What are the first noticeable symptoms of AIDS?
In recent years there have been more and more people consulting about AIDS in outpatient clinics, including online clinics, which means that the epidemic has subsided a bit during this time. One of the biggest misconceptions about AIDS is that many people think that AIDS is very contagious, but in fact it is not, in the infectious disease community AIDS contagiousness is also the level of elementary school students, the conditions of survival in vitro is extremely weak, and the transmission conditions are harsh.
The onset of AIDS is relatively insidious, and about 50-70% of people infected with the disease develop atypical symptoms one month after infection, such as high fever, a symmetrical rose rash, diarrhea, and headache. This is similar to adult viral rash or syphilis, and it is not possible to diagnose AIDS just by looking at the symptoms. These symptoms usually subside within a month and then enter a long asymptomatic incubation period, while the other 50% or so will have no symptoms from the time they are infected until the onset of the disease.
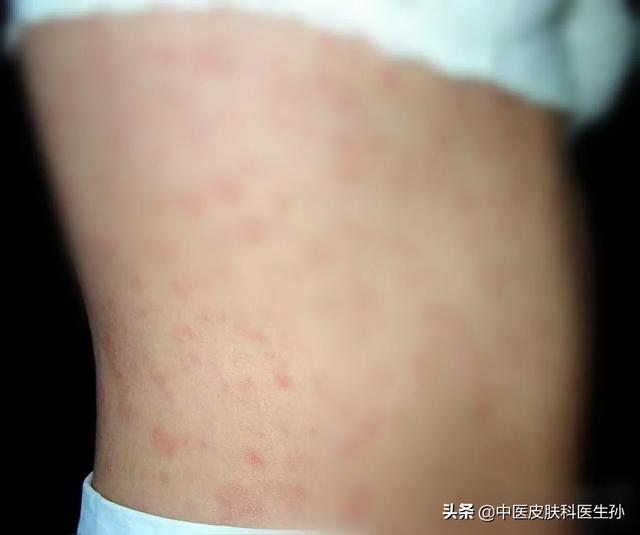
I read some responses that say that during asymptomatic infection with HIV there is weight loss, night sweats, easy to catch a cold, etc., but there is actually no basis for this. Most of the weight loss and night sweats are hysteria caused by HIV-phobic people scaring themselves.
At the beginning of an AIDS attack, there are various symptoms of the infection, which can also be seen in normal people, but in AIDS patients, the infection occurs more frequently, the duration of the attack is longer, and the symptoms are more severe. For example, there are recurring herpes on the lips and mouth, and herpes on the hands and eyes in addition to the lips and mouth. Then there's shingles, which in AIDS is widespread throughout the body or invades multiple nerve segments, rather than just a small pile on the lower back as in the general population. And then there are the various types of pneumonia, where one day bacterial pneumonia happens to be followed by viral pneumonia the next.
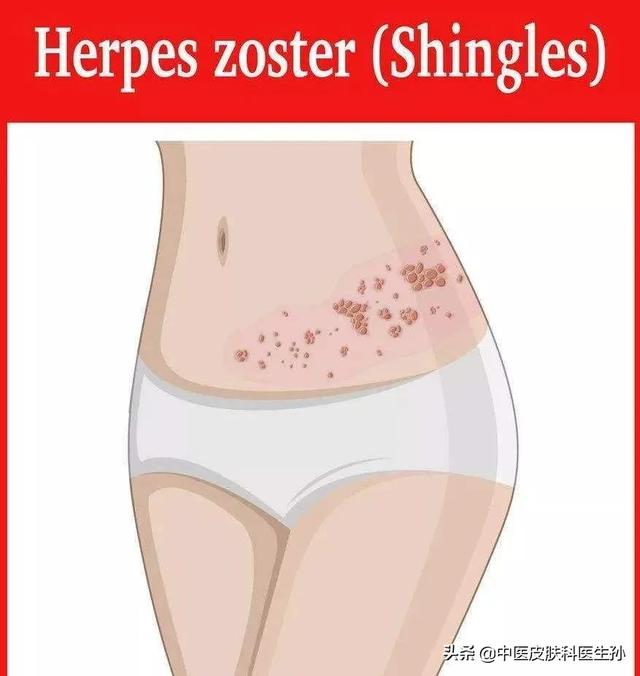
As for the more typical sporotrichosis and Kaposi's sarcoma, they all begin to appear in the later stages of AIDS, and the symptoms usually occur when they are infected and not treated on time.
The title should be changed to What are the telltale symptoms of acute HIV infection?
To answer your question as an infectious disease physician!
AIDS is divided into three clinical stages: acute infection, asymptomatic and AIDS (late stage).
Currently consulting patients with the most symptoms or acute infection, after an acute infection and then enter the asymptomatic period, the asymptomatic period of time about 2-8 years, but not absolutely, some patients with poor immunity from the acute infection to the late stage of the patient is also more rapid.
So why are there so many symptoms in the acute infection phase? The most important reason is-due to AIDS toxemia and acute impairment of the immune system.
The symptoms are:
Fever, rash, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, pharyngitis, malaise, sweating, lymphadenopathy, and diarrhea. Some also develop acute aseptic encephalitis, usually indicated by headache, neurologic symptoms, and meningeal irritation. On peripheral blood examination, the total number of white blood cells is normal, or there is a decrease in lymphocytes and an increase in monocytes. The acute phase of AIDS usually occurs about 7-15 days after high-risk behavior. Symptoms are usually mild and easily overlooked during the acute phase of HIV infection.
To summarize a bit:Symptoms during the acute infection phase of HIV are similar to a cold and are not specific.
So when a patient who has had a history of high sexual risk, it is important to consult a medical professional and not to suffer from a severe form of Islamophobia.

