Does every diabetic have complications?
 Diabetes is a lifelong disease that requires treatment throughout life, and with diabetes, I believe sugar lovers have heard the saying that diabetes itself is not scary, but the complications of diabetes, which are the direct cause of the eventual death of diabetics.
Diabetes is a lifelong disease that requires treatment throughout life, and with diabetes, I believe sugar lovers have heard the saying that diabetes itself is not scary, but the complications of diabetes, which are the direct cause of the eventual death of diabetics.
So, do you all get complications from having diabetes? The answer is yes. It's a bit cruel, but it's true. In fact, it's as much a part of life as "not aging" and a natural part of the disease process.
There is this set of statistics
The chance of developing complications is more than 46% for diabetics over 3 years old, more than 61% for diabetics over 5 years old, and more than 98% for diabetics over 10 years old.
Looking at such figures, diabetics may think it is too demoralizing, what is the point of treatment if this is the case? This is a big mistake, first of all, there are many kinds of complications of diabetes, it can be said that diabetes is the source of all diseases, the resistance of diabetic people will be reduced, for example, easier than others to catch a cold is also a complication of diabetes.
So our goal in treating diabetes is to improve our own resistance to disease and to stop or slow down the development of various complications as much as possible. Just like we can't stop aging, but we can slow down the time and speed of aging through various methods.
Therefore, there is no need for diabetics to worry about the complications that will eventually occur, as long as they try to do what they should do, can effectively delay the occurrence of complications, and do not give themselves regrets, is the biggest beneficiary. For this reason, life should be done:
Scientific diet and reasonable exercise
Keep blood glucose as close as possible to acceptable ranges: fasting blood glucose under 8 mmol/L, two-hour postprandial blood glucose under 10 mmol/L, and glycosylated hemoglobin under 6.5%.
Do your best to avoid severe hypoglycemic events; one hypoglycemic event is more harmful than 100 hyperglycemic events.
Keep a close eye on lipids and blood pressure; the combination of the three highs will promote the rapid onset of various complications.

Regular testing of liver and kidney function, especially urine microalbumin, is significant for early detection of renal complications.
Regular examination of the fundus, the only blood vessel in our body that can be seen with the naked eye, is important for detecting early vascular damage and evaluating systemic lesions.
Do not exclude insulin therapy, diabetes caused by insulin deficiency and insufficiency, what is missing to supplement what is the most targeted treatment, and help to protect the function of the remaining pancreatic islets.
I hope this answer can help you, click on the attention of the daily listening to health, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge!
Thanks for the invite. It's not necessarily.
Complications are more dangerous than diabetes itself
This is a good question. Not everyone with diabetes will have complications, and good blood sugar control can greatly reduce the risk of complications.The cause of death in most diabetic patients is not actually the disease itself, but rather the result of complications, especially cardiovascular and renal disease.Clinical data show that about 10 years after the onset of diabetes, 30% to 40% of patients will experience at least one complication, and once complications arise, it is difficult to reverse them with medication. However, there are still many patients who do not pay enough attention to the control of blood glucose, or rely on medication and ignore lifestyle changes, resulting in unstable blood glucose levels and a much higher risk of complications.
What is the pathogenesis of diabetic complications?
Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus include microangiopathy (diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy), macrovascular disease (coronary artery, cerebrovascular, peripheral vascular) and neuropathy. The pathogenesis of diabetic complications is complex, and in 2004 Brownlee et al. proposed the doctrine of oxidative stress mechanism, which means that when the body is subjected to various harmful stimuli, the body produces too many free radicals, and the oxidation level exceeds the capacity of the body's antioxidant system and leads to tissue damage. In the case of hyperglycemia, the antioxidant response is inhibited and the glycolytic oxidative response is increased, which ultimately leads to DNA damage, cellular dysfunction, and diabetic complications. In a nutshell.Fluctuating hyperglycemia as well as persistent hyperglycemia can trigger complications in diabetics.
Besides taking medication, what else do I need to do on a daily basis to control my blood sugar?
