How much blood sugar is normal?
Now everyone's standard of living is getting better and better, which also leads to more and more people with diabetes, so many people say that high blood sugar is a "rich man's disease". But for the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, many people do not know very well, so how much alcohol glucose is considered normal value, how much can diagnose diabetes? Today Dr. Liu give you a talk.

What is a normal blood glucose level? How is diabetes diagnosed?
Before we get into what is considered a normal blood glucose level, let's give you a few definitions, namelyFasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, and random blood glucose.
Fasting blood glucose is generally defined as the blood glucose value obtained in the morning after waking up after an overnight fast (at least 8 hours without any food, except water);
Postprandial blood glucose values generally refer to blood glucose values 2 hours after a meal, that is, counting the time from the beginning of the meal and then measuring the blood glucose values obtained 2 hours later;
Randomized blood glucose refers primarily to blood glucose values measured at any given time, that is, at any point in time during a 24-hour day, regardless of whether or not you have eaten, and regardless of how long you have eaten.
So what's a normal blood sugar level?If the measurementfasting blood sugarThen it is generally recognized thatBlood glucose values between 3.9 and 6.1 mmol/L are normal.IfFasting blood glucose values between 6.1 and 7.0 mmol/L are indicative of impaired fasting glucose regulation.The impaired regulation of fasting blood glucose belongs to the pre-diabetic stage, that is to say, if the patient does not pay attention to controlling blood glucose at this stage, then it may soon turn into diabetes, and if the patient can regulate and pay attention to controlling blood glucose in time at this stage, the blood glucose value can be restored to within the normal range; when theFasting blood glucose greater than 7.0 mmol/L is indicative of diabetes.。
If the measurementpostprandial glucose levelSo.Normal blood glucose values should be between 4.4 and 7.8 mmol/LIf the 2-hour postprandial glucose value is between 7.8 and 11.0 mmol/L, then it suggests impaired glucose tolerance, while if the 2-hour postprandial glucose value isDiabetes mellitus is diagnosed when it is greater than 11.1 mmol/L.。
If it's a measurementMeasure random blood glucose, then a random blood glucose greater than 11.1 mmol/L is indicative of diabetes mellitus。

Of course, Dr. Liu needs to remind here is that, for the measurement of blood glucose, if the measurement is abnormal once, it can not be fully diagnosed diabetes, at this time, it is recommended to review again in another day's time, if the review is also within the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, then the diagnosis of diabetes can be made.
What to do in your daily life if you have high blood glucose levels and are diagnosed with diabetes?
If diagnosed with diabetes, then we have to understand that it is a life-long will accompany your disease, generally there is no way to completely cure, but as long as the blood glucose control is good, generally will not affect our life treatment and survival time, so, in addition to the need for medication, daily life in the conditioning is also very important, here Dr. Liu to give you three points of advice:
I. Pay attention to dietary modifications.
We told you at the beginning of the article, the reason why there are so many diabetic people nowadays is mainly because the standard of living is better, the food is too good, and a lot of diabetes is eaten out, so for diabetic people, dietary regulation is very important, the diabetic people's diet emphasizes small meals, light diet, reduce the intake of high-sugar foods (such as high carbohydrates), and try not to eat spicy stimulating and fried foods. The diet should be based on rice, wheat and mixed grains as much as possible, together with vegetables, beans, lean meat and eggs, especially more fresh vegetables and fruits. Secondly, try to fix the meal time on the diet, so as to eat regularly.

Second, pay attention to sports conditioning.
Exercise is also very crucial for people with diabetes, exercise is a very effective method of non-drug treatment, reasonable exercise can effectively control blood sugar, and then avoid the occurrence of various types of diabetes complications. Exercise is not only able to lose weight and lower body weight; at the same time, exercise can also change the sensitivity of our body tissues to insulin, promote the absorption and utilization of glucose by the tissues, thus lowering blood sugar.
Of course, diabetic people in the exercise must pay attention to the intensity of the exercise and the way of exercise, only to choose the appropriate intensity and way of exercise, can play twice the effect with half the effort. Dr. Liu suggests that we try to choose medium and low intensity exercise methods, such as jogging, brisk walking, tai chi and so on.