Privacy about infectious diseases can be concerned about and private letter to Dr. Li Ping, will certainly protect your privacy, health road with me!
The course of AIDS is divided into three periods. Acute infection, latent (asymptomatic) and AIDS. Patients in the acute infection and latent phases are called HIV-infected patients. A patient in the AIDS stage is called an AIDS patient. In this way, answering the initial symptoms of AIDS needs to be answered in terms of two time periods. One time is the initial symptoms of HIV infection and the other time is the initial symptoms of the onset of AIDS period.
The initial symptoms of HIV infection are similar to those of a common cold or flu, such as fever, sore throat, muscle aches, joint pains, fatigue and swollen lymph nodes. They usually return to normal after 2 to 3 weeks. It appears in about 70% to 80% of people infected with the virus. Due to the mild symptoms, it is sometimes overlooked by patients.
There can be many pre-symptoms of HIV stage. For example, loss of appetite, mild fever, weight loss, night sweats, etc. Mild opportunistic infections such as swollen superficial lymph nodes, oral mucosal infections, gingivitis, fungal skin infections, herpes zoster, etc. are present.
This is a very good question! According to the relevant provisions of China's Law on Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases, AIDS is managed as a Category B infectious disease in China, but the reporting and control measures of a Category A infectious disease must be taken.
We know that HIV has a long incubation period, averaging 6-8 years, but ranging from a few months to several decades.
From the initial infection with HIV to the final stage of the disease, there is a long and complex evolution of the disease, which is roughly divided into three phases: acute infection, asymptomatic infection, and symptomatic infection (terminal stage).
So, what are the obvious symptoms in the early stage of HIV infection, that is, the acute stage of infection? They are summarized below for reference only.
What is the cause of AIDS to begin with?
First let's find out what causes AIDS.
Simply put, AIDS is caused by the HIV virus, abbreviated as HIV, invading our body and destroying our body's immune cells, specifically CD4+ T lymphocytes, thus causing defects in the immune function of our body's cells, and ultimately leading to a decline in our body's ability to fight infections, including the ability to defend against tumor cells.

Symptoms in the early stages of AIDS
In the early stages of AIDS, i.e., the acute stage of infection, the HIV virus (HIV) reaches the localized lymph nodes of the body in a very short period of time, between about 24-48 hours; then, after less than a week, about 5 days, the HIV virus is detected in the blood of the suspected patient, leading to the appearance of a number of acute symptoms of infection.
Some people with AIDS in the acute phase of infection will have some representative symptoms, which generally appear between 2-4 weeks after the initial HIV infection, i.e., in the form of aCharacterized by feveraccompanied byNausea, vomiting, diarrhea;orSore throat, night sweats, rash;There are also patients who exhibitJoint pain, swollen lymph nodesAs well as neurological symptoms and more.
These initial symptoms are due to the development of HIV toxemia and acute damage to the immune system, but in most infected patients these symptoms are mild and resolve spontaneously after 1-3 weeks.