1. Choose carbohydrate foods carefully
Having diabetes doesn't mean you have to completely refuse carbohydrates. Choose carbohydrates that break down slowly in the body and provide a steady supply of energy, such as whole grains, legumes, nuts, and fresh vegetables and fruits. Yes, fruits are sweet, but they can still be consumed by diabetics. The main thing is to control the right amount of carbohydrate intake at every meal.
2. Lose weight if you need to
If the patient is overweight, losing just a few pounds can also improve the body's ability to utilize insulin, which helps with blood sugar and improves blood pressure and lipid levels. In addition to not exercising enough, the patient's energy intake is usually excessive. In the beginning, try reducing excess fat, sugar and energy in the diet first - for example, by replacing red meat with fish and not drinking beverages.
3. Getting enough sleep
Sleeping too much or too little can increase appetite and enhance cravings for high-sugar foods. This can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of complication episodes, such as heart disease. Therefore you should get seven to eight hours of sleep every night. If you suffer from sleep apnea, then treating it will improve your sleep and lower your blood sugar levels.
4. Adherence to exercise
Choose your favorite activity - walking, dancing, riding or just walking back and forth while on the phone. Exercise for half an hour a day; gradually if necessary. Exercise reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, lowers cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and keeps weight from rising. Exercise also relieves stress and may help reduce the intensity of diabetes medication.
5. Monitor blood sugar daily
Checking your blood glucose levels can help you avoid diabetes complications, such as nerve pain, or prevent them from getting worse. Checking your blood sugar also helps you understand how food and exercise affect you and whether your treatment plan is working. Your doctor can help you set a target blood sugar range. The closer you get to your target range, the better your body will feel.
6. Stress management
After developing diabetes, stress can also cause blood sugar levels to rise. Both physical and mental stress should be avoided at all costs. Learn coping skills for getting along with others. Relaxation techniques such as breathing exercises, yoga, and meditation are especially effective if you have type 2 diabetes.
7. Eat less salt
Reduce the amount of salt you consume in your diet; this will help lower your blood pressure and protect your kidneys. Even if the food on your plate may not be salty enough, don't add more salt. Avoid convenience foods and choose fresh ingredients whenever possible. When cooking, use herbs and spices instead of salt for flavor.
Adults 51 years of age and older, as well as patients with high blood pressure, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease should talk with their doctor to determine the extent to which they should reduce their sodium intake. Typically, patients with diabetes should reduce their sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day, although their doctor may recommend further reductions beyond that.
8. Controlling the risk of heart disease
Heart disease is a serious complication of diabetes. Monitor your risk of developing the disease in real time by checking the following points:
Glycated hemoglobin level.. This index measures average blood glucose control over a recent 2-3 month period. Patients may need to be checked once or twice a year. Talk to your doctor about setting a goal.
cholesterol. Goal: 140/80 mm Hg or less.
blood lipidObjectives. Targets: LDL cholesterol less than or equal to 100 mg/dl or or less than 3 mmol/L; HDL cholesterol greater than 40 mg/dl or 1 mmol/L for men and 50 mg/dl or 1.2 mmol/L for women; triglycerides less than 150 mg/dl or 1.7 mmol/L.
9. Attention to bruises and abrasions
Diabetes increases the risk of infection and slows healing, so treat even small cuts or scrapes quickly. Clean the wound properly and dress it with an antibacterial ointment and a sterile bandage. If the wound doesn't get better in a few days, see a doctor. Check your feet daily for blisters, scratches, sores, redness or swelling. Moisturize your feet to prevent dryness and cracking.
10. Smoking cessation
Diabetics who smoke are twice as likely to die prematurely than non-smokers. Quitting smoking is good for the heart and lungs. It also lowers blood pressure and reduces the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, nerve damage, and kidney disease. Seek help from your doctor to quit smoking.
11. Choose superfoods and say goodbye to super-sized portions
There is no such thing as a purely diabetic diet. But there are some dietary principles to keep in mind: choose foods such as berries, potatoes, fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and dark green leafy vegetables. Read food labels and avoid saturated and trans fats. Choose mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as olive oil and flaxseed oil.