Also want to remind you is that, in order to avoid the occurrence of hypoglycemia, diabetic people in the process of exercise is best to carry some candy, if in the process of exercise appeared to be hungry, dizziness, panic and other symptoms, be sure to immediately take candy, because then it is very likely that when the hypoglycemia caused by.

Third, pay attention to emotional regulation, maintain a relaxed mood.
Emotional regulation for the diabetic population is also very critical, a good mood allows us to have a stronger resistance and immunity, can reduce the occurrence of many diabetic complications, many diabetic patients is because of nervousness, emotional and other factors, which in turn caused by the rise in blood glucose, and even some acute complications; therefore, diabetic people to maintain a relaxed mood is very important.

summarize
Diabetes is a very common chronic disease in our country, we must pay great attention to actively control blood sugar, only in this way, we can reduce the harm caused by diabetes to our body, have a healthier body.
I am Dr. Liu, the code is not easy, if you agree with my views, help point a concern, follow me, learn more health, medical knowledge.
How much blood sugar is considered normal? Mainly refer to the following indicators:
1. Normal values of fasting blood glucose:Typical fasting whole blood glucose is 3.9 to 6.1 mmol/l.
2. Normal values of postprandial blood glucose:1 hour postprandial, blood glucose 6.7-9.4 mmol/L; 2 hours postprandial, blood glucose ≤7.8 mmol/L; 3 hours postprandial: normalization after the third hour.
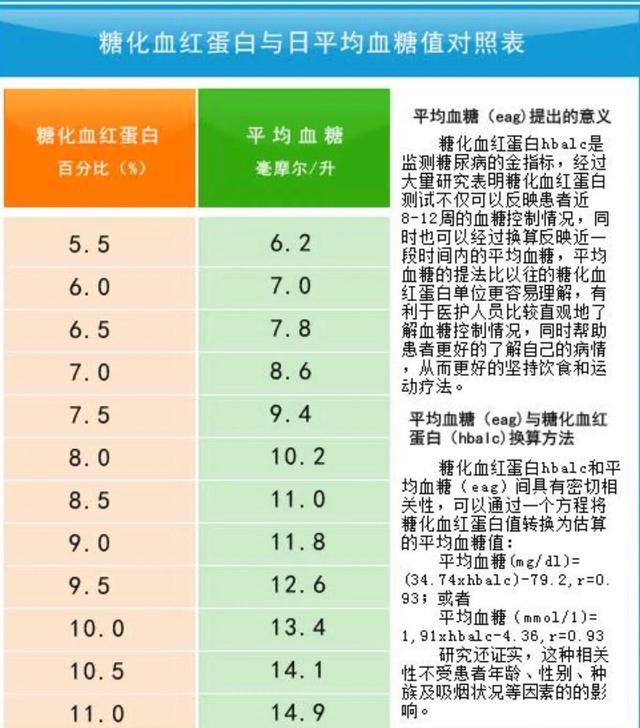
3. Glycosylated hemoglobin value:Glycosylated hemoglobin values of 4% to 6% indicate normal glycemic control; 6% to 7% indicate relatively good glycemic control; 7% to 8% indicate fair glycemic control; 8% to 9% indicate suboptimal control; and >9% indicate very poor glycemic control.
 Impaired glucose tolerance:If fasting blood glucose is 6.1-7.0 mmol/L or 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is 7.8-11.1 mmol/L, consider impaired glucose tolerance as pre-diabetes and actively pursue dietary and lifestyle interventions.
Impaired glucose tolerance:If fasting blood glucose is 6.1-7.0 mmol/L or 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is 7.8-11.1 mmol/L, consider impaired glucose tolerance as pre-diabetes and actively pursue dietary and lifestyle interventions.
Diabetes diagnosis:If two measurements (because its results can be affected by the amount of dinner eaten the day before, mood fluctuations and changes, good or bad night sleep, etc.) are taken, diabetes can be considered. Therefore, 2 measurements are needed to diagnose diabetes mellitus) fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L can be considered diabetes mellitus; it is recommended to review the fasting blood glucose, glucose tolerance test. Diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed if random blood glucose is greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/L.
