What is the current success rate for herniated disc surgery? How effective is minor surgery?
Heartbreaking to see your question, the success rate of lumbar herniated disc surgery, different doctors do it differently, in one person that probability means even less, whether it's X%, when it happens to one person that's 100%, no room for bargaining.
Minor surgery?
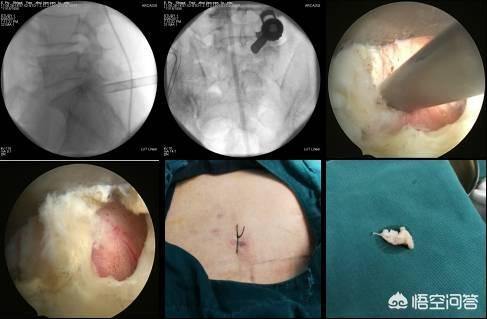
By minor surgery you mean minimally invasive? There are many kinds of minimally invasive, or the same, different doctors operate, in different conditions of people, the effect can be sky-high, which there is no way to go to talk about how the effect is, now the best minimally invasive at present is the foramen ovale, but minimally invasive is also for the open surgery to say, is not traumatized very tiny.
Come in if you've had surgery?
This question, may be you want to inquire about the truest post-operative feeling, but you should know that so many people who have had the surgery, there are good results, and there are many poor results, and everyone has their own feelings and opinions, you will get lost in the answer, so we suggest that you get down to the facts and ask your doctor.
Does it require surgery?
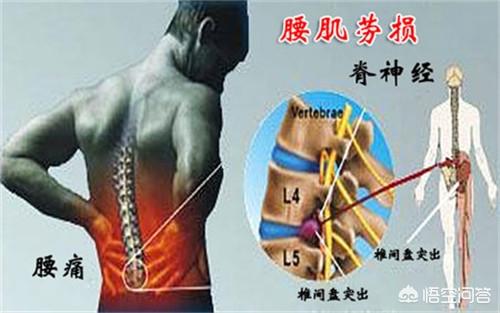
As for whether to have surgery for a herniated disc, it still depends on the symptoms, if you have cauda equina syndrome and incontinence, you still need to have surgery in time, but just low back and leg pain, even if it's more severe, most of it can still be conservative, and a large herniation and stenosis on the report is not a reason to have surgery.
See more people.
If you really want to get an accurate answer, ask the patient is just a reference, make sure to find a trusted doctor to communicate, after all, whether conservative or surgical, need him to operate, if this doctor does not feel good, change the next one, register and ask for a consultation fee is very small, delay a little bit of time to pick the right person, it is worth it!
Personally, I would recommend not having surgery until you have to! I herniated a disc a couple years ago! The doctor told me to have surgery. I didn't do it! Because I thought he was alarmist! Of course, during the period of illness, only the real experience of the acidity only know, can not get out of bed, can not bend down, all kinds of inconvenience! Also tried a variety of prescriptions, a variety of ointments, a variety of smoked take! Finally, I think I insisted on using hot salt bag hot compresses and massage, the whole good! Use a cloth bag with coarse salt! Microwave oven to beat the heat, hot compresses, and then is to adhere to the massage, now much more convenient, there are plug-in salt bag! Now I have three years without back pain! These years is to insist on massage! Basic half a month by once!
The incidence of lumbar disc herniation is too high, but the need for surgery is a very small part of the current medical development of lumbar disc herniation surgery is very mature, relatively very safe, as for minor surgery, such as intervertebral foramenoscopy surgery, the main surgical indications to master the effect is very good. But any surgery is risky, it is necessary to assess the specific situation, I often ask patients this way, how much the disease affects you, if you have back and leg pain, affecting your daily life, conservative treatment is also ineffective, seriously affecting the quality of life, why should we dwell on the danger of a very low incidence?