12. Go to the hospital regularly for checkups
Go to the hospital two to four times a year. More frequent visits may also be needed if there is insulin being used, or if you need help balancing your blood sugar levels. You will also receive a full body and eye exam once a year. Patients should receive eye scans, nerve as well as kidney damage and other complications. Visit the dentist twice a year. And, be sure to tell everyone who provides health services to you about the fact that you have diabetes.
I am glad to answer your question, diabetics do not necessarily get complications, the key still lies in personal control. Some people with diabetes feel that if they have diabetes, complications will find them sooner or later. Although many people who have diabetes will have complications to varying degrees within 5 or 10 years. But this is ultimately caused by lack of control.People should not be misled by such negative perceptions because blood glucosePeople with good control have not experienced complications for even a decade or more.
The first and foremost point for sugar lovers to stay away from complications is to control their blood sugar. Keeping blood sugar within the normal range is the first line of defense against complications, and can largely reduce the damage caused by blood sugar fluctuations. In addition to daily blood glucose monitoring, sugar users should also regularly monitor glycosylated hemoglobin, which is a reflection of blood glucose control "gold standard", doctors recommend that sugar lovers keep their glycosylated hemoglobin below 7%.
Of course, it's not always the case that if your blood sugar is under control, you won't have complications, and there are several other indicators that sugar lovers should be aware of.
1. Weight control. Obesity is simply the root of all evil, and it is a risk factor for many chronic diseases. Reducing weight to within the normal range reduces insulin resistance, can reduce blood sugar levels overall, and facilitates blood pressure and lipid control.
2. Control blood lipid. Lipid disorders are a major cause of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, control of blood lipids, mainly in the control of high-fat and high-cholesterol food intake.
3. Control blood pressure. Studies have found that diabetics are often accompanied by high blood pressure, which increases the risk of complications such as stroke, heart disease, kidney disease and eye disease.
Not only to control the three highs, sugar lovers also need to have regular checkups every year, including eye exams, glycosylated hemoglobin, microalbumin and so on. Regular checkups help to detect early complications, and the earlier the treatment, the better the outcome and the lower the financial cost.
So it's still a long way to go for sugar lovers who don't want to get complications. Although it seems to be more difficult to adhere to, but for the sake of their own health, I believe that the vast majority of people are willing to discipline themselves, go for it, sugar lovers!
Sugar man health network, a temperature control of sugar platform, welcome to pay attention to the questions and answers!
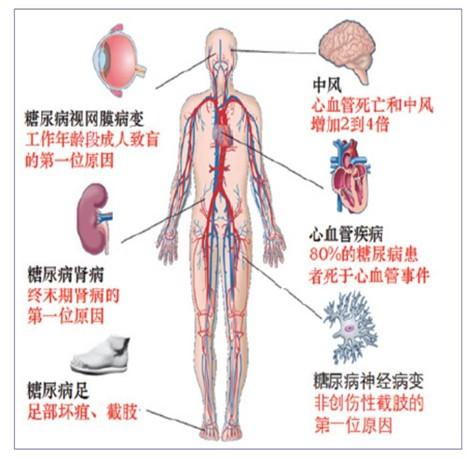
To answer this question it is first necessary to clarify what exactly are all the complications of diabetes?
Complications of diabetes mellitus (DM) are categorized into acute and chronic complications
I. Acute complications:
1, diabetic ketoacidosis: DM patients due to absolute or relative insulin insufficiency and excessive ketone body production and acidosis. When the patient urine ketone bodies or blood ketone bodies higher than normal for ketosis. On this basis, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, abdominal distension, abdominal pain and other symptoms for ketosis; such as the development of acidemia (PH value decreased) for ketoacidosis.
2. Non-ketotic hyperosmolar diabetic coma (hyperglycemic, hyperosmolar syndrome HHS): It is characterized by patients with severe hyperglycemia, blood glucose greater than 33.3 mmol/L, dehydration, and elevated blood osmolality greater than 320 mmol/L, but no or only mild ketosis. It occurs mostly in milder patients with type 2 DM, especially in the elderly, and is easily missed and misdiagnosed, with a mortality rate of 25%-70%.