In summary: In the early stages of HIV infection, some patients will experience concomitant symptoms characterized by fever, such as sore throat, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Do you agree with me?
Daily update on health hotspots, medical pain points; if what I say, is exactly what you think, then please like, retweet, follow Zhu Xiaojun said health!
Initial Symptoms of AIDS
AIDS, also known as Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is caused by the body being infected with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) also known as AIDS.
If HIV is allowed to develop, immune cells will gradually be destroyed by HIV and the barrier protecting the body will disappear.
Without immune cells, the ability to heal diseases is lost, and when the number of immune cells is reduced to a certain level, healthy people become infected with uninfected bacteria and viruses and develop various types of diseases such as pneumonia. In addition, the destruction of immune cells prevents the growth of cancer cells in the body and therefore increases the chances of malignant lymphoma and skin cancer.
The average incubation period of AIDS is 6 to 8 years on average, which can be as short as a few months or as long as a few decades, and so far, about 38 million people have died of AIDS worldwide.
When infected with HIV, the HIV virus begins to multiply rapidly in the body and destroys immune cells within 2 to 4 weeks after infection. Early symptoms such as the flu may appear 2 to 4 weeks after infection.
The main initial symptoms also include:1:Fever 2:Swollen lymph nodes 3:Sore throat 4:Muscle pain/arthralgia 5:Nausea/vomiting, 6 Diarrhea and other symptoms. If it develops quickly, severe cases may also show signs of central nervous system symptoms.
Therefore most people who experience these symptoms will think they have a cold or are overworked and will not take it seriously.
If these early symptoms occur, then it is recommended to go to the hospital for examination and treatment.
I am a medical doctor, a resident, specializing in the popularization of medical knowledge for the benefit of human health, if you want to know more, please pay attention to me, have questions can be left a message, will respond!
What are the first noticeable symptoms of AIDS?

When it comes to AIDS, I guess we all know more about it, it is a sexually transmitted disease, mainly through blood, mother and child, sexual behavior and other ways of transmission. But I guess not many people know what are the early symptoms of AIDS, today I will share the early symptoms of AIDS.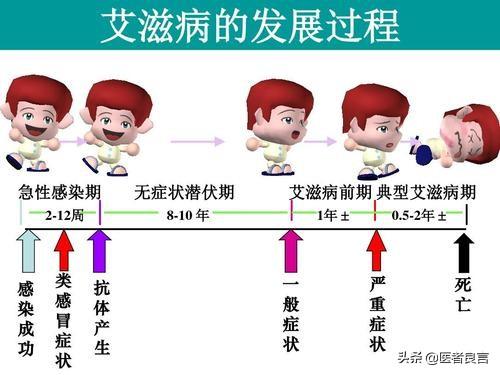
1. Fever:
Most AIDS patients may not have any obvious symptoms in the early stage, but if the infected person has a situation where HIV enters the bloodstream or the immune system is acutely damaged, the patient can mostly show fever, usually with a temperature of 38 ℃ or less, mostly appearing 2 to 4 weeks after high-risk behavior , .
2. Fatigue and weakness:
In the early stage of HIV infection, many people will feel tired and weak, and it may last for a long time, but many people will not care about it, because this lack of specificity, and if you stay up late, overwork, overindulgence and so on can cause fatigue and weakness, so many people ignore it;
3. Weight loss:
Some AIDS patients may experience significant weight loss in the early stages of the disease. This is mainly due to the fact that HIV destroys the body's immunity, causing the body's digestive system to be attacked by bacteria, and so the ability to absorb food decreases, thus causing weight loss;
4. Headaches:
Since pain can occur for many reasons such as staying up late, taking certain medications, and catching a cold, no one will notice that they are infected with HIV;
5. Rash:
When HIV violates the body's immunity, it can cause a decrease in the skin's ability to clear pathogens, which can lead to viral or bacterial infections of the skin, which can cause some AIDS patients to develop symptoms of a rash;
6. Recurrent infections:
AIDS patients are especially prone to recurrent infections after their immunity has been compromised, and they are not easy to treat, for example, some fungal infections are very difficult to control;
7. Prolonged diarrhea:
If the immune system of the intestines is disrupted by HIV, then it is particularly easy for the intestines to become infected because there are a lot of E. coli bacteria in the intestines, and normally they are in a kind of equilibrium, and once the equilibrium is disrupted, it can cause diarrhea;
8. Others: e.g. swollen lymph nodes, nausea, vomiting, night sweats, etc.
Final Summary: AIDS early may indeed have some obvious symptoms, but most lack of specificity, so many people will ignore, but if there is a high-risk behavior, then go to the hospital as soon as possible to make a clear diagnosis; some of the symptoms of early AIDS is summarized as above.
The above is my answer to the question, purely hand-typed, it is not easy, if you feel that the writing can be rewarded with a praise, if you have any questions you can leave a message below ......
Infected with AIDS early generally have no symptoms, only when suffering from a cold to find their resistance to decline, with what drugs are not obvious, and the body is getting worse and worse, the body more and more weak and feeble, once infected with the disease, fever and coughing, lung infection is difficult to control.
Since AIDS is an immune system disease, once the immune function is low or lost, any bacteria or virus can invade with impunity, which is a consequence we can imagine.
At present, domestic county hospitals are generally able to carry out the initial screening test for AIDS, and for those with positive results, specimens need to be sent to the municipal CDC for retesting to confirm the diagnosis.
Symptoms of the acute phase of HIV, which statistically appear in about 50% of infected people, usually appear 2 to 4 weeks after the occurrence of high-risk behaviors, and as short as one week later. The so-called high-risk behaviors include high-risk sex, contact with blood or blood products of HIV-infected people.
The initial symptoms, which are generally nothing special, are medically called nonspecific.
The more common symptom is fever, similar to the symptoms of the flu, if the sleep sweating, which is often referred to as night sweats, which is related to fever, it is also thought to be the occurrence of high-risk behaviors after sleeping poorly, mental tension caused by plant nervous function disorders.
In some cases, there are swollen lymph nodes on the surface of the body, such as the neck, armpits, and groin, which last for more than three months and for which no other cause can be found.
There is also the appearance of diarrhea many times a day, in the form of watery stools, repeated episodes; body fatigue, loss of appetite, significant weight loss; shortness of breath, dry cough that lasts generally more than half a month; oral mucosa and skin appear reddish blotchy, painless and itchy; male scrotal skin patches, female vaginal or anal itching, leukorrhea and persistent, and so on.
If there is high-risk behavior, timely testing for HIV can confirm or rule it out. Of course, this needs to be done three months after the risky behavior has occurred. It should be noted that a very small number of infected people do test positive within three months or six months after the risky behavior.
If an infected person develops Kaposi's sarcoma, which is commonly found on the feet and legs, or develops pneumonia infected by fungal spores, it signals that the infected person is in an advanced stage or what is called a late stage of infection.
About 50% of infected individuals do not show acute phase manifestations and can remain latent for 2 to 3 years, even 7 to 8 years, and up to 15 years, before showing symptoms.
Because of his work, he had been in contact with some HIV-infected people.
A young man from a good family, who has been diagnosed as infected for more than 10 years, has good treatment compliance, adheres to taking medication under the guidance of a specialist, has relatively good control of his condition, and looks no different from a healthy person on the outside.
However, what I have observed is that it is prone to colds, a small cold with a dry cough that doesn't heal for more than half a month and has to be treated with strong antibiotics. It also takes longer to heal small wounds on its body surface, so it seems that both immunity and healing ability are still significantly reduced.
There was also a woman who was only 30 years old, who had contracted AIDS through drug abuse and was in very poor health. She often came to the clinic to get medication, and later had great difficulty in walking, and she lost a lot of weight, and was very pale and severely malnourished, and when I saw her, I could not help but think of the Jews who had been imprisoned for a long time in Auschwitz, and felt that they were just skeletons moving forward slowly and that soon they would have to come to the prescription for medication in a wheelchair.
Early one morning after another month, her mother found me and said that her daughter had left yesterday. I advised her to think positively, for her daughter herself is also a kind of relief, is already advanced, the disease develops very quickly, the body is failing very badly, is to stay in the hospital is no good, can not live a few days more.
There are other such examples witnessed.
At present, it can be determined that high-risk sex is the most common way of contracting AIDS, and in the absence of better preventive measures, cleanliness and avoidance of high-risk sex are the most effective preventive measures against AIDS!
I'm Dr. Kang. Thank you, friends, for your attention!