Glycemic control goals for patients with diabetes:Fasting blood glucose ≤ 6.1 mmol/L; postprandial blood glucose ≤ 7.8 mmol/L; glycosylated hemoglobin ≤ 6.5%.
Thanks for the answer, I'm still bummed about this question, and worried about the questioner's blood sugar, which is not only not in the normal range for blood sugar at 11+, but is also the norm for diabetes.
The Chinese Type 2 diabetes guidelines state that normal adult fasting blood glucose ranges from 3.9 mmol/l to 6.1 mmol/l, and glucose tolerance 2-hour glucose should be <7.8 mmol/l. The diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus are a fasting glucose ≥7.0 mmol/l, a glucose tolerance 2-hour glucose ≥11.1 mmol/l, or a randomized blood glucose (that is, any time of the day) ≥11.1 mmol/l. Seeing this criterion, you probably know what is happening to blood glucose 11 points or more. Seeing this criteria, you probably know what it is like to have a blood sugar of 11+. Regardless of whether it is a fasting blood sugar, a postprandial blood sugar, or a random blood sugar, the criteria for diabetes have been met. If this blood sugar occurs in children, middle-aged and young people, then it means that you should be very concerned about your blood sugar. If the blood sugar control is not good, all kinds of complications will spring up. Once the complications of diabetes occur, they are irreversible and can only be slowed down by good blood sugar control. Complications of diabetes include diabetic neuropathy, macrovascular lesions, and small vessel lesions. Neuropathy is mainly caused by abnormal nerve sensation at the ends of the limbs; macrovascular disease is mainly caused by sclerosis and thrombosis of the arteries and veins of the lower limbs and neck; and small-vessel disease is mainly caused by diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy. These lesions do not all come out at once, but they are devouring the patients' quality of life little by little.
However, if this blood glucose is the postprandial blood glucose of an elderly person over the age of 70, then it is much more optimistic and is considered normal blood glucose. This is because glycemic control in the elderly has to be relatively lax because they are not sensitive to hypoglycemia, which can be fatal to the elderly.
The authoritative interpretation of Pharmaceutical Affairs, unauthorized reproduction, plagiarism will be punished.
Many people test their own blood sugar at home once in a while and think they are diabetic when they get a little high.
This is wrong and needs attention:
1. The blood glucose of the hospital indicator is venous plasma glucose, not the fingertip blood glucose (capillary glucose) that you usually measure at home.
2. Fasting blood glucose: The blood glucose value measured from bedtime to the next morning without eating any food (except water) for at least 8 hours.
3. The 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is the blood glucose measured by the glucose load test (sugar-water test/bun meal test), not the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose of a meal you casually eat at home.
What is normal human blood sugar? Let's take a look at the criteria for the hospital OGTT (Glucose Load Test) test:
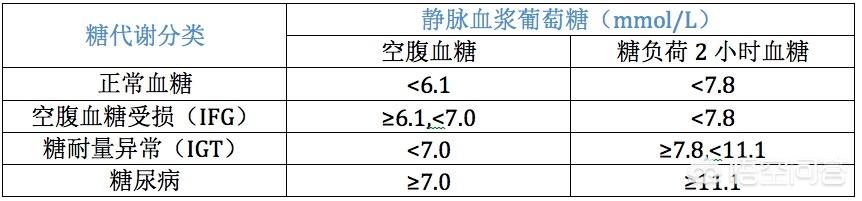
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, refer to the following control goals while ensuring that your blood glucose meter does not have a large margin of error:

So how do you make sure your own blood glucose meter is accurate?
You can find a day in the morning to go to the hospital to measure fasting blood glucose at the same time with their own blood glucose meter to measure a fingertip blood glucose, to see if the fingertip blood and the hospital blood glucose value is within the error range of the blood glucose meter.
If you have any questions, you can leave them in the comments section and I'll respond when I see them.
The above answer is provided by Ms. Song Mingyue, a registered dietitian of MicroSugar

If your fasting blood sugar is between 6.1-7.0 mmol/L or your two-hour postprandial blood sugar is between 7.8-11.0 mmol/L, ask your doctor am I diabetic? The answer is: not yet. Should add: but soon! China has 400-500 million people with "pre-diabetes" who have exceeded the maximum blood glucose level and do not have enough diagnostic criteria, which is scary!