3, lactic acidosis: lactic acid is the product of anaerobic metabolism of glucose, elevated blood lactate and cause acidosis, called lactic acidosis.
II Chronic Complications:
1, Diabetic retinopathy: fundus microangiopathy caused by DM.
2, diabetic nephropathy: diabetic nephropathy is a kind of microangiopathy, is one of the common DM complications
3, diabetic neuropathy: there are three main types: distal symmetric diabetic neuropathy, such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy, insidious onset, often symmetrically distributed, progressive exacerbation; focal neuropathies, such as cranial neuropathy, trunk neuropathy; autonomic neuropathy, such as gastric paralysis, painless cardiac ischemia, and so on.
Knowing these complications of DM, do all diabetic patients have complications? Generally DM reaches ten years before complications become apparent,. A proportion of DM patients have no complications despite a history of diabetes for many years, while some DM patients have more serious complications despite their mild disease and short history. What causes this? Among the risk factors related to the development of diabetes, some are unavoidable such as: genetic factors, age factors, environmental factors, and so on. Others are controllable such as obesity, poor lifestyle, lack of exercise. Strict glycemic control, good lifestyle and reasonable exercise can effectively delay the onset of diabetes complications. If diabetes is preventable. Diabetes complications are even more preventable. In other words diabetes can be prevented and diabetic complications can be delayed. Acute complications of diabetes are completely preventable.
By Jing Yun Zhang in Fengtai Hospital, Beijing, member of Pharmacy Network, July 11, 2018
The authoritative interpretation of Pharmaceutical Affairs, unauthorized reproduction, plagiarism will be punished.
As we all know, there is no cure for diabetes, and complications often occur in various tissues, especially in the eyes, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, nerves, etc., which seriously jeopardize people's health. So, does every diabetic suffer from complications?
In fact, this question cannot be answered in a "one-size-fits-all" manner. The key to whether a diabetic will get complications lies in personal control, and people with good blood sugar control may not even have complications for more than a decade.
Keeping blood glucose within the normal range is the first line of defense in preventing complications, and can largely reduce the damage caused by blood glucose fluctuations. Therefore, in addition to daily blood glucose monitoring, sugar users should also regularly monitor glycated hemoglobin, which is the "gold standard" for reflecting blood glucose control, and doctors recommend that sugar users keep their glycated hemoglobin below 7%.
Of course, it's not always the case that if your blood sugar is under control, you won't have complications, and there are several other indicators that sugar lovers should be aware of.
1. Weight control. Obesity is the root of all evil, and it is a risk factor for many chronic diseases. Reducing weight to within the normal range reduces insulin resistance, can reduce blood sugar levels overall, and facilitates the control of blood pressure and blood lipids.
2. Control blood lipid. Lipid disorders are a major cause of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, and controlling blood lipids mainly lies in controlling the intake of high-fat and high-cholesterol foods.
3. Control blood pressure. Studies have found that diabetics are often accompanied by high blood pressure, which increases the risk of complications such as stroke, heart disease, kidney disease and eye disease.
In addition, sugar patients need to have regular annual checkups, including eye exams, glycosylated hemoglobin, microalbumin, and so on. Regular checkups help to detect early complications, and the earlier the treatment, the better the outcome.

Click on the bottom of the page [Learn More] to see more answers or ask the doctor a question for free!
Follow "Family Doctor Online" headline, more health Q&A easy to see~~~~
Thanks for the invite!
Not necessarily, not every diabetic will develop complications. We always say that diabetes is not scary, it's the complications that are scary because they can kill you. So if it is detected early, prevented early, and blood sugar control is smooth, there will be no complications.
China's diabetes to type 2 diabetes mellitus, accounting for 95%, more than half of the type 2 diabetes, the symptoms are not obvious, especially in the middle-aged overweight or obese people, mostly light patients, mostly for some kind of complications or accompanying symptoms to go to the doctor, or in the health care center was detected, so that if these light patients are not always vigilant, will be very easy to be underdiagnosed. So that later long-term blood sugar instability for many years, resulting in complications. In addition, there is also a part of the people, after the examination found that the blood sugar is very high, the doctor prescribed hypoglycemic drugs, told him to go home to pay attention to dietary control, but many people do not care, do not care about the main reasons are as follows.