Image from the web
Infection with HIV usually enters the acute phase half a month after infection, and the acute phase usually lasts 7-10 days. During this period, there will be colds, persistent low-grade fever, sore throat, muscle aches, nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss, diarrhea, swollen lymph nodes on the body (which can be felt under the chin, under the armpits, and in the groin), etc. Some people have more symptoms than others, and some have fewer. Some people have more symptoms in the acute phase and some have fewer, depending on the person. If you experience similar symptoms within half a month or so of high-risk behavior, you should be vigilant.
In recent years, the rate of AIDS has been gradually increasing because people's sexual attitudes have become more open. Everyone has heard of AIDS and knows that there is no complete cure for this disease. However, many people have a misunderstanding about AIDS, thinking that it is easier to transmit this disease. In fact, there is a very clear way to transmit this disease. As long as you pay more attention, you will not catch this disease.

There are three main ways of spreading AIDS, one is blood transmission, one is sexual contact transmission, and the other is mother-to-child transmission. The more widespread form of transmission is sexual, so some extra care should be taken. It is also important to be aware of blood transmission. If a person with AIDS has a wound, try not to get blood stains on it.
On an essential level, AIDS is not easy to detect, so if you have it, what are the telltale symptoms at the beginning?

1. Within 2 to 4 weeks of developing AIDS, some people will develop AIDS toxemia, and others will develop an acute impairment of the immune system, but it is not obvious.
2. After it lasts for 2 weeks, some people will have a persistent fever and may experience discomfort all over the body, similar to a cold.
3. Some patients may have headache, sore throat, diarrhea and so on. And there will also be swollen lymph nodes, which can be felt by touching with one's own hands and will not hurt when pressed.
4. Early headache and dizziness, high fever, virus damage to the immune system, low immunity will appear night sweats as well as joint swelling and pain.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.