China's diabetes can be diagnosed patients have reached 115 million, which refers to fasting blood glucose greater than 7.1mmoI / L or two hours after meals blood glucose up about 11.1mmol / L, one of these two indicators to reach or exceed can be diagnosed as diabetes. It has its general rationale for most people, but it also has some loopholes.
With the growing concern for health, as well as physical examination is generally carried out, it is found that some people fasting blood glucose is greater than 6.1mmol / L or even more than 7.1mmoI / L (fasting normal value of 3.9-6.1mmol / L, if the fasting blood glucose is greater than 6.1mmol / L-7.0mmol / L is "prediabetic "also known as" impaired fasting blood glucose "), should belong to the pre-diabetes or has been enough diagnostic criteria for diabetes, often the doctor will let the patient and then check a postprandial glucose, glucose tolerance test, glycated hemoglobin, the results of these people glucose tolerance, postprandial glucose and glycated hemoglobin are in the normal range, some even normal range! The results of these people's glucose tolerance, glucose tolerance test and glycated hemoglobin are all in the normal range, and some of them are even in the low normal range (the normal value of 2-hour postprandial glucose should be 4.6-7.8mmol/L, if it is in the range of 7.8-11.1mmol/L, it can also be regarded as "pre-diabetic" or abnormal glucose tolerance), and the value of glycated hemoglobin is really in the normal range (normal value 4%-6%). Normal value 4%-6%) 6% is equivalent to the average value of your blood sugar in the last three months has reached 7.8mmol / L. American doctors have long suggested that glycated hemoglobin is greater than 5.5% is prediabetic, you should immediately change the current poor lifestyle, eat less and move more to prevent the development of diabetes. Encountered these fasting blood glucose increase greater than 7.1mmol / L, and two hours after the meal blood glucose is normal, this may let the doctor for the difficult, in the end can diagnosed as diabetes? If the postprandial blood sugar and glycation are normal, this person should not be diagnosed with diabetes.
Can this situation be explained by the dawn phenomenon? The so-called dawn phenomenon refers to some non-diabetic patients due to the night's rest, wake up in the early morning in the sympathetic overactive state, so the body's hormone secretion of various hormones: such as adrenaline glucocorticoid, saline corticosteroid (epinephrine, etc.), pancreatic hyperglycemia and so on in the high secretion state will cause early morning fasting blood glucose elevated state. However, after meals, the islet cells function normally and are able to secrete sufficient amounts of insulin, so that postprandial blood glucose is normal or even below 6mmol/L, and the islet cells have enough stress capacity to secrete enough insulin to lower blood glucose to normal. If you do a glucose tolerance test, it will reflect the stress capacity of islet cells to secrete insulin after you eat 100 grams of glucose.
Therefore, two small inches of postprandial blood glucose is more valuable than fasting blood glucose for diagnosing early diabetes.
Glycated hemoglobin reflects the average value of blood glucose over a three-month period (see the chart below for conversion of glycated hemoglobin and average blood glucose values) because blood glucose and hemoglobin in red blood cells do not separate once they are combined, and red blood cells generally have a lifespan of three months. The prerequisite is that there is no anemia or erythrocytosis and the hemoglobin is normal. China has never taken the value of glycosylated hemoglobin as a diagnostic criterion for diabetes, but from 2021, the Chinese Diabetes Association will diagnose diabetes with a glycosylated hemoglobin greater than 6.5%.
When asked "What is normal for blood sugar? The normal ranges for fasting and two-hour postprandial blood glucose in diabetes are described above. There is a problem that has never attracted widespread attention from medical professionals and readers: when we read the laboratory indicators, we are often accustomed to see whether the results of the test exceed the maximum value of the normal range, as long as the maximum value of the normal range are considered normal, in fact, the closer to the maximum value that is close to the normal range is close to the abnormal. The normal range is a norm obtained through large-scale population sampling, which means that most people fall within this range for a particular test. Excluding individual differences due to various factors, de-heading uses 80-90% of the test values as the normal range. The problem is that we tend not to pay attention to the lower limit values, in fact, when the test indicators are close to the highest limit of the "normal range", it is likely that in the "near future" it will become abnormal, and will be diagnosed as a disease that requires treatment.