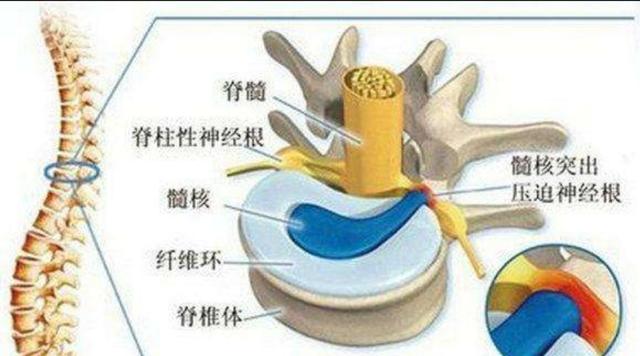
Lumbar disc herniation is a lesion that occurs when the intervertebral disc protrudes outward under the action of external forces, compresses, and irritates the nerves causing low back and leg pain as the main symptom.
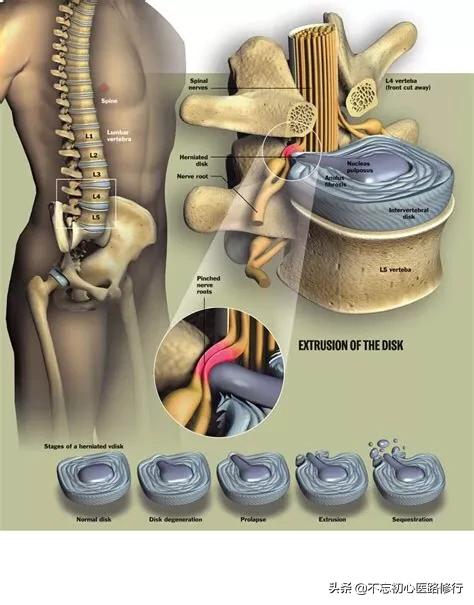
The indications for surgery are: severe symptoms of low back and leg pain, recurrent attacks, after more than half a year of conservative treatment is ineffective, the condition gradually aggravates, affecting work and life.
Choice of Surgical Procedure;
1、Minimally invasive surgery, currently more popular is the intervertebral foramina technology.
Suitable for: Lumbar discogenic low back pain: i.e. disc herniation is not obvious, but low back pain is obvious, recurrent and conservative treatment is ineffective. At this time, the intervertebral disc has already appeared structural damage, thus causing pain. Lumbar disc herniation, prolapse and intravertebral free;
Contraindications to laminectomy:
- Combined spinal stenosis.
- Combined segmental instability.
- Accompanied by multisegmental degeneration.
2. Posterior open pedicle decompression pedicle screw internal fixation surgery.
Usually procedures that cannot be solved by laminectomy can be solved by this procedure.
In conclusion: it is important to grasp the indications for surgery, or as the saying goes, the best treatment is the one that suits you, no disease can be solved by one type of surgery, and it should be strictly chosen according to the indications.
Herniated lumbar discs have become known as a routine surgery, and there are two main types: a direct removal procedure and a fusion procedure. Next, Dr. Wang and you will explain each of them.
What is the purpose of lumbar disc surgery?
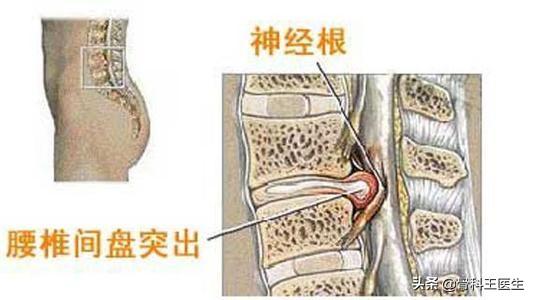
A lumbar disc herniation is low back pain and radiating pain in the lower extremities caused by a herniated disc pressing on a nerve root.The purpose of the surgery is to remove the herniated disc. With the herniated disc gone, the nerve root is not compressed and there is no pain. The risk is whether the nerve will be damaged when the disc is removed.