① Feeling that you are still young and that illness and death are far away, or feeling that it is impossible for these things to happen to you.
② Because the symptoms are mild and don't affect your work, study, food or drink, you don't pay attention to them.
③ Lack of health knowledge about diabetes, poor health awareness, do not value life, think that it is predestined
④ Long-term disinterest, years of poor glycemic control, and then attention when complications arise, when it's too late
So it's about your health, put it on someone else and think it's a joke, but put it on yourself and it's a tragedy.
For diabetes prevention do.
① Develop good living habits, balanced diet, adequate sleep, moderate exercise, no smoking and alcohol, and maintain a good state of mind.
② Care and manage your weight, if you are in overweight or obese you need body control.
③For those who are over 40 years old and overweight or obese, it is important to remember to have annual medical checkups to detect problems and provide timely management and treatment.
④When you inadvertently find out that your blood glucose is high during a physical examination, even if you don't have any symptoms, don't ignore it and take immediate action to control your sugar.
⑤ Because of the fluctuation of blood sugar when the blood sugar is high, this time the blood sugar is high point, has not entered the diabetes, this section is called the pre-diabetes area, if you do not pay attention to, three years and four years, you quickly enter the diabetes, if it is already diabetes, you do not care about it, do not control it, seven years and eight years you produce complications, from high blood sugar to complications is a certain amount of time, to you to leave ten years of time you do not care about it, then you can not blame the God is unfair.
(6) As long as you care a little bit and don't care too much, and your blood sugar is controlled smoothly, even if you have diabetes, you can live just as long as a normal person, too.
Thanks for the invitation! Diabetes is a deficiency of spleen and kidney yang, and there are two types of diabetes. One, Yin deficiency and fire type, two, qi and yin deficiency type. Yin deficiency and fire exuberance eat more, fast hunger, thirst, emaciation, polyuria, constipation, dysentery. These complications. The qi and yin deficiency type, obesity, fatigue, dissipation without thirst, yellow skin, face oil, these complications. Thank you!
Hello! Nourish thought that, in theory, it is possible to live without diabetic complications. However, in practice, the Nutritionist can only apologize to say that more or less, diabetic complications can occur.
1. Ideal state
We all know that the reason why diabetes has complications is because of poor blood glucose control, often high or low. If the blood sugar is too low, it is an acute complication, at the drop of a hat, by hypoglycemic coma possible.
Well, if we can control our sugar in time when diabetes first appears, and always keep our blood sugar within the normal range. Then surely there would be no diabetic complications.
2. The actual situation
In our actual life, sugar lovers remember, how they were found out to have diabetes?
Isn't it either discovered by a physical exam or discovered because of complications. That means that before diabetes is detected, the abnormalities in blood sugar have already caused some damage to the blood vessels.
And it's hard to keep your blood sugar at normal levels all the time in your daily life. Anyone can give themselves a break, have a cold or something, etc. This can lead to blood sugar overshooting. This can lead to blood sugar overshooting, and in the long run, complications are bound to occur to a greater or lesser extent.
Therefore, in the opinion of the health gentleman, diabetics should try to delay the emergence of complications. For example, 70-80 years old diabetes complications, that means you control sugar very successful!
Finally, I wish all of you, diabetics, to stay away from complications!
I hope the above suggestions can help you, get more information about diabetes, please pay attention to the health care fine-tuning!
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. Long-term metabolic disorders can cause multi-system damage, leading to chronic progressive lesions in multiple tissues and organs such as eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, nerves, etc., and complications, which can seriously jeopardize the life and health of patients. Whether diabetic patients will develop complications is related to the patient's blood glucose control, the duration of the disease, and their own physical status and other factors. Next, I will popularize the complications of diabetes for you.

What are the causes of diabetic complications?
Diabetic complications are divided into acute and chronic complications. Acute complications are mainly caused by high blood glucose, which leads to metabolic disorders, resulting in imbalance of the body's water, electrolyte and acid-base balance; while chronic complications are mainly caused by the activation of multiple pathways and the increase of various reaction products.