Why is it that as the level of medical science and technology continues to develop, the incidence of disease, treatment, disability and death rates continue to climb. This is the passive mode of diagnosing and treating diseases in the modern society with only the biomedical education model. The biomedical model of clinical medicine is only limited to certain biological, physical and chemical factors that lead to the production of pathological phenomena in a certain organ, what clinical manifestations and symptoms can be produced, through what increasingly modern diagnostic means to determine, as well as the use of a variety of advanced medicines, devices, surgery for symptomatic treatment of the standard model, for the broader sense of medicine will of course have its limitations. Only the prevention of disease is the most effective measure to improve human health and longevity, and can greatly reduce the cost of investing in medical care. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a good and healthy life pattern from childhood, and to develop good socialization and psychological resilience from childhood, which is the most effective way to ensure the health and longevity of ourselves and our future generations. Otherwise, we will be trapped in a vicious circle of more and more illnesses!
Type II diabetes is eating out of the disease, long-term uncontrolled eating into the blood glucose rise of a variety of high-calorie carbohydrates, sugars and animal and vegetable fats, non-but the consumption of a large amount of insulin, and lead to obesity produces insulin resistance, so that the pancreatic islet cell function premature decline, if there is a family history of diabetes in the person, the onset of their may eat more and less overweight or obesity, so that diabetes can appear ten years earlier twenty years or even thirty years; because your genetic decline in islet cell function is far worse than people without a family history of diabetes. Or even 30 years earlier; because the decline in insulin cell function that you inherit is far worse than in people without a family history of diabetes. Therefore, people whose blood sugar has approached the high limit of the normal range or has reached the diagnosis of "pre-diabetes" must first resolve to change the previous unhealthy lifestyle, eat less and move more, so that excess fat in the state of starvation through the body's tricarboxylic acid cycle is converted into blood glucose and glucose, and only when the body weight has dropped by 15-30 pounds, blood glucose, blood lipids, blood glucose and blood glucose will be reduced by 15-30 pounds. Only with a significant weight loss of 15-30 pounds, blood sugar, blood lipids and blood pressure will return to normal.
WHO/EASD/IDF, etc. do not accept the diagnostic category "pre-diabetes".The reason is: "pre-diabetes" seems to mean that the patient will eventually develop diabetes, in fact, it is true that some of the "pre-diabetic" people do not develop diabetes. People did not develop diabetes, of course, understand that their blood sugar abnormalities so strict control of eating high-calorie foods, increased exercise, so that weight loss, then the pancreatic islet cell function has been damaged is possible in a healthy mode after weight loss after food intake has dropped blood sugar on insulin needs.
In short, it is still a word, prevention is far better than cure, do not get sick count you hard, when you get sick, you can not do...!
2020.12.12 #LearningShareOfficer#2020 Vitality Conference ## Industry Personnel Recruitment Program ##
Dr. Duan Answers Online 🚀 Recognizing Blood Sugar Highs and Lows 🚀
Blood glucose 11 o'clock, whether you measured before meals, or measured after meals, is not normal. It is recommended to go to the hospital as soon as possible to improve the relevant examination, to clarify the real situation of blood glucose, and under the guidance of the doctor, to intervene and treat as soon as possible!

There are a few things to keep in mind for blood sugar:
(1) To determine normal blood glucose levels, or to diagnose diabetes, the results must be from a blood test, not from a glucose meter.
Therefore, if the blood glucose is found to be 11 points above the blood glucose meter, you need to go to the hospital as soon as possible to checkFasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, to clarify your true blood glucose level. If conditions permit, use a 75g glucose tolerance test instead, which will reflect true fasting and two-hour postprandial blood glucose.
(2)glycosylated hemoglobinIt can reflect blood sugar levels for an average of 3 months, independent of diet and mood, and is checked at the same time as blood sugar is drawn.
(3) Fasting blood glucose is defined as - checking early in the morning and fasting for at least 8 hours. Postprandial 2-hour blood glucose means - timing from the first bite of the meal and measuring blood glucose 2 hours later.