Why are there two surgical approaches?
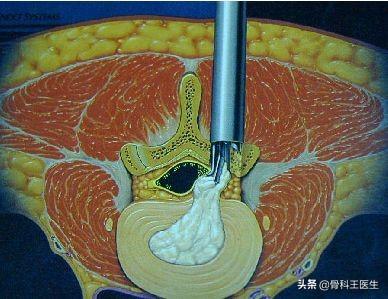
This is because when a herniated disc is removed, part of the stabilization between the vertebrae is missing, which may cause low back pain as well as accelerated degeneration of the back. So, for older patients, who have previously unstable backs, it is possible to have a one-time fusion surgery, which involves removing all of the discs, placing fusion devices, and fixing the back with internal fixation. The risks of this procedure are greater than removal alone; after all, there are more steps in the procedure and it takes longer.
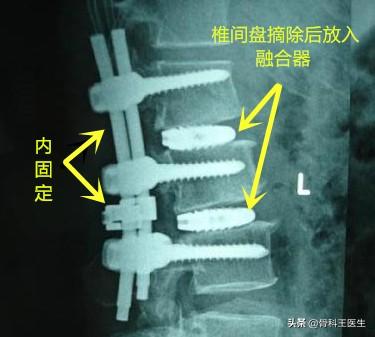
How effective is minor surgery?
No matter how big or small the surgery is, it is definitely effective for nerve compression symptoms like reflex pain in the lower extremities, but small surgeries don't solve the problem of lumbar instability, and major surgeries are, after all, so traumatic that they can be avoided as much as possible. So, some people should have minor surgery, some people should have major surgery, this is not a multiple choice question, it is a single choice question, there is only one answer for a particular patient.
What are the risks of surgery?
Because of the maturity of the technology, the overall surgical risks are minimal. Long-term low back pain has a serious impact on your life, so you may want to have a surgical solution.
Surgery for herniated lumbar discs.
The treatment of herniated discs is based on non-surgical treatment.
Surgery is a risky and invasive treatment.
There are strict indications for surgery for herniated discs, and surgery is recommended when the following conditions are present
I. Ineffective by conservative treatment, symptoms recurring, affecting normal life.
Secondly, it is found that there is spinal cord and nerve damage, muscle atrophy of the lower limbs, diathesis symptoms, and persistent forced position.
What is the success rate of herniated disc surgery?
There are many surgical options for lumbar discs.
With the traditional surgical approach, the larger the surgical incision, the better the line of sight and the better the operating space.
It is suitable for multisegmental, heavy compression and more complex herniated lumbar discs. Excluding surgical risks, the so-called surgical failures that may occur are loosening of the internal fixation, detachment, and non-healing of the incision. This is rarely the case.
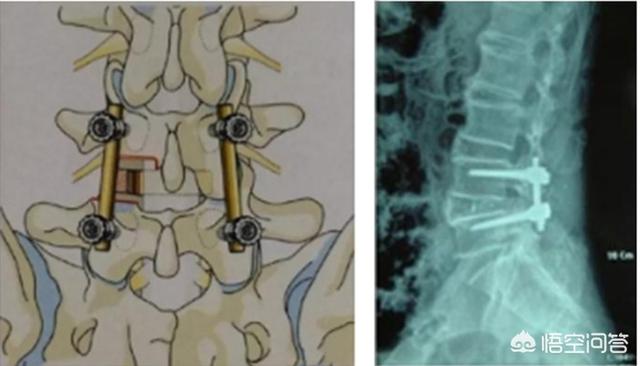
Advantages: complete removal of the lesion.
Cons: Large incisions and trauma.
Minimally invasive surgery with a small relative operating line of sight and little room to maneuver.
Suitable for single cut segments, simpler procedures.
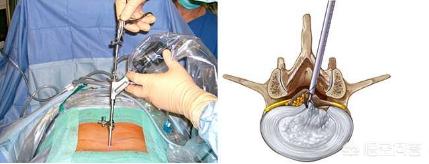
Advantages: little side damage and quick recovery after surgery.