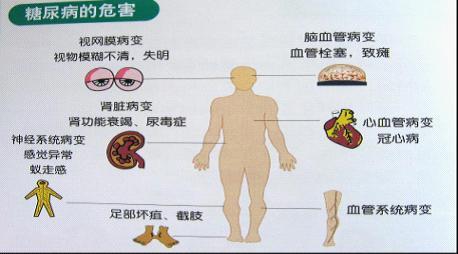
What are the common complications?
- Diabetic ketoacidosis:The most common acute complications of diabetes, mainly manifested as "three more and one less" symptoms worsening, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, polyuria, dry mouth, headache, breathing deeply and quickly exhaled gas has a "rotten apple" smell. It is necessary to send to the hospital as soon as possible.
- Microangiopathy:The main ones are diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Long duration of disease, poor glycemic control, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, and genetic background are the main risk factors
- Diabetic foot:Manifestations include foot ulcers, infection and deep tissue necrosis.in less severe casesfor foot deformities, dry and cold skin, etc..in extreme casesUlceration and necrosis of the foot. Depending on the situation, amputation is required.
- Neuropathy:The main ones are ischemic stroke, accelerated brain aging, Alzheimer's disease, feeling numbness and pain in the hands and feet, and abnormal acceleration of the heartbeat at rest.
How can I prevent complications?
- Low-salt, light foods, abstaining from late nights, excessive hard work, sedentary behavior, and developing healthy living and eating habits.
- Actively cooperate with the treatment, adhere to regular and on-time medication, and regularly measure blood glucose at home to keep it under control.
- Regular hospital follow-ups to check the functional status of the eyes, kidneys, brain and other organs.
- Maintain a positive and optimistic mindset towards a correct and objective view of diabetes.

Summary:Diabetes is not scary, if we know enough about it, we can live a good life as long as we cooperate actively with the treatment. If you are close to someone with diabetes, please forward my popular science articles, I hope to give them some help and inspiration.
I am Dr. Zhao who insists on popularizing medical knowledge, and if you are interested in my content, please like and follow me. Your support is my greatest motivation to create.
Thanks for the invitation. There are many complications associated with poorly controlled diabetes, but properly controlled, you can reduce the risk of complications striking, or delay them!
First let's learn about diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body has a relative or absolute deficiency of insulin or a reduced sensitivity of target cells to insulin, or a structural defect in insulin itself that results in a carbon-hydration
A chronic disease characterized by disturbances in the metabolism of compounds, fats, and proteins.
Primary cause.
I. Genetic factors.
Secondly, obesity caused by eating too much and reduced physical activity is the most important environmental factor in type 2 diabetes. type 1 diabetics have an abnormal immune system, which leads to autoimmune reactions after infection with certain viruses such as coxsackie virus, rubella virus, parotid virus, etc., destroying the insulin β-cells.
Complications of diabetes are usually caused by the lack of proper control of blood sugar and the long-term stimulation of excessive blood sugar, which causes damage to many organs and tissues. The main complications are.
1. Drowsiness.
2, heart failure, myocardial infarction: the most serious is heart failure, myocardial infarction leads to death.
3, cerebral infarction cerebral hemorrhage: found that the treatment is not timely, the patient will be stunned, shock, and casually life-threatening.
4, diabetic foot: foot skin ulceration does not heal for a long time, seriously leading to amputation.
5, eye disease: the initial stage may be just unclear vision, or bleeding, severe cases of blindness.
6. Diabetic nephropathy: renal insufficiency, which can cause lesions of the kidney.
7. Sexual dysfunction: girls may be amenorrheic and men may be impotent.
To minimize complications, it is important to look at the causes of diabetes. Genetic factors cannot be changed, but lifestyle habits can be changed.
Sedentary lifestyle is a major hidden danger of obesity and diabetes, therefore, we need to be more active and participate in physical exercise. At the same time, low-salt, low-sugar, low-fat diet, pay attention to the rationality of the nutritional mix, and do not take a single overdose of any food.
Another important aspect is the early use of insulin. Avoid pancreatic failure and complications.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.