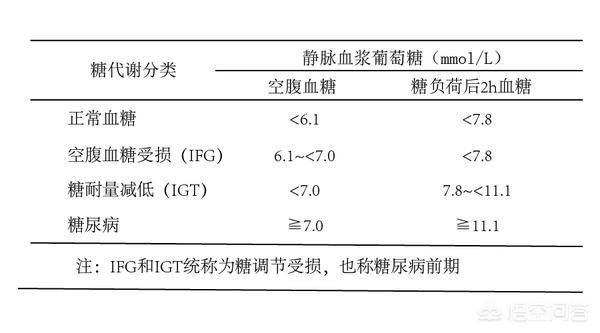
Normal blood sugar and diabetic values:
Normal blood glucose: fasting blood glucose <6.1 mmol/L, and two-hour postprandial blood glucose <7.8 mmol/L;
Diabetes mellitus: fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L, or two-hour postprandial blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L, or random blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L.
Values between normoglycemia and diabetes are considered pre-diabetic.
Based on the results of the blood tests, you will determine whether your blood sugar is normal or not, and choose the appropriate treatment.
(1) If diagnosed as pre-diabetes, lifestyle modification should be carried out first, including reducing sugar intake, low salt and low fat, quitting smoking and restricting alcohol, and exercising appropriately. Later, review the blood glucose, strict lifestyle still can't control the blood glucose (glycated hemoglobin >7%, then medication is needed.
(2) If diabetes mellitus is diagnosed for the first time and glycated hemoglobin is ≥9%, it is best to start intensive insulin therapy immediately, which improves pancreatic (insulin-secreting) function.
(3) If diabetes mellitus is diagnosed, but glycated hemoglobin is between 7 and 9%, consider lifestyle control along with oral medication.

Dr. Duan specifically warned:
(1) Based on the fact that you measured your blood sugar at 11+, it should not be a normal blood sugar. If you have done all the tests and your blood sugar is normal, it can only mean that there is something wrong with the first blood sugar measurement or the instrument used to measure it.
(2) Once diagnosed with diabetes or pre-diabetes, early intervention and medication should be used. Because, high blood sugar is an important risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
👇 Follow Dr. Duan for health and wellness! 👇
Blood glucose >11.1 mmol/L at any time is likely to be diabetes mellitus. It is recommended to go to the hospital to check the fasting blood glucose and do an oral glucose tolerance test to diagnose whether you have diabetes mellitus.
Once diagnosed, diabetes needs to be treated early to prevent complications. Self-management in terms of medication, blood glucose monitoring, diet and exercise.
1, once diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, to follow the doctor's instructions to take medication, in the control of blood glucose at the same time, but also pay attention to lipid regulation, antihypertensive treatment. The medication should be taken on time and in accordance with the dosage, do not reduce, change or stop the medication on your own, so as not to delay the treatment. If you have to take several kinds of medicines every day, you can prepare a classified pill box and put the medicines you have to take every day in a classified way, so that you can avoid the occurrence of missing medicines.
2、According to your blood glucose situation, make a blood glucose monitoring program under the guidance of your doctor, do a good job of monitoring your blood glucose, and record the results of your blood glucose monitoring, and show them to your doctor when you review your blood glucose.
3, diet, control the total intake of a day, pay attention to the rational mix of nutrition, diet light and easy to digest, less oil, less salt, moderate amount of dairy, eggs, lean meat, eat more fresh vegetables, staple food coarse and fine with millet, corn, oats, sweet potatoes and other coarse grains to replace part of the fine grains, first eat vegetables, and then eat the main food. Eat slowly and chew, small meals. Eat less or no high-sugar, high-fat foods, such as candy, cookies, sweet snacks, sweet drinks, fried foods, pickled foods, fatty meats and so on.
4. Exercise in moderation. Exercise can reduce blood glucose, blood pressure, blood fat, enhance insulin sensitivity, improve cardiorespiratory function. You can choose fast walking, cycling, tai chi, aerobics and other aerobic exercise. The amount of exercise is increased gradually and according to the strength. Exercise for 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week, and reach a level of slight heat and slight shortness of breath when exercising. Carry your diabetes card with you when you go out to exercise, and bring sugary foods such as candy and drinks to prevent hypoglycemia.