Cons: Possible recurrence, or need for intermediate openings.
How effective is minor surgery?

Each procedure has its indications and choosing the right one is also known as preoperative evaluation.
The decision to operate is based on the specific status of the individual.
The results of the surgery are good when you choose a regular, professional hospital and a regular surgical procedure.
Recommendation:

About the examination and treatment of the disease to the regular hospital specialties.
Feel free to leave comments and corrections in the comments section.
Before answering the question about the success rate of surgery, we must be clear about two things: first, our diagnosis must be correct, that is, the clinical symptoms and imaging must match; and second, the pain must be caused by a herniated lumbar disc and not due to a soft tissue lesion such as myofascial.
It is currently believed that lumbar disc herniation causes low back pain by two mechanisms, one is the compression mechanism, that is, the protruding nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc directly compresses the spinal nerve root, and the other is the inflammation-mediated mechanism, after the annulus fibrosus ruptures, the protruding nucleus pulposus releases inflammatory mediators, stimulating the spinal nerve root to cause pain.

Surgery for lumbar disc herniation, now there are two kinds of minimally invasive and open. Minimally invasive surgery, there are radiofrequency, plasma, intervertebral foramenoscopy, etc. The first two types of surgery are carried out more in the pain department, which is less traumatic and quicker to recover, but only for the smaller cases of disc herniation, and according to the past experience, the pain-relieving effect is still very good at the time of acute onset.
Radiofrequency thermocoagulation uses a 0.7mm diameter radiofrequency needle, which is punctured under C-arm or CT guidance, and accurately reaches the diseased disc and turns on the thermocoagulation. It relies on thermal radiation to reduce the size of the herniated nucleus pulposus and relieve nerve root compression. The difference between plasma surgery and radiofrequency thermocoagulation is that it vaporizes the herniated nucleus pulposus tissue directly.
Larger herniated discs are better with intervertebral foramenoscopy, which has a small incision, usually about 7mm, does not damage the paravertebral muscles and ligaments, bleeds less, and has no effect on spinal stability, and provides rapid relief of pain symptoms due to removal of neural compression after the surgery. The open surgery is for patients with lumbar disc herniation accompanied by lumbar vertebral degeneration, osteophytes, spinal stenosis and nerve root canal stenosis, ligamentous calcification, as well as patients with obvious lumbar spine instability.

Hi, I'm happy to answer your question. What is the success rate of lumbar herniated disc surgery? Definitely is an unknown, because to do surgery, there are unpredictable risks, in fact, a lot of lumbar disc herniation, it can be said that about ninety-five percent, do not need to do surgery, because it has not reached the indications to do surgery.
So here's what then here's what are the indications for surgery for lumbar synostosis? The main points include the following? After conventional conservative treatment, the effect is not obvious, showing a trend of gradual aggravation, the cauda equina syndrome, urinary and fecal incontinence, loss of sensation in the lower limbs, progressive muscular atrophy, and even paralysis of the lower limbs.
Due to the current level of medical care is very advanced, conventional surgical treatment of lumbar disc herniation, or very successful, but there is one thing to note, lumbar disc herniation, about five years after the operation recurrence rate of about 80%.
Therefore, with lumbar synostosis, do not want to easily choose surgical treatment, first of all, choose conservative treatment, conventional closed small surgery is also a good choice, such as small knife, ozone, etc., have good results.
In my clinical practice, I have cured countless patients through the small needle knife therapy basically about 80% of the patients can be recovered, and there are some patients with spinal stenosis, but also achieved satisfactory results. I have also encountered a lot of patients who had recurrence after the surgery, and after the surgery, their life and work were seriously affected, and they no longer dared to do heavy work.
Once treated with surgery, it's a bit of a stretch to go back to conservative treatment methods when recurrence occurs later.
