated in a timely manner.
A reliable test is to measure the level of beta-hydroxybutyric acid in the blood, which exceeds 0.5 mmol/L, suggesting diabetic ketosis.
8.Diabetes-related antibodies
These include glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody (GADA), islet cell antibody (ICA), and insulin autoantibody (IAA), which are primarily used for typing diabetes.
All three antibodies are negative in healthy individuals as well as in type 2 glycosurfactors, while type 1 glycosurfactors tend to be positive, with glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies being the most diagnostic, with a positive rate of up to 90% and persisting for many years.
9. Blood Lipids
Lipids in glycemic patients should be controlled at: total cholesterol <4.5 mmol/L, triglycerides <1.5 mmol/L, HDL cholesterol >1.1 mmol/L, and LDL cholesterol <2.6 mmol/L.
Warm Tip:
It should be noted that the normal values of the indicators may not be exactly the same because the methods and conditions of diabetes testing vary from one medical unit to another.
Follow me and share health every day! #HealthyLifeManager
Diabetes is a common chronic disease and is also one of the major killers of coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction and other diseases in our country. Because sugar is sweet, diabetes is also called the sweet killer. About diabetes, it is estimated that most people have heard of, but the knowledge about diabetes, many people are still half-understood, today we will walk into diabetes, take a look and diabetes related to those knowledge.
I. What is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the pancreas secretes insulin in a dysfunctional manner, or the insulin secreted is dysfunctional, resulting in abnormal blood sugar metabolism in the body. Because of the abnormal metabolism of sugar in the body, the patient has elevated blood sugar and urine sugar, which in turn causes a series of complications.

Second, what are the symptoms of diabetes?
A lot of diabetes can be asymptomatic and is only detected by an elevated blood sugar during a medical checkup or when diabetes is being treated for another condition. However, there are still many diabetes that have symptoms. For example, the common diabetes symptoms are mainly three more and one less, which means eating more, drinking more, urinating more and losing weight all the time. That is what we often call the three more and one less symptoms.
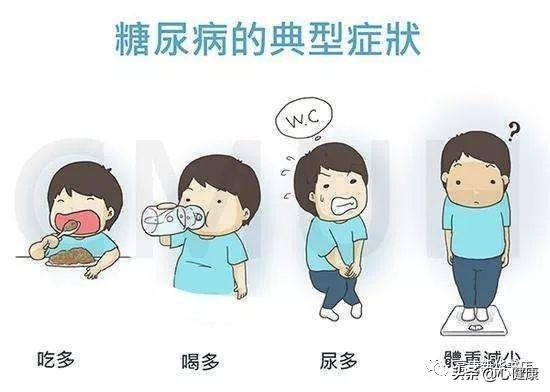
Third, how to check out diabetes?
Most diabetes can be diagnosed with a single blood glucose measurement, but when a patient's blood glucose is right on the verge of a diagnosis of diabetes, more things need to be tested to confirm the diagnosis. For example, glycated hemoglobin, urinalysis, monitoring of fasting and postprandial blood glucose, and glucose substitution tests are performed to clarify whether or not the patient is diabetic.

IV. How can diabetes be prevented?
Diabetes is preventable! To prevent diabetes, the main thing is to keep your mouth shut and your legs open, stay away from bad habits, and control your weight. Only by keeping your mouth shut and exercising properly can you reduce the likelihood of diabetes.
Diabetes is not scary, what's scary is having diabetes and we don't know it, or even knowing it's diabetes and we don't control it. That's what's scary. See what I mean? Follow us and get updated science pushed to you every day!
How is diabetes tested? What are the symptoms?
More than 100 million people in China have been diagnosed with diabetes, and nearly as many have diabetes that goes undetected and undiagnosed. Because these people have mild diabetes or no obvious symptoms, the diagnosis is overlooked and delayed. Understanding the clinical signs of diabetes can help patients recognize that they have diabetes at an early stage.
1. Oral symptoms:The presence of dry mouth, thirst, oedema of the mucous membranes inside the mouth, and burning sensation are most often precursors to the development of diabetes mellitus.
2. Changes in body shape:A recent unexplained weight loss from a previously fat person.
3. Vision loss:Diabetes mellitus can cause acute retinopathy and result in vision changes, especially noteworthy in middle-aged people.
4. Itchy skin with numbness of hands and feet:Particular attention should be paid to recurrent skin or vulvar infections, such as folliculitis, vulvitis, and foot odor, especially in women with pruritus ani. Diabetes can also cause peripheral neuritis, with numbness of the hands and feet, burning sensation, ants sensation, and walking as if stepping on cotton pads. In later stages, hyperpigmentation occurs and the nails become thicker. The skin breaks down and ulcers do not heal.
5. Urinary tract infections and others:The deposition of urinary sugar in the kidneys causes hematuria. It leads to acute pyelonephritis. This causes the patient's immunity and resistance to decline. Diabetes mellitus can also cause plant nerve disorders, resulting in gastrointestinal dysfunction, diarrhea, constipation. The use of antibiotic treatment is ineffective. Especially in middle-aged men, sudden impotence of unknown origin should be alert to the possibility of diabetes.
The above performance may be the first sign of furunculosis, should be taken seriously, and regularly go to the hospital to draw blood for fasting blood sugar, to facilitate early detection, early diagnosis, early treatment.

There are also some that fall under complications. For exampleThe skin is scratchy and prone to boils, and there is also a manifestation called anterior tibial black spot.A black patch on my leg when I touch it. It doesn't go away quickly, and before it does, there's another patch, another black one. The front of the leg is black. Many diabetics have this. There is also poor vision. You can't see well from far away or near, and it doesn't necessarily have to be an ophthalmic complication. Rather, because the blood sugar is high, the eyes are victimized, and the patient always can't see clearly. Of course there are some complications, like cataract, retinopathy. There are also complications of growth and development, such as in children with diabetes, which affects growth and development. Don't give up on these clues, in fact, as long as there is diabetes, there is nothing you can't think of, nothing you can't find out, and nothing you can't find out.It's easy to find out if you want to check for diabetes, just go to the hospital and find out with a drop of blood, don't delay.
I am Pharmacist Wang, insisting on spreading the knowledge of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases with simple and easy-to-understand words, and dedicating my own small efforts for a healthy China. If you think my answer is helpful to you, please leave a like it! In addition, if you still have questions related to diabetes, welcome to leave a message, we discuss together!
Glucose tolerance, decreased insulin secretion or resistance testing
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.