5, obese patients need to control the weight is no longer growing, and slow weight loss.
 The first thing to say is that your blood glucose level does not determine whether you have diabetes or not, there are diagnostic criteria for diabetes, not all high blood glucose is diabetes, the blood glucose that you casually measured may be normal, why?
The first thing to say is that your blood glucose level does not determine whether you have diabetes or not, there are diagnostic criteria for diabetes, not all high blood glucose is diabetes, the blood glucose that you casually measured may be normal, why?
A person's blood sugar is constantly changing throughout the day, especially in relation to eating meals. When we eat food, it is digested into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream as blood sugar. It takes time for food to be digested and is absorbed gradually, so blood sugar grows gradually after meals.
Under normal circumstances, blood glucose begins to rise after meals, between 30 minutes - 60 minutes is to reach the peak, and then began to decline, to 120 minutes when the absorption process is basically complete, into the blood glucose consumption time, to 180 minutes blood glucose is basically close to the level of fasting.
 In this process, the highest peak of absorbed blood glucose is between 30 minutes and 60 minutes, the general blood glucose test can not accurately find this highest point, so usually we will not go to specifically test the peak of postprandial blood glucose, but it can be affirmed that the highest peak of postprandial blood glucose in normal people will not exceed 11.1mmol/L.
In this process, the highest peak of absorbed blood glucose is between 30 minutes and 60 minutes, the general blood glucose test can not accurately find this highest point, so usually we will not go to specifically test the peak of postprandial blood glucose, but it can be affirmed that the highest peak of postprandial blood glucose in normal people will not exceed 11.1mmol/L.
But for 2 hours after the meal this point is a clear point in time, this point of blood glucose testing is meaningful, the normal value is not more than 7.8mmol / L; the same reason, 8-12 hours after the meal into, that is, we say fasting blood glucose also helps us to judge the change of blood glucose in a day, the normal value is not more than 6.1mmol / L. This is the diabetic patients daily test blood glucose to measure the Fasting blood glucose and 2 hours after meal blood glucose. The diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus were determined by analyzing the changes in blood glucose throughout the day and the clinical significance of blood glucose at various time points:
The diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus were determined by analyzing the changes in blood glucose throughout the day and the clinical significance of blood glucose at various time points:
- Fasting blood glucose greater than or equal to 7.0 mmol/L
- 2-hour postprandial blood glucose greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/L
- Random blood glucose greater than or equal to 11.1 mmol/L
Therefore, if the blood glucose is measured randomly, it depends on when it is measured, for example, if it is measured 40 minutes after a meal, as long as it does not exceed 11.1 mmol/L, it is normal and there is no need to worry.
In addition, it is necessary to understand is that the clinical down the above mentioned diagnostic criteria for diabetes, but also delineated a blood glucose range called pre-diabetes, that is, in such a blood glucose range, although can not be recognized as diabetes, but has been an abnormality of blood glucose, do not pay attention to the development of diabetes will soon be pre-diabetic blood glucose range is:
- Fasting blood glucose: between 6.1 and 7.0 mmol/L
- 2-hour postprandial blood glucose: between 7.8 and 11.1 mmol/L
I hope this answer can help you, click on the attention of the daily listening to health, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge.
Regular medical checkups can be the first time to detect a condition and keep you informed of your health condition, which is one of the effective disease prevention measures recommended by doctors. However, after getting the physical examination report, some people are at a loss, looking at the results on the examination report, and do not know whether there is any abnormality. If you want to read the checkup report, you should first clarify the normal values of these common indicators below.
I. Blood pressure
Hypertension is a highly prevalent disease in today's society and blood pressure is measured with both systolic and diastolic values. In the previous year, the United States issued a new hypertension guideline, the systolic/diastolic blood pressure is greater than 130/80, that is, hypertensive patients. However, this has not been updated in China, which means that 140/90 is still used as the diagnostic criterion for hypertension.