Regardless of the success rate of lumbar protrusion surgery, it is crucial that the indications for surgery are met first and foremost.
With a herniated disc, if the symptoms are not severe, it is best to opt for conservative treatment.
Herniated disc surgery is a molding procedure that focuses on patients with particularly severe disc symptoms. The success rate referred to by the surgery does not refer to the probability of the surgery failing, but is based on the results of significant improvement after the surgery, i.e., the excellent rate.
If the indications are chosen correctly, the success rate of the procedure can be 90% or 95% or more. If the indications are not properly selected, the success rate will basically be around 60%. Specific indications for surgery are that the patient first presents with lumbar pain, tingling in both lower limbs, positive straight leg raising test, markedly weakened dorsal extensor strength in both thumbs, and markedly limited functional lumbar activity.
The success rate lies in the experience and proficiency of the doctor, but also more so in whether you value your discs.
Nowadays, they are all minimally invasive treatments, with incisions of no more than 1 centimeter, with little damage and quick recovery!
Lumbar herniated disc herniation compression of the nerve caused numbness and pain in the legs to people suffering from lumbar spondylosis in life caused a great deal of trouble, not only the image of the quality of life and even affects the mental aspect, so that the temperament deteriorated to produce a depression in the minority! These are often conservative effect is not good, do not want to suffer pain again, in the friends and doctors see a little, then went to do the surgical treatment.
So why does lumbar disc herniation recur after surgery? A lot of people will ask this, especially those who have had surgery, did not do the surgery I did this will not recur after? A face of confusion, have done surgery and recurrence is a face of helplessness!
Generally speaking, as long as the diagnosis is clear and the localization is accurate, there will not be many chances for the surgery to go smoothly and recur completely. So why do some have serious back and leg pain symptoms again in less than six months or a year after three or four months of surgery? Simply put, there are two main categories.
I. Patients' own factors
(1) The cause of the disease in other segments has not been removed. The lumbar spine has 5 sections about 10 nerves, but mostly in the lumbar 4 lumbar 5, even if the two sections about 4 nerves, surgery is only to deal with the diseased section, the diseased section cured due to their own physical reasons for re-injury so that did not do the operation of the other sections and produced a protruding nucleus pulposus compression of the nerves triggered by the symptoms of lumbar and leg pain, and obviously not the surgery is not done.
(2) recovery after surgery, there are many people in the postoperative period did not follow the doctor's orders, did not do the relevant rehabilitation training, in the absence of rehabilitation, premature heavy labor, and incorrect posture image of the surgical site of the soft tissue repair, so that the original surgical area of the soft tissue edema healing deformity produced scarring caused by the new nerve root or spinal cord compression factors and produce symptoms.
II. Medical personnel factors
1. Preoperative diagnostic errors There is no detailed preoperative examination, and CT or MRI examination is taken as the only diagnostic basis! Too much reliance on auxiliary equipment, easy to misdiagnose. There are many lumbar CT examination of lumbar disc herniation but lumbar protrusion is not equal to lumbar disc herniation, these patients often have complex conditions also mixed with the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, pyriformis muscle, and sciatic nerve causes, and these are often misdiagnosis of the factors, coupled with the doctor did not listen carefully to the patient's medical history and a detailed physical examination, photographs at a glance of the lumbar disc protrusion, nucleus pulposus removal and removal of surrounding soft tissues, in which case the surgical effect is certainly done! Soft tissue, in which case the surgical effect must be the same as if it had not been done, right?