II. Blood sugar
Blood glucose is categorized into fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose depending on the time of measurement, with the former being greater than or equal to 7.0mmol/L or the latter being greater than 11.1mmol/L. If either of these conditions is met, diabetes is initially considered to be diabetes mellitus, which requires multiple measurements to be determined. Currently, diabetes is treated with insulin injections and long-term medication, and there is no cure.
III. Triglycerides
The value of triglyceride takes 1.7mmol/L as the watershed, higher than 1.7, it means the value is on the high side and needs more attention. If it just happens to be over 1.7mmol/L, you can start by adjusting your diet without medication to see if you can bring it down to a normal value. However, if it has exceeded 2.26mmol/L, it is necessary to take lipid-lowering drugs under the advice of a doctor to avoid other complications.
IV. Lipoprotein cholesterol
There are two types of lipoprotein cholesterol. The good lipoprotein cholesterol is called high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), which reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, and the higher the concentration, the better. The bad lipoprotein cholesterol is called low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and the higher the concentration, the more harmful it is, which may induce coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis and other diseases.
V. Total serum protein
The value of total serum protein is a reflection of liver function and will be in the range of 60-80 g/L in normal individuals.
VI. Uric acid
High uric acid indicates a higher risk of ventilation and gout is a common disease among people today. When it comes to uric acid values, there will be differences between genders. Men should have a uric acid value of less than 420 mmol/L, while women should have a value of less than 360 mmol/L. When the uric acid value is high, you should limit your intake of foods such as animal liver, beer, and seafood.
VII. Platelets
The number of platelets in the body should be 100-300,000/mm³, and test results below this number should alert you to the possibility of metastatic tumors or acute leukemia, which are more serious diseases that require a visit to the hospital for further examination.
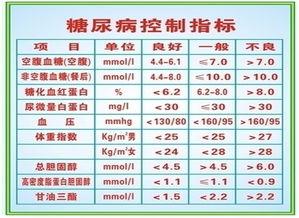
According to the 2013 edition of the Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Fasting blood glucose was controlled to 4.4-7.0 mmol/L.
Non-fasting blood glucose <10 mmol/L.
Also important for diabetics to juggle is a very important blood glucose value called glycosylated hemoglobin (HBA1C) <7%.
Blood sugar fluctuations are affected by many factors, such as illness, surgery, trauma, or missed medication, emotional stress, poor rest, poor diet and exercise, all of which can cause fluctuations and abnormalities in blood sugar.
So, self monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) can help diabetics to stay out of harm's way.
You can keep track of your blood sugar fluctuations. Your doctor can guide your diet, exercise and optimize your medication regimen based on your blood sugar.
It can help patients prevent and mitigate the onset and progression of complications. Studies have shown that patients who self-monitor their blood sugar are significantly less likely to experience complications.
That's why it's a must for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar.
Here's what to pay special attention to
fasting blood sugar
The blood glucose value (the value of glucose in the blood) measured by blood taken before breakfast after an overnight fast (at least 8 to 10 hours without any food, except drinking water) is the most commonly used test for diabetes mellitus, reflecting the function of pancreatic β-cells, and generally representing the secretion of basal insulin.
postprandial glucose
It generally refers to the two-hour postprandial blood glucose, which is timed two hours from the first bite of the meal.
In fact, it is a simplified glucose tolerance test. Clinically, postprandial blood glucose can reflect the insulin secretion and the body's sensitivity to insulin to a certain extent, and it is the most commonly used method for screening and discovering diabetic patients with normal fasting blood glucose.
glycosylated hemoglobin
It is the average of the previous two to three months of blood glucose. It has been used clinically as the gold standard for long-term glycemic control.
The test does not require fasting, any time of day, and venous blood is more responsive to long-term blood glucose.
But glycated hemoglobin does not accurately reflect the risk of hypoglycemia or characterize blood sugar fluctuations.
For people with diabetes, in addition to the above three indicators, it is also important to take into accountBlood pressure, blood lipids, weight and waist circumference and urine proteinThe situation.
Author Bio.
Li Zi (1902-1995), Chinese communist leader
National Level II Nutritionist
Participants of the fifth session of the Wang Xingguo Special Training Course
Diabetes Education Specialist
Senior Nursery Nurse
physiotherapists
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.