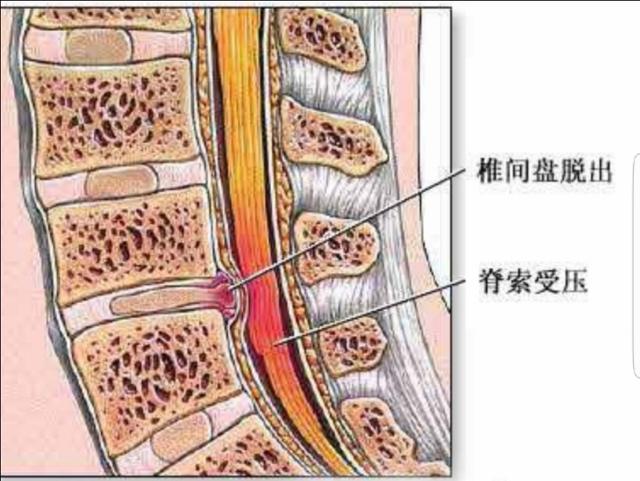
2.Surgical segmental localization In the surgical localization of some patients with multi-segmental herniation, lumbar 4, lumbar 5 have serious herniation, lumbar 4, 5 have appeared to compress the nerves caused by leg pain and numbness, and then combined with the tablets will often be the first choice of herniation of a larger section of a section to go to surgery, which can not be said to be the fault of anyone, the doctor is also a human being is not a god! But sometimes the real "mastermind" is often inconspicuous, the large protrusion removed, but the small protrusion is the real "murderer"! In the operation generally only give the patient to do a segmental lesion, another uncut segment due to exertion and other factors and produce new compression symptoms, so experienced doctors will routinely probe the upper and lower two segments of the status of the operation, found that there is a "protrusion" or "stenosis Therefore, experienced doctors will routinely investigate the condition of the upper and lower segments during the operation, and if any "protrusion" or "stenosis" is found, it should be resected together in order to prevent recurrence after the operation! Therefore, a simple and effective examination is still essential.
3. Surgery is not complete Now surgery is minimally invasive doctors to learn minimally invasive and minimally invasive through skilled surgery has been very good, but surgery often have some complex factors in it, both to ensure that the operation goes smoothly but also the patient's safety under the operating table, the
III. Intraoperative and postoperative
Minimally invasive surgery has advantages and disadvantages, the intervertebral foramenoscopy damage is small and the recovery is fast, but there are also limitations in the surgery bleeding will affect the surgical field, the space is too small and coupled with the lumbar vertebral body deformation caused by the surgery can not be cleaned thoroughly! The efficacy of the surgery and the recurrence of the surgery depends largely on the thoroughness of the intravertebral surgery. Doctors also have trade-offs will not pursue thorough cleaning and cause nerve damage, because there are many uncertainties during surgery, these are one of the reasons for postoperative recurrence! Doctors want to do a good job of surgery, so that the patient recovered well, in the postoperative management is also particularly important, there will be bleeding during surgery. Post-operative incision without placing a drain or drain tube is not fluent formation of hematoma, which is also one of the important factors that will form nerve adhesions, the doctor not only want to do a good job of surgery, but also can not be separated from the nurses careful observation after the operation.
To summarize: the patient's own physical fitness, and the smoothness of the surgery, the post-surgery treatment, and the post-surgery rehabilitation after discharge from the hospital are all important in determining whether or not to recur after the surgery.
Lumbar spondylosis advice: the doctor surgery to do a good job, not as good as usual attention to good protection of their own back is good!
I am the small Li who sticks to the front line in the countryside like to give me a nod of approval yo!
(The above content is organized and written based on my own years of experience and represents my personal views only!)

I thought there was no cure for a herniated lumbar disc?
I'm a sufferer of this disease myself.
I'm a third degree [three knots to four knots protruding]
It's still uncomfortable on rainy and cloudy days ~ and it hurts when I'm tired.
It's the medicine that's poisonous 💊 Sickness fishing under this is also related to rheumatism
It's related... I'm afraid of being tired when I have this disease.
It's useless to be afraid of back pain, surgery, or curing.
Because it treats the symptoms and not the root cause!
Just do rehabilitation exercises. Don't get too tired.
Take good care of it!
I'm Yang Yang ~ please leave a message in the comments section!
Thanks for the invite!

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.